Linux文本处理命令详解
一。选取命令:
Cutting and Pasting(提取指定内容):
• cut –blist [-n][file-list](以字节为单位进行分割)
• cut –clist [file-list](以字符为单位进行分割)中文必备
• cut –flist [-dchar][-s][file-list](与-d一起使用,指定显示哪个区域)
1.who|cut -b 3//提取who每一行的第3个字节(多个用逗号隔开)
2.如果是中文,用-c则会以字符为单位,输出正常;而-b只会傻傻的以字节(8位二进制位)来计算,输出就是乱码。
3.cut -f1,2 student_record//提取第一、第二个字段
4.没有指定分隔符时,不能提取以非tab(制表符)分隔的文件
其实cut的-d选项的默认间隔符就是制表符,所以当你就是要使用制表符的时候,完全就可以省略-d选项,而直接用-f来取域就可以了。
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ cat /tmp/cut.demo
one yi
two er
three san
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ cut -f1 cut.demo
one yi
two er
three san
5.指定分割字符提取(只能是一个相隔空格)
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ cut -f1 -d" "cut.demo // s12507@Linux:/tmp$cut -d' '-f1 cut.demo
one
two
three
Grep:Linux系统中grep命令是一种强大的文本搜索工具,它能使用正则表达式搜索文本,并把匹配的行打印出来。
Options:
– i Ignore the case of letters(不区分大小写)
– n Print line numbers along with matched lines(显示匹配行及行号)
– v Print nonmatching lines(显示不包括匹配文本的所有行)
– c Print the number of matching lines only(只输出匹配行的个数)
– w Search for the given pattern as a string(寻找给定模式为字符串)
– l Print only the names of files with matchinglines(查询多文件时只输出包含匹配字符的文件名)
eg:
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ grep John /tmp/students //关键字查询
John Doe ECE 3.54 [email protected] 111.222.3333
John Clark ECE 2.68 [email protected] 111.111.5555
John Lee EE 2.64 [email protected] 111.111.2222
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ grep '^R' /tmp/students //正则表达式使用
Rick Marsh CS 23.34 [email protected] 111.222.6666
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ grep -i john /tmp/students //忽略大小写–i(ignored)
John Doe ECE 3.54 [email protected] 111.222.3333
John Clark ECE 2.68 [email protected] 111.111.5555
John Lee EE 2.64 [email protected] 111.111.2222
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ grep -n printf /tmp/hello.c //顺便显示查找内容的行号
4: printf("hello world!\n");
注意:一些正则表达试在某些特定的命令下才能操作
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ egrep -w 'CS|MBA' /tmp/students // CS或者MBA 系的学生
Al Davis CS 2.63 [email protected] 111.222.2222
Ahmad Rashid MBA 3.74 [email protected] 111.222.4444
Rick Marsh CS 23.34 [email protected] 111.222.6666
James Adam CS 2.77 [email protected] 111.222.7777
Jake Zulu CS 3.00 [email protected] 111.111.9999
练习:(With grep(/tmp/databook)
1. Print all lines containing thestring San. grep ‘San’ /tmp/databook
2. Print all lines where theperson's first name starts with J. grep ‘\<J’ /tmp/databook
3. Print all lines ending in 700. grep ‘700$’ /tmp/databook
4. Print all lines that don'tcontain 834. grep ‘834’ –v /tmp/databook
5. Print all lines where birthdaysare in December.grep ‘:/12’ /tmp/databook
6. Print all lines where the phonenumber is in the 408 area code.grep ‘:/408-’ /tmp/databook
7. Print all lines containing anuppercase letter, followed by four lowercase letters, a comma, a space, and oneuppercase letter.
