关于二叉堆(优先队列)的其他操作及其应用
【0】README
0.1)本文总结于 数据结构与算法分析;源代码均为原创, 旨在了解到我们学习了优先队列后,还能干些什么东西出来, 增加学习的interest;
0.2)以下列出了 关于二叉堆(优先队列)的其他有用的操作, 其内容基本可以囊括大部分的优先队列知识点, 亮点是这里还引入到了 堆排序;
0.3)二叉堆的insert 和 deleteMin 基本操作和概念,参见 http://blog.csdn.net/pacosonswjtu/article/details/49498023
【1】二叉堆的操作应用
1.1)降低关键字的值——decreaseKey
- 1)decreaseKey概述: decreaseKey(P, △, H) 操作降低在位置 P处的关键字的值, 降值的幅度为正的量△; 由于这可能破坏堆的序, 因此必须通过 上滤 对堆进行调整;
- 2)decreaseKey应用: 该操作对 系统管理程序是有用的, 系统管理程序能够使它们的程序以最高的优先级来运行;
1.2)增加关键字的值——increaseKey
- 1)increaseKey概述: increaseKey(P, △, H) 操作增加在位置 P处的关键字的值,增值的幅度为正的量△; 由于这可能破坏堆的序, 因此必须通过 下滤 对堆进行调整;
- 2)increaseKey应用: 许多os 调度程序自动地降低正在过多地消耗 CPU 时间的进程的优先级;
1.3)删除某个位置上的元素——deleteElement
- 1)deleteElement概述: delete(P, H)操作删除堆中位置P 上的节点,这通过首先执行 decreaseKey(P, ∞, H), 然后再执行 deleteMin 来完成;
- 2)deleteElement 应用:当一个进程被用户终止(而不是正常终止时), 它必须从优先队列中除去;
1.4)构建堆——buildHeap
- 1)buildHeap 概述: buildHeap(H) 操作把N个关键字作为输入并把他们放入空堆中;显然, 这可以使用 N个相继的insert操作来完成;
- 2)buildHeap 应用:
1.5)优先队列的应用(我这里只列出 了选择问题, 当然远远不止这一个应用, 这个应用我还没有编写源代码实现)
- 1)我们将要考察的第一个问题是选择问题: 当时的输入是 N 个元素以及一个整数 k, 这N 个元素的集可以是全序的,该选择问题是要找出 第k个最大的元素;
- 2)利用优先队列来解决(二叉堆属于优先队列): 对上述N个元素建立 大根堆, 然后删除k-1个最大元素, 那么二叉堆的根节点的元素就是第k个最大元素;
- 3)堆排序: 注意, 如果我们对 k=N 运行该程序并在 元素离开对时记录他们的值, 那么实际上已经对输入文件以时间 O(NlogN) 做了排序,这样就得到一种快速的排序算法——堆排序;
Attention)
- A1) 改动的节点的儿子情况只有3种: 要么一个儿子都没有, 要么只有一个左儿子,要么有两个儿子 (不可能只有一个右儿子);
- A2) 就编程而言,上滤的难度 小于 下滤的难度;
其他堆操作的源代码(核心是 堆的上滤 percolateUp 和下滤percolateDown操作):
【2】source code+printing
2.0)Warning of percolateDown :
- W1)因为涉及到利用下滤操作把随机数组(下标从0开始)建立堆(buildHeap 操作) , 然而在堆的其他操作,如插入,删除操作中,使用的下标是从1开始以便于编程;所以我们的下滤操作分为下标从0开始的percolateDownFromZero 和 下标从1开始的percolateDownFromOne,不过上述percolateDown 的两个版本的 编程idea 都是一样的,只是数组的起始下标不一样而已,这是我们应该注意的;
- W2) 代码中, 只有buildHeap 使用的下滤 percolateDownFromZero 版本,而其他操作使用的是 percolateDownFromOne;
- W3)你要知道实现 堆操作的代码核心是: 上滤percolateUpFromOne 和下滤操作 percolateDownFromOne + percolateDownFromZero;
2.1)download source code :
https://github.com/pacosonTang/dataStructure-algorithmAnalysis/tree/master/chapter6
2.2)source code at a glance:
[1st file binaryheap.h]
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define ElementType int
#define Error(str) printf("\n error: %s \n",str)
struct BinaryHeap;
typedef struct BinaryHeap *BinaryHeap;
void swap(ElementType *x, ElementType *y);
BinaryHeap initBinaryHeap(int capacity);
void insert(ElementType value, BinaryHeap bh);
ElementType deleteMin(BinaryHeap);
int isFull(BinaryHeap bh);
int isEmpty(BinaryHeap bh);
void percolateUp(int index, BinaryHeap bh);
void percolateDownFromOne(int index, BinaryHeap bh);
void printBinaryHeap(BinaryHeap bh);
void printBinaryHeapFromZero(BinaryHeap bh);
struct BinaryHeap
{
int capacity;
int size;
ElementType *elements;
};[2st file binaryHeapBasicOperation.c]
#include "binaryheap.h"
//judge whether the BinaryHeap is full or not , also 1 or 0
int isFull(BinaryHeap bh)
