High Performance Mysql 读书笔记——创建高性能索引
以下内容针对BTree索引。
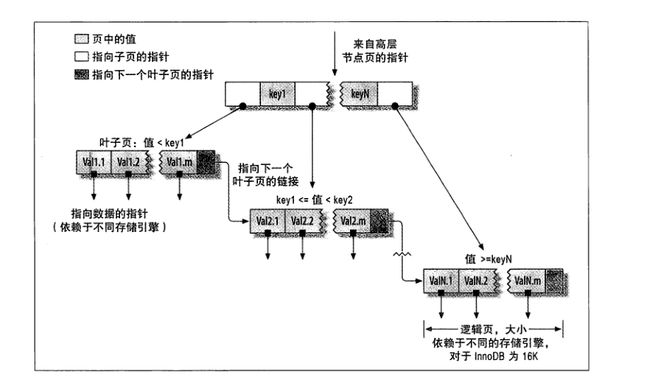
叶子节点:没有子节点的节点。
节点页:存放索引列
叶子页:存放行的全部数据。
为什么要使用索引
1.使用索引可以大大减少服务器需要扫描的数据量。
2.使用索引可以帮助服务器避免排序或者临时表
3.索引是随机I\O变为 顺序I\O.
索引的适用范围
索引并不是适用于任何情况。对于中型、大型表适用。对于小型表全表扫描更高效。而对于特大型表,考虑”分区”技术。
B-Tree 索引的限制(其他类型索引:略)
1.必须按照索引最左列开始查找.最左前缀原则。
2.不能跳过索引中的列.
示例:
mysql> show create table people \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: people
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `people` (
`last_name` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`first_name` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`dob` date NOT NULL,
`gender` enum('m','f') NOT NULL,
KEY `last_name` (`last_name`,`first_name`,`dob`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> explain select * from people where last_name="Smith" \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: people
type: ref
possible_keys: last_name
key: last_name
key_len: 152
ref: const
rows: 1
Extra: Using index condition
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from people where last_name="Smith" and dob="1990-10-20"
\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: people
type: ref
possible_keys: last_name
key: last_name
key_len: 152
ref: const
rows: 1
Extra: Using index condition
1 row in set (0.00 sec)其中的key_len没有变化,说明两个sql走的索引长度一致。
mysql> explain select * from people where last_name="Smith" and dob="1990-10-20"
and first_name="a"\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: people
type: ref
possible_keys: last_name
key: last_name
key_len: 307
ref: const,const,const
rows: 1
Extra: Using index condition
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from people where last_name="Smith" and first_name="a" a
nd dob="1990-10-20"\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: people
type: ref
possible_keys: last_name
key: last_name
key_len: 307
ref: const,const,const
rows: 1
Extra: Using index condition
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
比对后知道,组合索引中,遵循最左前缀的前提下,其后的列的查询排列顺序(但不能缺少某个查询),并不影响索引的使用情况。
高性能的索引策略
- 独立的列
示例: 需要保证actor_id在等号左边独立一列。
mysql> explain select * from actor where actor_id+1=2 \G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: actor
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 4
Extra: Using where
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
ERROR:
No query specified
mysql> explain select * from actor where actor_id=1 \G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: actor
type: const
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 4
ref: const
rows: 1
Extra: NULL
1 row in set (0.00 sec)前缀索引与索引选择性
对于比较长的字符串类型的列,可以创建自定义哈希索引。
另外,可以索引开始的部分字符串(取代全部),大大节约索引空间,提高索引效率。但这样会降低索引的选择性。
什么是索引的选择性:
索引的基数(Cardinality) / 表的总记录数(#T)
范围从 1#T ~ 1 ,值越高查询效率越高。唯一索引的选择性是:1.
注:索引的基数(Cardinality)不重复的索引值。此处计算的基数(Cardinality),与explain执行计划显示的并不一致!
所以,对比较长的 (Varchar、Text、BLOB等等数据类型)列查询,要保证索引的选择性,又要不能太长以节省空间。所以“前缀”需要选的恰到好处:
- “前缀”索引的基数应该接近完整的列索引的基数。
示例:前7个字符的前缀索引
mysql> select count(Distinct last_name)/count(*) from people ; +------------------------------------+ | count(Distinct last_name)/count(*) |
+------------------------------------+
| 0.7059 |
+------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.07 sec)
------------------------------------------------------------
mysql> select count(Distinct left(last_name,5))/count(*), count(Distinct left(la st_name,6))/count(*) ,count(Distinct left(last_name,7))/count(*) from people \G *************************** 1. row *************************** count(Distinct left(last_name,5))/count(*): 0.6471
count(Distinct left(last_name,6))/count(*): 0.7059 count(Distinct left(last_name,7))/count(*): 0.7059
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> alter table people add key (last_name(6))前缀索引是能够使索引更小,更快的方法,但是无法使用前缀索引做 Group By\Order By,也不能用前缀索引做覆盖查询(Using Index)。
多列索引
对于一个B-Tree 多列索引,索引列的顺序意味着索引首先会按照最左列进行排序,其次是第二列,依次列推。
所以如何选择一个列作为组合索引的最左索引列?
选择性 越高越好(计算方法见上文) 或者 频繁使用到的列
mysql> explain select * from t where c1=1 and c2=1 \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t
type: ref
possible_keys: c1c2
key: c1c2
key_len: 10
ref: const,const
rows: 7
Extra: NULL
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from t where c1=1 and c2=1 and c3=10 \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t
type: ref
possible_keys: c1c2
key: c1c2
key_len: 10
ref: const,const
rows: 7
Extra: Using where
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select sum(c1=1), sum(c2=1), sum(c3=10),count(1) from t \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
sum(c1=1): 90
sum(c2=1): 29
sum(c3=10): 0
count(1): 454
1 row in set (0.00 sec)聚簇索引
InnoDB通过主键聚集数据,如果没有主键,InnoDB会选择一个唯一且非空索引代替。如果这个也没有,InnoDB会隐式的定义一个主键作为聚簇索引。
InnoDB只会聚集一个页面中的数据,相邻键值的数据物理上可能相距甚远。
覆盖索引
mysql> show index from t\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: t
Non_unique: 1
Key_name: c1c2
Seq_in_index: 1
Column_name: c1
Collation: A
Cardinality: 454
Sub_part: NULL
Packed: NULL
Null: YES
Index_type: BTREE
Comment:
Index_comment:
*************************** 2. row ***************************
Table: t
Non_unique: 1
Key_name: c1c2
Seq_in_index: 2
Column_name: c2
Collation: A
Cardinality: 454
Sub_part: NULL
Packed: NULL
Null: YES
Index_type: BTREE
Comment:
Index_comment:
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select c1,c2 from t \G
*************************** 1. row ********************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t
type: index
possible_keys: NULL
key: c1c2
key_len: 10
ref: NULL
rows: 454
Extra: Using index冗余与重复索引
- 重复索引:相同列上按照相同顺序创建的相同类型的索引。
- 冗余索引:已有索引(A,B),现在 创建索引 (A)就是一个冗余索引,因为,索引(A)完全可以被 (A,B)替代。然而,(B,A)、(B) 并不是 (A,B)的冗余索引。
另外当Id列是主键,(A,Id)是冗余索引,因为二级缓存的叶子节点包含了主键值。直接使用(A)作为索引即可。
未使用的索引 也是累赘。建议删除。
http://blog.codinglabs.org/articles/index-condition-pushdown.html
待续…………