grep '[A-Z][a-z]\{4\}, [A-Z]'/tmp/databook
8. Print lines where the last namebegins with K or k. grep ‘^[A-Za-z] + [kk]’ /tmp/databook
9. Print lines preceded by a linenumber where the salary is a six-figure number. grep –n ‘:[0-9]\{6\}$’ /tmp/databook
10. Print lines containing Lincolnor lincoln (remember that grep is insensitive to case)., grep ‘[Ll]incoln’ /tmp/databook
二。排序命令:
sort: Ordering aset of items according to some criteria
– b Ignore leading blanks(忽略每行前面开始出的空格字符)
– f Consider lowercases anduppercase letters to be equivalent(排序时,忽略大小写字母)
– d Sort according to usual alphabetical order(根据通常的字母顺序排序)
– r Sort in reverse order(以相反的顺序排序)
– k Specify a field as the sortkey(选择以哪个区间进行排序)
– n Compare according to stringnumerical value(依照数值的大小排序)
– t Specify field separator(<分隔字符> 指定排序时所用的栏位分隔字符)
1.默认以文件开头字母来排序,只跟文件名字的时候
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ sort /tmp/myStudent
2.根据第二个字段来排序
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ sort -k2 myStudent
第三个:s12507@Linux:/tmp$ sort –k3 myStudent
3.指定字段分割符:-t
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ sort -t: -k4 myStudent //表示指定分割符为“:”
4.注意语言:
(1)字符为中文时,小写字母在排在前面
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ echo $LANG
zh_CN.UTF-8 //中文
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ sort /tmp/sort.demo
alan
Alice
Jack
Tom
(2)字符为英文时,小写字母在排在后面
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ echo $LANG
C
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ sort /tmp/sort.demo
Alice
Jack
Tom
alan
三。Streameditor – Sed:
sed是一个很好的文件处理工具,本身是一个管道命令,主要是以行为单位进行处理,可以将数据行进行替换、删除、新增、选取等特定工作,下面先了解一下sed的用法
sed命令行格式为: sed [-nefri] ‘command’输入文本
-n∶使用安静(silent)模式。在一般 sed 的用法中,所有来自 STDIN的资料一般都会被列出到萤幕上。但如果加上 -n 参数后,则只有经过sed 特殊处理的那一行(或者动作)才会被列出来。
-i∶直接修改读取的档案内容,而不是由萤幕输出。
删除空白行:Delete blank line
sed'/^$/d' student_record
删除前十行:
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ sed '1,10d' /tmp/students
删除计算机系的学生:
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ sed '/\<CS/d' /tmp/students
修改EECS系为CS系:(默认一行)
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ sed 's/EECS/CS/' /tmp/students
全文替换:
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ sed 's/EECS/CS/g' /tmp/students
打印第二到第五行的内容:
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ sed -n'2,5p' /tmp/students
James Davis ECE 3.71 [email protected] 111.222.1111
Al Davis CS 2.63 [email protected] 111.222.2222
Ahmad Rashid MBA 3.74 [email protected] 111.222.4444
Sam Chu ECE 3.68 [email protected] 111.222.5555
在指定位置前插入:
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ sed '/\<CS/i good students' /tmp/students
指定位置后插入:
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ sed '/\<CS/a good students' /tmp/students
打印所有计算机系的学生:
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ sed -n '/\<CS/p' /tmp/students
Al Davis CS 2.63 [email protected] 111.222.2222
Rick Marsh CS 23.34 [email protected] 111.222.6666
James Adam CS 2.77 [email protected] 111.222.7777
Jake Zulu CS 3.00 [email protected] 111.111.9999
非计算机系的学生:
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ sed -n '/\<CS/!p' /tmp/students
作业(With sed(/tmp/databook).
1. Change Jon's name to Joanthan sed ‘s/Jon/Joanthan/’ /tmp/databook
2. Delete the first three lines sed ‘1,3d’ /tmp/databook
3. Print lines 5 through 10 sed –n ‘5,10p’ /tmp/databook
4. Delete lines containing Lane sed ‘/Lane/d’ tmp/databook
5. Print all lines where the birthdays are inNovember orDecember sed –n ‘/:1[12]\//p’ /tmp/databook
6. Replace the line containing Jose withJOSE HAS RETIRED. sed ‘s/jose.*/JOSE HASRETIRE/’ /tmp/databook
7. Change Popeye's birthday to 11/14/46 sed ‘/Popeye/s/[0-9]*\/[0-9]*\/[0-9]*/11\/14\/46/’ /tmp/databook
8. Delete all blank lines sed ‘/^$/d’ /tmp/databook
四。Awk:
awk是一个强大的文本分析工具,相对于grep的查找,sed的编辑,awk在其对数据分析并生成报告时,显得尤为强大,具有一定的编程能力。
Formof awk command:
awk ‘pattern’ filename
awk ‘{action}’filename
awk ‘pattern {action}’ filename
parameter(参数):
– F specify the field separator(指定字段分隔符)
Awk'spattern is similar to C expression:
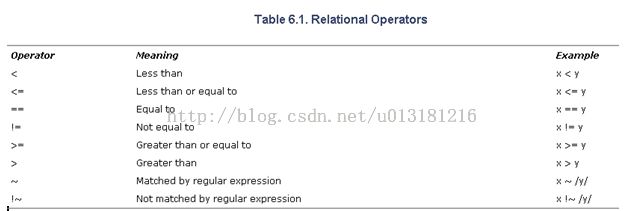
– Relationship expression
– Conditional expression
– Arithmetic expression
– Compound patterns
– Range patterns
Awk's main action is print
Awk's pattern
Eg:
1.以J开头的所有行:
s12507@Linux:/tmp$ awk '/^J/' databook
2.打印第一列和第二列
s12507@Linux:~$ awk '{print $1,$2}' /tmp/student_record
John Doe
James Davis
3.打印计算机系的学生
s12507@Linux:~$ awk '/\<CS/{print $1,$2}' /tmp/student_record
Al Davis
Rick Marsh
James Adam
Jake Zulu
4.打印绩点大于3.5的:
s12507@Linux:~$ awk '$4>3.5' /tmp/student_record
John Doe ECE 3.54
James Davis ECE 3.71
Sam Chu ECE 3.68
Arun Roy SS 3.86
Art Pohm ECE 4.00
Nabeel Ali EE 3.56
Tom Nelson ECE 3.81
Pat King SS 3.77
John Lee EE 3.64
Sunil Raj ECE 3.86
Diane Rover ECE 3.87
Aziz Inan EECS 3.75
4. 打印绩点大于3.5的名单:
s12507@Linux:~$ awk '$4>3.5{print $1,$2}' /tmp/student_record
John Doe
James Davis
Sam Chu
Arun Roy
Art Pohm
Nabeel Ali
Tom Nelson
Pat King
John Lee
Sunil Raj
Diane Rover
Aziz Inan
5.输出last name以R开头的:
s12507@Linux:~$ awk '$2~/^R/' /tmp/student_record
Ahmad Rashid MBA 3.04
Arun Roy SS 3.86
Sunil Raj ECE 3.86
Charles Right EECS 3.31
Diane Rover ECE 3.87
打印名单:
s12507@Linux:~$ awk '$2~/^R/{print $1,$2}' /tmp/student_record
Ahmad Rashid
Arun Roy
Sunil Raj
Charles Right
Diane Rover
6.打印绩点加0.5后大于4的:
s12507@Linux:~$ awk '$4+0.5>4' /tmp/student_record
John Doe ECE 3.54
James Davis ECE 3.71
Sam Chu ECE 3.68
Arun Roy SS 3.86
Art Pohm ECE 4.00
Nabeel Ali EE 3.56
Tom Nelson ECE 3.81
Pat King SS 3.77
John Lee EE 3.64
Sunil Raj ECE 3.86
Diane Rover ECE 3.87
Aziz Inan EECS 3.75
7.打印计算机系且绩点大于2.5的行:
s12507@Linux:~$ awk '$3=="CS" && $4>2.5' /tmp/student_record
Al Davis CS 2.63
James Adam CS 2.77
Jake Zulu CS 3.00
8.以冒号为分割符,打印用户名和工作目录
s12507@Linux:~$ awk -F ':' '1541{print $1,$6}' /etc/passwd
s12486 /home/s12486
s12488 /home/s12488
s12490 /home/s12490
s12492 /home/s12492
s12493 /home/s12493
s12494 /home/s12494
9.绩点2.77的学生
s12507@Linux:~$ awk ‘$4~2.77’ /tmp/student_record
10.几个常见内置变量:
NF:每一行拥有的字段数
NR:表示目前处理的是“第几行”数据 {print NR},NR=1( )NR>2( )
FS:目前的分割符,默认是空格键{FS=':'}
BEGIN:扫描前,显示预设变量
END:扫描后,输出最终结果
还有一些求和等算数内置函数,使用起来非常方便。
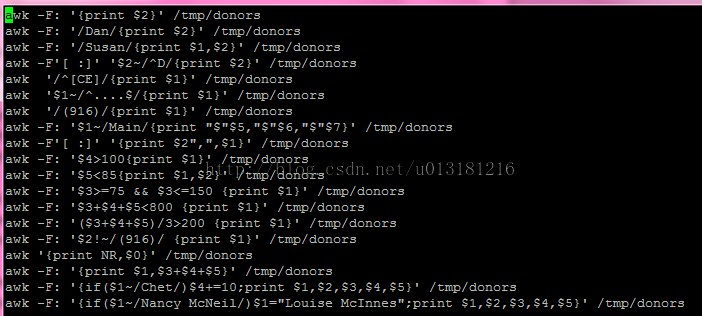
作业With awk(/tmp/donors)::
1.Print all the phone numbers
2.Print Dan's phone number
3.Print Susan's name and phone number
4.Print all last names beginning with D
5.Print all first names beginning witheither a C or E.
6.Print all first names containing onlyfour characters.
7.Print the first names of all those in the916 area code.
8.Print Main’s campaign contributions. Eachvalue should be printed with a leading dollar sign; e.g., $250 $100 $175.
9.Print second name followed with a commaand first name
10.Print the first and last names of thosewho contributed more than $100 in the second month.
11.Print the names and phone numbers ofthose who contributed less than $85 in the last month.
12.Print the names of those who contributedbetween $75 and $150 in the first month.
13.Print the names of those who contributedless than $800 over the three-month period.
14.Print the names and addresses of those withan average monthly contribution greater than $200.
15.Print the first name of those not in the916 area code.
16.Print each record preceded by the numberof the record.
17.Print the name and total contribution ofeach person.
18.Add $10 to Chet's second contribution.
19.Change Nancy McNeil's name to LouiseMcInnes.
五。其他命令:
1.统计命令: wc -l 行数,-w字数,-m字符数,没有option表示三者。
2.双向重定向:tee (不仅在实现重定向,还在屏幕输出) -a表示累加进去。
3.文件分割: split -b 大小(200K) -l行数(10)
4.去重复命令:uniq -c 记录重复次数