使用灰度共生矩阵实现指纹分割
灰度共生矩阵,Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix,简写为GLCM
由于纹理是由灰度分布在空间位置上反复出现而形成的,因而在图像空间中相隔某距离的两象素之间会存在一定的灰度关系,即图像中灰度的空间相关特性。灰度共生矩阵就是一种通过研究灰度的空间相关特性来描述纹理的常用方法。
取图像(N×N)中任意一点 (x,y)及偏离它的另一点 (x+a,y+b),设该点对的灰度值为 (g1,g2)。令点(x,y) 在整个画面上移动,则会得到各种 (g1,g2)值,设灰度值的级数为 k,则(g1,g2) 的组合共有 k 的平方种。对于整个画面,统计出每一种 (g1,g2)值出现的次数,然后排列成一个方阵,再用(g1,g2) 出现的总次数将它们归一化为出现的概率P(g1,g2) ,这样的方阵称为灰度共生矩阵。
关于灰度共生矩阵的详细描述,请参考我的另一篇博文:http://blog.csdn.net/computerme/article/details/39805257
本文主要是采用灰度共生矩阵来实现指纹的分割,所谓的指纹分割就是把有指纹的区域从图像中提取出来。下图是的我代码的流程图
源代码如下
#include <iostream>
#include "highgui.h"
#include "cv.h"
#define GLCM_DIS 2 //灰度共生矩阵的统计距离
#define GLCM_CLASS 8 //计算灰度共生矩阵的图像灰度值等级化
#define GLCM_ANGLE_HORIZATION 0 //水平
#define GLCM_ANGLE_VERTICAL 1 //垂直
#define GLCM_ANGLE_DIGONAL_45 2 //45度对角
#define GLCM_ANGLE_DIGONAL_135 3 //135度对角
int threshold = 15;
#pragma region calGLCM
int GetMax(CvMat* bWavelet,int& max_value,int& min_value)
{
int i,j;
int width,height;
int max = 0;
int min = 0;
width = bWavelet->width;
height = bWavelet->height;
for (i = 0;i<height;i++ )
{
for(j = 0;j<width;j++)
{
if (CV_MAT_ELEM(*bWavelet,float,i,j)> max)
max = CV_MAT_ELEM(*bWavelet,float,i,j);
if(CV_MAT_ELEM(*bWavelet,float,i,j) < min)
min = CV_MAT_ELEM(*bWavelet,float,i,j);
}
}
max_value = max;
min_value = min;
return 1;
}
int calGLCM(CvMat* bWavelet,int angleDirection,double* featureVector)
{
int i,j;
int width,height;
int min,max;
if(NULL == bWavelet)
return 1;
width = bWavelet->width;
height = bWavelet->height;
int * glcm = new int[GLCM_CLASS * GLCM_CLASS];
int * histImage = new int[width * height];
if(NULL == glcm || NULL == histImage)
return 2;
//灰度等级化---分GLCM_CLASS个等级
//uchar *data =(uchar*) bWavelet->imageData;
//GetMax(bWavelet,max,min);
//printf("max = %d,min = %d ",max,min);
//system("pause");
int relative_value = 0;
for(i = 0;i < height;i++){
for(j = 0;j < width;j++){
histImage[i * width + j] = (int)(CV_MAT_ELEM(*bWavelet,float,i,j) * GLCM_CLASS / 256);
//relative_value = CV_MAT_ELEM(*bWavelet,float,i,j) - min;
//histImage[i * width + j] = (int)(relative_value * GLCM_CLASS / (max-min+1));
//printf("%d ",histImage[i * width + j]);
}
}
//初始化共生矩阵
for (i = 0;i < GLCM_CLASS;i++)
for (j = 0;j < GLCM_CLASS;j++)
glcm[i * GLCM_CLASS + j] = 0;
//计算灰度共生矩阵
int w,k,l;
//水平方向
if(angleDirection == GLCM_ANGLE_HORIZATION)
{
for (i = 0;i < height;i++)
{
for (j = 0;j < width;j++)
{
l = histImage[i * width + j];
if(j + GLCM_DIS >= 0 && j + GLCM_DIS < width)
{
k = histImage[i * width + j + GLCM_DIS];
glcm[l * GLCM_CLASS + k]++;
}
if(j - GLCM_DIS >= 0 && j - GLCM_DIS < width)
{
k = histImage[i * width + j - GLCM_DIS];
glcm[l * GLCM_CLASS + k]++;
}
}
}
}
//垂直方向
else if(angleDirection == GLCM_ANGLE_VERTICAL)
{
for (i = 0;i < height;i++)
{
for (j = 0;j < width;j++)
{
l = histImage[i * width + j];
if(i + GLCM_DIS >= 0 && i + GLCM_DIS < height)
{
k = histImage[(i + GLCM_DIS) * width + j];
glcm[l * GLCM_CLASS + k]++;
}
if(i - GLCM_DIS >= 0 && i - GLCM_DIS < height)
{
k = histImage[(i - GLCM_DIS) * width + j];
glcm[l * GLCM_CLASS + k]++;
}
}
}
}
//135度对角方向
else if(angleDirection == GLCM_ANGLE_DIGONAL_135)
{
for (i = 0;i < height;i++)
{
for (j = 0;j < width;j++)
{
l = histImage[i * width + j];
if(j + GLCM_DIS >= 0 && j + GLCM_DIS < width && i + GLCM_DIS >= 0 && i + GLCM_DIS < height)
{
k = histImage[(i + GLCM_DIS) * width + j + GLCM_DIS];
glcm[l * GLCM_CLASS + k]++;
}