{
return bh->size == bh->capacity - 1 ? 1 : 0 ;
}
//judge whether the BinaryHeap is empty or not , also 1 or 0
int isEmpty(BinaryHeap bh)
{
return bh->size == 0 ? 1 : 0 ;
}
void swap(ElementType *x, ElementType *y)
{
ElementType temp;
temp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = temp;
}
// get the left child of node under index with startup 1
int leftChildFromOne(int index)
{
return index * 2;
}
ElementType deleteMin(BinaryHeap bh)
{
ElementType minimum;
ElementType *data;
if(isEmpty(bh))
{
Error("failed deleting minimum , for the BinaryHeap is empty, from func deleteMin !");
return -1;
}
data = bh->elements;
minimum = data[1];
swap(&data[1], &data[bh->size]);
bh->size-- ; // size-- occurs prior to percolateDownFromOne
percolateDownFromOne(1, bh) ;
return minimum;
}
// Attention, the index of the heap starts from 1
void insert(ElementType value, BinaryHeap bh)
{
int i;
if(isFull(bh))
{
Error("failed insertion , for the BinaryHeap is full, from func insert!");
return ;
}
for(i = ++bh->size; bh->elements[i/2] > value; i /= 2)
bh->elements[i] = bh->elements[i / 2];
bh->elements[i] = value;
}
BinaryHeap initBinaryHeap(int capacity)
{
BinaryHeap bh;
ElementType *temp;
bh = (BinaryHeap)malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryHeap));
if(!bh) {
Error("out of space, from func initBinaryHeap");
return NULL;
}
bh->capacity = capacity;
bh->size = 0;
temp = (ElementType *)malloc(capacity * sizeof(ElementType));
if(!temp) {
Error("out of space, from func initBinaryHeap");
return NULL;
}
bh->elements = temp;
return bh;
}
void printBinaryHeap(BinaryHeap bh)
{
int i;
ElementType *temp;
if(!bh)
Error("printing execution failure, for binary heap is null, from func printBinaryHeap");
temp = bh->elements;
for(i = 1; i < bh->capacity; i++)
{
printf("\n\t index[%d] = ", i);
if(i <= bh->size)
printf("%d", bh->elements[i]);
else
printf("NULL");
}
printf("\n");
}
//print the binary heap who starts from index 0
void printBinaryHeapFromZero(BinaryHeap bh)
{
int i;
ElementType *temp;
if(!bh)
Error("printing execution failure, for binary heap is null, from func printBinaryHeap");
temp = bh->elements;
for(i = 0; i < bh->capacity; i++)
{
printf("\n\t index[%d] = ", i);
if(i < bh->size)
printf("%d", bh->elements[i]);
else
printf("NULL");
}
printf("\n");
}
[3rd file binaryHeapOtherOperation.c]
#include "binaryheap.h"
#define Infinity 10000
// switch the elements
void swap(ElementType *x, ElementType *y)
{
ElementType temp;
temp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = temp;
}
// get the parent of the element with index
int parentFromOne(int index)
{
return index / 2;
}
// percolating up the element when its value is greater than children (minimal heap)
//Attention: all of bh->elements starts from index 1
void percolateUpFromOne(int index, BinaryHeap bh)
{
