基数排序
【0】README
0.1) 本文总结于 数据结构与算法分析,但源代码均为原创;旨在理清 基数排序的具体步骤;
0.2) 要知道, 基数排序 等价于 多次桶排序,所以了解基数排序的前提是了解桶排序,桶排序的详情,参见: http://blog.csdn.net/pacosonswjtu/article/details/49685749
Attention) 基数排序,说白了就是进行多次的桶式排序;
【1】算法介绍
1.1)基数排序的思想:“多关键字排序”。
1.2)基数排序有两种实现方式:最高位优先+最低位优先
- 1.2.1)第一种叫做最高位优先:即先按最高位排成若干子序列, 再对每个子序列按次高位来排,以此类推。
- 举个荔枝(扑克牌): 就是先按花色排成4个子序列, 再对每种花色的13张牌进行排序, 最终使所有扑克牌有序;
- 1.2.2)第二种叫做最低位优先: 这种方式不必分成子序列。每次排序全体元素都参与。
- 举个荔枝(扑克牌): 可以先按数字将牌分配到13个桶中, 然后从第一个桶开始依次收集; 再将收集好的牌按照花色分配到4个桶中,然后还是从第一个桶开始依次收集,结果两次分配和收集,最终使牌有序;
【2】最低位优先的基数排序执行流程
2.1)看个荔枝:
原始序列:110 245 895 658 321 852 147 458 469 159 357 028
2.2)执行流程:每个元素的每一位都是由数字构成, 数字范围0~9; 所以准备10个桶来放元素。要注意, 组成的元素的每一位不一定是数组。如果元素的某一位是扑克牌的花色, 因为花色有4种, 所以在按花色那一位排序时, 要准备4个桶。同样的道理, 如果元素有一位英文字母, 那么按这一位排序, 就要准备26个桶。
Attention)这里说的桶, 其实是一个先进先出的队列(数据从桶的上面进,下面出);
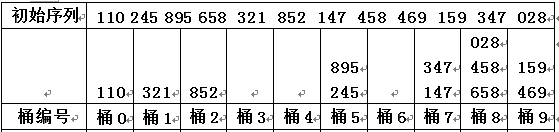
step1)第一趟分配和收集数据,按照最后一位:
step1.2)从桶中收集数据
按桶0~桶9的顺序收集, 注意数据从桶的下面出;
将每桶收集的数据依次排开, 所以第【1】趟收集后的结果为: 110, 321, 852, 245, 895, 147, 347, 658, 458, 028, 469, 159 ;- Result)注意观察, 最低位是有序的, 这就是第1趟基数排序后的结果;
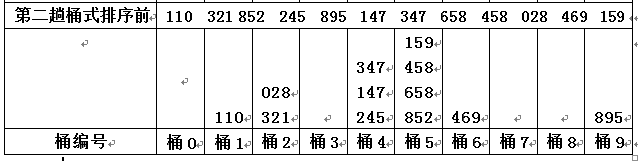
step2)第二趟分配和收集数据,按照次低位(3位数中间那一位):
step2.2)从桶中收集数据
将每桶收集的数据依次排开, 所以第【2】趟收集后的结果为:110 321 028 245 147 347 852 658 458 159 469 895 ;- Result)此时, 次低位有序了, 并且次低位相同的那些元素, 其最低位也是有序的,这就是第2趟基数排序后的结果;
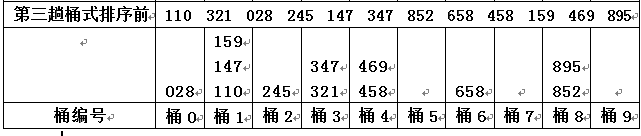
step3)第三趟分配和收集数据,按照次次低位(3位数最高那一位):
step3.2)从桶中收集数据
将每桶收集的数据依次排开, 所以第【3】趟收集后的结果为: 028 110 147 159 245 321 347 458 469 658 852 895- Result)此时, 次次低位(最高位)有序了, 并且 次次低位相同的那些元素, 其次低位也是有序的;次低位相同的元素,其最低位时有序的, 这就是第3趟基数排序后的结果, 也即整个序列有序, 基数排序过程结束;
【3】source code + printing result
3.1)download source code :
https://github.com/pacosonTang/dataStructure-algorithmAnalysis/tree/master/chapter7/radixSort
3.2)source code at a glance:
[1st file : p189_bucketSort.h ]
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MAX 10
#define ElementType int
#define Error(str) printf("\n\t error: %s \n",str)
struct Node;
typedef struct Node *Node;
Node *initBuckets();
void bucketSort(Node* buckets, ElementType data, int index);
void radixSort(Node* buckets, ElementType* data, int size);
void bucketsToData(Node* buckets, ElementType *data);
void printBuckets(Node* data);
void printArray(ElementType data[], int size);
Node makeEmpty();
struct Node
{
int value;
Node next;
};[2nd file : p189_bucketSort.c ]
#include "p189_bucketSort.h"
// allocate the memory for the bucket and bucket ptr
Node *initBuckets()
{
Node* buckets;
int i;
buckets = (Node*)malloc(MAX * sizeof(Node));
if(!buckets)
{
Error("out of space, from func bucketSort!");
return NULL;
}
for(i=0; i<MAX; i++)
buckets[i] = makeEmpty();
return buckets;
}