if(j - GLCM_DIS >= 0 && j - GLCM_DIS < width && i - GLCM_DIS >= 0 && i - GLCM_DIS < height)
{
k = histImage[(i - GLCM_DIS) * width + j - GLCM_DIS];
glcm[l * GLCM_CLASS + k]++;
}
}
}
}
//45度对角方向
else if(angleDirection == GLCM_ANGLE_DIGONAL_45)
{
for (i = 0;i < height;i++)
{
for (j = 0;j < width;j++)
{
l = histImage[i * width + j];
if(j + GLCM_DIS >= 0 && j + GLCM_DIS < width && i - GLCM_DIS >= 0 && i - GLCM_DIS < height)
{
k = histImage[(i - GLCM_DIS) * width + j + GLCM_DIS];
glcm[l * GLCM_CLASS + k]++;
}
if(j - GLCM_DIS >= 0 && j - GLCM_DIS < width && i + GLCM_DIS >= 0 && i + GLCM_DIS < height)
{
k = histImage[(i + GLCM_DIS) * width + j - GLCM_DIS];
glcm[l * GLCM_CLASS + k]++;
}
}
}
}
//计算特征值
double entropy = 0,energy = 0,contrast = 0,homogenity = 0;
for (i = 0;i < GLCM_CLASS;i++)
{
for (j = 0;j < GLCM_CLASS;j++)
{
//熵
if(glcm[i * GLCM_CLASS + j] > 0)
entropy -= glcm[i * GLCM_CLASS + j] * log10(double(glcm[i * GLCM_CLASS + j]));
//能量
energy += glcm[i * GLCM_CLASS + j] * glcm[i * GLCM_CLASS + j];
//对比度
contrast += (i - j) * (i - j) * glcm[i * GLCM_CLASS + j];
//一致性
homogenity += 1.0 / (1 + (i - j) * (i - j)) * glcm[i * GLCM_CLASS + j];
}
}
//返回特征值
i = 0;
featureVector[i++] = entropy;
featureVector[i++] = energy;
featureVector[i++] = contrast;
featureVector[i++] = homogenity;
delete[] glcm;
delete[] histImage;
return 0;
}
#pragma endregion calcGLCM
double calc_variance(double a[4])
{
double sum;
double mean;
double variance;
sum = a[0]+a[1]+a[2]+a[3];
mean = sum/4.0;
variance = (a[0]-mean)*(a[0]-mean) + (a[1]-mean)*(a[1]-mean) + (a[2]-mean)*(a[2]-mean)+(a[3]-mean)*(a[3]-mean);
variance = variance/4.0;
return sqrt(variance);
}
void main()
{
clock_t start,finish;
int WIDTH,HEIGHT;
threshold = 8.5;
IplImage* src_img = cvLoadImage("8.bmp",0); //load the picture
WIDTH = src_img->width;
HEIGHT = src_img->height;
int step = src_img->widthStep; //the width of each row
printf("width: %d step: %d depth: %d channels: %d",WIDTH,step,src_img->depth,src_img->nChannels);
IplImage* msk_img = cvCreateImage(cvSize(WIDTH,HEIGHT),8,1);
cvZero(msk_img);
IplImage* dst_img = cvCreateImage(cvSize(WIDTH,HEIGHT),8,1);
cvZero(dst_img);
cvNot(dst_img,dst_img);
start = clock();
//cvSmooth(src_img,src_img,CV_GAUSSIAN);
//cvSmooth(src_img,src_img,CV_MEDIAN,2);
float sum;
cvNamedWindow("src");
cvShowImage("src",src_img);
CvMat* cwindow = cvCreateMat(5,4,CV_32FC1); //store the temperate 3*3 matrix
//CvMat* cwindow = cvCreateMat(5,5,CV_32FC1); //store the temperate 3*3 matrix
double features[10];
double entropy[4] = {0};
double energy[4] = {0};
double contrast[4] = {0};
double homogenity[4] = {0};
double variance;
uchar* gray_ptr = NULL;
uchar* msk_ptr = NULL;
gray_ptr = (uchar*) (src_img->imageData);
msk_ptr = (uchar*) (msk_img->imageData);
int x,y;
for(y = 2; y<src_img->height-2; y = y+2)
{
for ( x = 2; x<src_img->width-2; x = x+2)
{
/*CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,0,0) = gray_ptr[(y-2)*step+(x-2)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,0,1) = gray_ptr[(y-2)*step+x-1];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,0,2) = gray_ptr[(y-2)*step+x];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,0,3) = gray_ptr[(y-2)*step+(x+1)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,0,4) = gray_ptr[(y-2)*step+(x+2)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,1,0) = gray_ptr[(y-1)*step+(x-2)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,1,1) = gray_ptr[(y-1)*step+x-1];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,1,2) = gray_ptr[(y-1)*step+ x];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,1,3) = gray_ptr[(y-1)*step+(x+1)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,1,4) = gray_ptr[(y-1)*step+x+2];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,2,0) = gray_ptr[y*step+(x-2)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,2,1) = gray_ptr[y*step+(x-1)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,2,2) = gray_ptr[y*step+x];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,2,3) = gray_ptr[y*step+(x+1)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,2,4) = gray_ptr[y*step+(x+2)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,3,0) = gray_ptr[(y+1)*step+(x-2)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,3,1) = gray_ptr[(y+1)*step+x-1];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,3,2) = gray_ptr[(y+1)*step+x];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,3,3) = gray_ptr[(y+1)*step+(x+1)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,3,4) = gray_ptr[(y+1)*step+(x+2)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,4,0) = gray_ptr[(y+2)*step+(x-2)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,4,1) = gray_ptr[(y+2)*step+x-1];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,4,2) = gray_ptr[(y+2)*step+x];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,4,3) = gray_ptr[(y+2)*step+(x+1)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,4,4) = gray_ptr[(y+2)*step+x+2];*/
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,0,0) = gray_ptr[(y-2)*step+(x-2)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,0,1) = gray_ptr[(y-2)*step+x-1];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,0,2) = gray_ptr[(y-2)*step+x];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,0,3) = gray_ptr[(y-2)*step+(x+1)];
//CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,0,4) = gray_ptr[(y-2)*step+(x+2)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,1,0) = gray_ptr[(y-1)*step+(x-2)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,1,1) = gray_ptr[(y-1)*step+x-1];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,1,2) = gray_ptr[(y-1)*step+ x];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,1,3) = gray_ptr[(y-1)*step+(x+1)];
//CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,1,4) = gray_ptr[(y-1)*step+x+2];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,2,0) = gray_ptr[y*step+(x-2)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,2,1) = gray_ptr[y*step+(x-1)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,2,2) = gray_ptr[y*step+x];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,2,3) = gray_ptr[y*step+(x+1)];
//CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,2,4) = gray_ptr[y*step+(x+2)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,3,0) = gray_ptr[(y+1)*step+(x-2)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,3,1) = gray_ptr[(y+1)*step+x-1];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,3,2) = gray_ptr[(y+1)*step+x];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,3,3) = gray_ptr[(y+1)*step+(x+1)];
//CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,3,4) = gray_ptr[(y+1)*step+(x+2)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,4,0) = gray_ptr[(y+2)*step+(x-2)];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,4,1) = gray_ptr[(y+2)*step+x-1];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,4,2) = gray_ptr[(y+2)*step+x];
CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,4,3) = gray_ptr[(y+2)*step+(x+1)];
//CV_MAT_ELEM(*cwindow,float,4,4) = gray_ptr[(y+2)*step+x+2];
calGLCM(cwindow,0,features);
contrast[0] = features[2];
//entropy[0] = features[0];
//energy[0] = features[1];
//homogenity[0] = features[3];
calGLCM(cwindow,1,features);
contrast[1] = features[2];
//entropy[1] = features[0];
//energy[1] = features[1];
//homogenity[1] = features[3];
calGLCM(cwindow,2,features);
contrast[2] = features[2];
//entropy[2] = features[0];
//energy[2] = features[1];
//homogenity[2] = features[3];
calGLCM(cwindow,3,features);
contrast[3] = features[2];
variance = calc_variance(contrast);
//printf("%f\n",contrast[3]);
//entropy[3] = features[0];
//energy[3] = features[1];
//homogenity[3] = features[3];
//if (variance >30)
// dst_ptr[y*step+x] = 0;
//else dst_ptr[y*step+x] = 255;
if (variance >threshold)
{
msk_ptr[(y-2)*step+(x-2)] = 255;
msk_ptr[(y-2)*step+x-1] = 255;
msk_ptr[(y-2)*step+x]=255;
msk_ptr[(y-2)*step+(x+1)]= 255;
//dst_ptr[(y-2)*step+(x+2)]= 255;
msk_ptr[(y-1)*step+(x-2)]= 255;
msk_ptr[(y-1)*step+x-1]= 255;
msk_ptr[(y-1)*step+ x]= 255;
msk_ptr[(y-1)*step+(x+1)]= 255;
//dst_ptr[(y-1)*step+x+2]= 255;
msk_ptr[y*step+(x-2)]= 255;
msk_ptr[y*step+(x-1)]= 255;
msk_ptr[y*step+x]= 255;
msk_ptr[y*step+(x+1)]= 255;
//dst_ptr[y*step+(x+2)]= 255;
msk_ptr[(y+1)*step+(x-2)]= 255;
msk_ptr[(y+1)*step+x-1]= 255;
msk_ptr[(y+1)*step+x]= 0;
msk_ptr[(y+1)*step+(x+1)]= 255;
//dst_ptr[(y+1)*step+(x+2)]= 255;
msk_ptr[(y+2)*step+(x-2)]= 255;
msk_ptr[(y+2)*step+x-1]= 255;
msk_ptr[(y+2)*step+x]= 255;
msk_ptr[(y+2)*step+(x+1)]= 255;
//dst_ptr[(y+2)*step+x+2]= 255;
//dst_ptr[(y+2)*step+x+2]= 0;
}
//dst_ptr[y*step+x] = 0;
else
{
msk_ptr[(y-2)*step+(x-2)] = 0;
msk_ptr[(y-2)*step+x-1] = 0;
msk_ptr[(y-2)*step+x]=0;
msk_ptr[(y-2)*step+(x+1)]= 0;
//dst_ptr[(y-2)*step+(x+2)]= 0;
msk_ptr[(y-1)*step+(x-2)]= 0;
msk_ptr[(y-1)*step+x-1]= 0;
msk_ptr[(y-1)*step+ x]= 0;
msk_ptr[(y-1)*step+(x+1)]= 0;
//dst_ptr[(y-1)*step+x+2]= 0;
msk_ptr[y*step+(x-2)]= 0;
msk_ptr[y*step+(x-1)]= 0;
msk_ptr[y*step+x]= 0;
msk_ptr[y*step+(x+1)]= 0;
//dst_ptr[y*step+(x+2)]= 0;
msk_ptr[(y+1)*step+(x-2)]= 0;
msk_ptr[(y+1)*step+x-1]= 0;
msk_ptr[(y+1)*step+x]= 0;
msk_ptr[(y+1)*step+(x+1)]= 0;
//dst_ptr[(y+1)*step+(x+2)]= 0;
msk_ptr[(y+2)*step+(x-2)]= 0;
msk_ptr[(y+2)*step+x-1]= 0;
msk_ptr[(y+2)*step+x]= 0;
msk_ptr[(y+2)*step+(x+1)]= 0;
}
}
}
cvNamedWindow("mask_before");
cvShowImage("mask_before",msk_img);
cvSmooth(msk_img,msk_img,CV_MEDIAN,19);
cvMorphologyEx( msk_img, msk_img, NULL, NULL, CV_MOP_OPEN, 3 );
// 开运算先腐蚀在膨胀,腐蚀可以清除噪点,膨胀可以修复裂缝
cvMorphologyEx( msk_img, msk_img, NULL, NULL, CV_MOP_CLOSE, 3 );
// 闭运算先膨胀后腐蚀,之所以在开运算之后,因为噪点膨胀后再腐蚀,是不可能去除的
cvNamedWindow("mask");
cvShowImage("mask",msk_img);
cvCopy(src_img,dst_img,msk_img);
cvNamedWindow("dst",CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cvShowImage("dst",dst_img);
finish = clock();
printf(" 计算时间%.2fms \n", (double) (finish - start));
cvWaitKey(0);
}
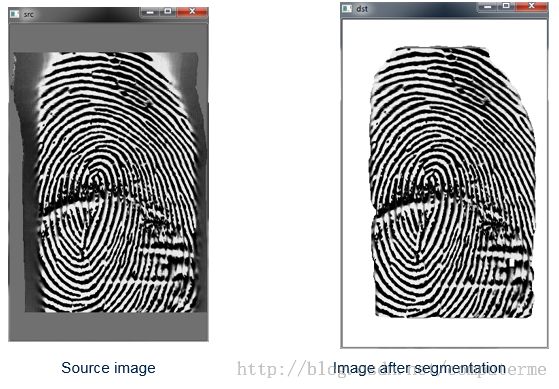
最后的运行如果如下:
测试图片及源代码下载:http://download.csdn.net/detail/computerme/8056957
本文系原创,转载请注明转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/computerme/article/details/40269357
Reference:
灰度共生矩阵在指纹图像分割中的应用. 李慧娜,郭超峰,平源,2012