ElementType *data;
ElementType temp;
int size;
int parent;
data = bh->elements;
size = bh->size;
for(temp = data[index]; parentFromOne(index) > 0; index = parent)
{
parent = parentFromOne(index);
if(parent == 0 || temp > data[parent])
break;
else
data[index] = data[parent];
}
data[index] = temp;
}
// get the left child of node under index with startup one
int leftChildFromOne(int index)
{
return index * 2;
}
// percolating down the element when its value is greater than children (minimal heap)
//Attention: all of bh->elements starts from index 1
void percolateDownFromOne(int index, BinaryHeap bh)
{
ElementType *data;
int size;
ElementType temp;
int child;
data = bh->elements;
size = bh->size;
for(temp = data[index]; leftChildFromOne(index) <= size; index = child)
{
child = leftChildFromOne(index);
if(child < size && data[child] > data[child+1])
child++;
if(temp > data[child])
data[index] = data[child];
else
break;
}
data[index] = temp;
}
//decreasing value of the element under index by increment
void decreaseKey(int index, ElementType decrement, BinaryHeap bh)
{
if(index > bh->size || index < 1)
{
Error(" failed decreaseKey, since overstep the boundary! ");
return ;
}
bh->elements[index] -= decrement; // update the element under given index
percolateUpFromOne(index, bh);
}
//increasing value of the element under index by increment
void increaseKey(int index, ElementType increment, BinaryHeap bh)
{
if(index > bh->size || index < 1)
{
Error(" failed increaseKey, since overstep the boundary! ");
return ;
}
bh->elements[index] += increment; // update the element under given index
percolateDownFromOne(index, bh);
}
//deleting the element under index
void deleteElement(int index, BinaryHeap bh)
{
decreaseKey(index, Infinity, bh); // 1st step, decreaseKey operation placing the element under index upto the root
deleteMin(bh); //2nd step, deleteMin deleting the element under the root;
}
// get the left child of node under index with startup zero
int leftChildFromZero(int index)
{
return index * 2 + 1;
}
// percolating down the element when its value is greater than children (minimal heap)
//Attention: all of bh->elements starts from index 0
void percolateDownFromZero(int index, BinaryHeap bh)
{
ElementType *data;
ElementType temp;
int size;
int child;
data = bh->elements;
size = bh->size;
for(temp = data[index]; leftChildFromZero(index) < size; index = child)
{
child = leftChildFromZero(index);
if(child < size - 1 && data[child] > data[child+1])
child++;
if(temp > data[child])
data[index] = data[child];
else
break;
}
data[index] = temp;
}
// building the heap with data in array randomly
void buildHeap(BinaryHeap bh)
{
int i;
ElementType *data;
data = bh->elements;
for(i = bh->size/2; i >= 0; i--)
percolateDownFromZero(i, bh);
}
int main()
{
ElementType data[] = {85, 80, 40, 30, 10, 70, 110}; // P141