//allocate the memory for the node and make it empty with evaluation of next
Node makeEmpty()
{
Node temp;
temp = (Node)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if(!temp)
{
Error("out of space, from func makeEmpty!");
return NULL;
}
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
void bucketsToData(Node* buckets, ElementType *data)
{
int i;
int j;
Node temp;
i = 0;
j = 0;
while(i< MAX) // and now, we update the data array from buckets
{
temp = buckets[i]->next;
while(temp)
{
data[j++] = temp->value;
temp = temp->next;
}
i++;
}
// updating over
}
// details of bucketSort for the input array data with size
void bucketSort(Node* buckets, ElementType data, int index)
{
Node temp;
temp = buckets[index];
while(temp->next)
temp = temp->next;
temp->next = makeEmpty();
temp->next->value = data;
}
void printBuckets(Node* buckets)
{
int i;
Node node;
for(i = 0;i<MAX; i++)
{
if(!buckets[i]->next)
continue;
for(node = buckets[i]->next; node != NULL; node = node->next)
printf("\n\t buckets[%d] = %d", i, node->value);
}
printf("\n");
}
void printArray(ElementType data[], int size)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
printf("\n\t data[%d] = %d", i, data[i]);
printf("\n\n");
} [3nd file : p189_radixSort.c ]
#include "p189_bucketSort.h"
#define Round 3
ElementType singleBit(ElementType value, int bit)
{
int i;
i = 1;
while(i++ < bit)
value = value / 10;
return value % 10;
}
//free the memory the buckets own
void clearBuckets(Node* buckets)
{
int i;
Node temp;
Node tempTwo;
for(i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
{
temp = buckets[i]->next;
buckets[i]->next = NULL;
while(temp)
{
tempTwo = temp->next;
free(temp);
temp = NULL;
temp = tempTwo;
}
}
}
// proceeding the radix sorting for the array
void radixSort(Node* buckets, ElementType* data, int size)
{
int i;
int j;
for(i = 1; i <= Round; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<size; j++)
bucketSort(buckets, data[j], singleBit(data[j],i));
// coducting bucket sorting for data array over
bucketsToData(buckets, data);// and now, we update the data array from buckets
clearBuckets(buckets);
}
}
int main()
{
int size;
Node* buckets;
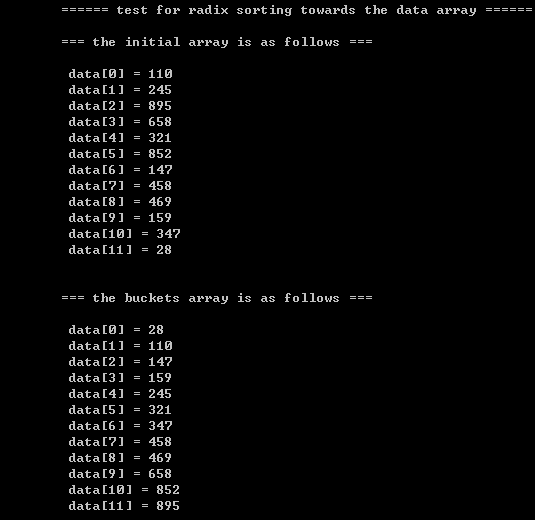
ElementType data[] = {110, 245, 895, 658, 321, 852, 147, 458, 469, 159, 347, 28};
printf("\n\t====== test for radix sorting towards the data array ======\n");
printf("\n\t=== the initial array is as follows ===\n");
size = 12;
printArray(data, size);
buckets = initBuckets();
printf("\n\t=== the buckets array is as follows ===\n");
radixSort(buckets, data, size);
printArray(data, size);
//printf("%2d", singleBit(28, 4));
return 0;
}