ElementType buildHeapData[] = {150, 80, 40, 30, 10, 70, 110, 100, 20, 90, 60, 50, 120, 140, 130};
BinaryHeap bh;
int size;
int i;
int capacity;
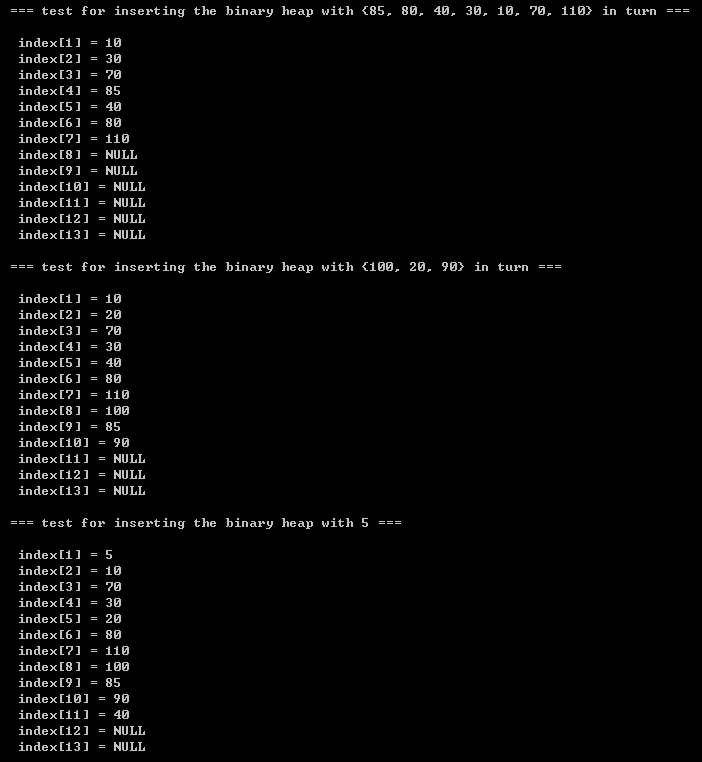
printf("\n\t=== test for inserting the binary heap with {85, 80, 40, 30, 10, 70, 110} in turn ===\n");
capacity = 14;
bh = initBinaryHeap(capacity);
size = 7;
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
insert(data[i], bh);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
printf("\n\t=== test for inserting the binary heap with {100, 20, 90} in turn ===\n");
insert(100, bh);
insert(20, bh);
insert(90, bh);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
printf("\n\t=== test for inserting the binary heap with 5 ===\n");
insert(5, bh);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
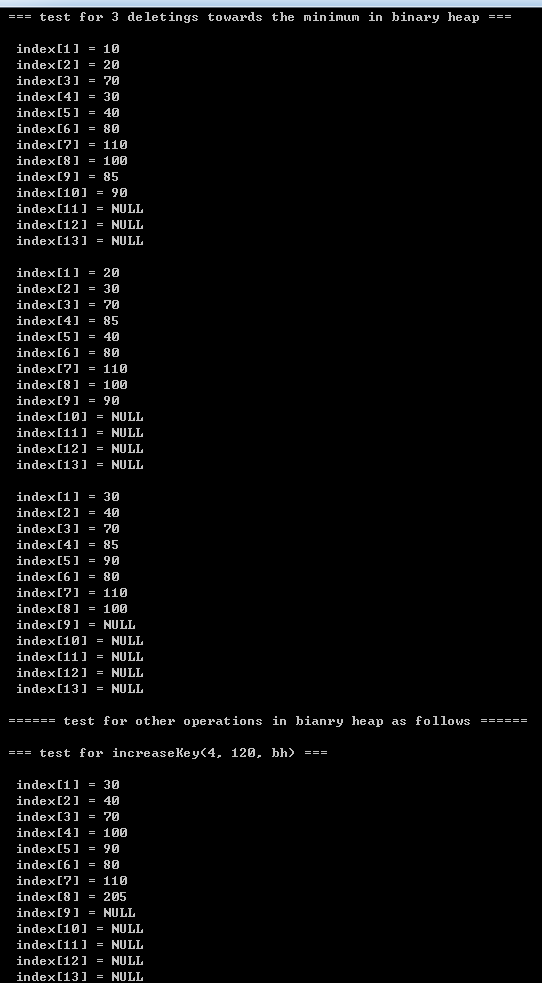
printf("\n\t=== test for 3 deletings towards the minimum in binary heap ===\n");
deleteMin(bh);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
deleteMin(bh);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
deleteMin(bh);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
// other operations in bianry heap
printf("\n\t====== test for other operations in bianry heap as follows ======\n");
printf("\n\t=== test for increaseKey(4, 120, bh) ===\n");
increaseKey(4, 120, bh);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
printf("\n\t=== test for increaseKey(2, 120, bh) ===\n");
increaseKey(2, 120, bh);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
printf("\n\t=== test for decreaseKey(9, 195, bh) ===\n");
decreaseKey(9, 195, bh);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
printf("\n\t=== test for decreaseKey(4, 90, bh) ===\n");
decreaseKey(4, 90, bh);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
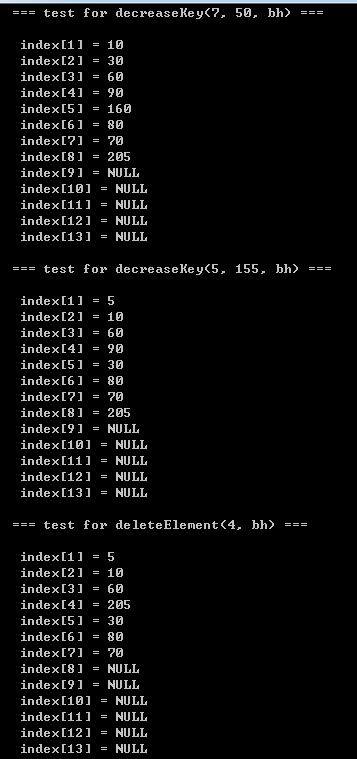
printf("\n\t=== test for decreaseKey(7, 50, bh) ===\n");
decreaseKey(7, 50, bh);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
printf("\n\t=== test for decreaseKey(5, 155, bh) ===\n");
decreaseKey(5, 155, bh);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
printf("\n\t=== test for deleteElement(4, bh) ===\n");
deleteElement(4, bh);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
printf("\n\t=== test for deleteElement(1, bh) ===\n");
deleteElement(1, bh);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
printf("\n\t=== test for deleteElement(3, bh) ===\n");
deleteElement(3, bh);
printBinaryHeap(bh); // test over , Bingo!
// as you know, the build heap operation is identical with other operations
printf("\n\t=== test for building heap with {150, 80, 40, 30, 10, 70, 110, 100, 20, 90, 60, 50, 120, 140, 130} ===\n");
capacity = 16;
bh = initBinaryHeap(capacity);
bh->size = 15;
bh->elements = buildHeapData;
buildHeap(bh);
printBinaryHeapFromZero(bh);
return 0;
}