JSP简介
前言
知识点
1.JSP是什么
java server page,java服务器端页面技术。其主要作用在服务器端动态生成页面, 其组成java代码和html,
2.JSP的组成
html:包括css/js
java
java代码段
<%java代码%>
表达式
<%=%>
3.隐含对象
对象不需要创建,可以直接调用。 out 、 request 、response;
4.指令
servelt引擎在将.jsp文件转换成servelt源文件时,所做的一些额外的处理。
语法:
<%@指令名 属性%>
常用的一些指令
<%@page import="java.util.*"%>
<%@page pageEncoding="utf-8" contentType="text/html;charset=utf-8"%>
pageEncoding: jsp文件在保存的时候需要按照什么样的编码格式来保存。
contentType:等同于response 的setContentType()
5.JSP的执行
jsp引擎 (servelt引擎 )会将jsp文件转换为一个servelt源文件,再去 调用其service方法
6.转换
html:放到service中,使用write输出
java: 放到service中,照搬
表达式:放到service中,使用print输出
7.转发
a.同一个应用中,一个组件完成部分请求,将未完成的请求转交给另外一个组件继续处理。 在这些组件之间HttpServeltRequest对象共享。
b.转发步骤:
//绑定数据到request对象中
request.setAttribute(String name, Object obj);
Object request.getAtrribute(String name);
如果name没有找到就返回 null
//创建转发器
RequestDispatcher rd=request.getRequestDispatcher("emplist.jsp");
rd.forward(request, response);
也可以这样写
request.getRequestDispatcher("emplist.jsp").forward(request, response);
c.转发和重定向的区别
1).重定向是这件事已经完成,转发是这件事完成了部分。
2).重定向的地址是任意的,转发是在同一程序内部组件之间。
3).重定向地址栏中的地址会发生改变,而转发不会改变。
8.路径问题
(1)链接 (2)表单提交 (3)重定向 (4)转发
相对路径:不以“/”开头的路径
绝对路径:以“/”开头的路径。
以(1)、(2)、(3)的情况,绝对路径从应用名开始,(4)绝对路径从应用名之后开始
正文
JSP
Java Server Page; JavaEE 规范
servlet的不足
servlet不善于做页面显示; 每次修改程序修改配置都必须重新部署重启服务器
Jsp的特点
善于做页面显示; 修改程序修改配置不需要重新部署重启服务器; 是一个特殊的servlet; 在HTML标签中嵌套java代码; 处理业务逻辑,程序的可读性不好
定义书写Jsp程序
文件的后缀名 .jsp
在jsp中书写java代码
1.脚本
脚本格式 <% java代码 %>
a.普通脚本
<% %>
特点:
书写java代码
不能在普通脚本中定义方法
不能在普通脚本中定义成员变量,定义的变量是局部变量
java语句一定要以分号结束
普通脚本中的java语句会定义在转换后的 servlet中的service方法中
b.定义脚本
<%! %>
特点:
定义方法,成员变量,不能书写普通java语句
定义脚本中的java语句定义在转换后的servlet中的类体中。
c.输出脚本
<%= %>
特点:不能定义方法,不能定义变量,java语句不能含有分号
输出脚本会将java语句定义在转换后的 servlet的service方法中的out.print(java语句);
注意:
脚本之间不能嵌套
脚本中不能嵌套HTML标签
HTML中必须合理嵌套脚本
Jsp中常用的指令
1.page指令
设置当前jsp页面的一些基本属性
<%@page
*language="java" 设置jsp页面融合的编程语言
*pageEncoding="编码方式" 设置request请求的编码方式
request.setCharacterEncoding();
*contentType="文件类型和编码方式" 设置当前输出内容的文件类型和编码方式
response.setContentType()
*import="类的全限定名" 引入依赖的类所对应的包
session="true/false" 设置当前页面是否支持session
extends="" 设置当前jsp的父类
buffer = "数字" 设置当前jsp缓存容量
isELIgnored = "true/false" 表示当前页面是否支持EL表达式
isErrorPage = "true/false" 表示当前页面是否是错误信息展示页面
errorPage = "目标页面" 设置错误信息展示页面
info = "" 当前jsp的描述信息
autoFlush = "true/false" 当前页面是否自动清理缓存
isThreadSafe = "true/false" 设置当前页面是否线程安全
%>
2.taglib指令
<%@taglib
prefix="" 设置引入标签库的标签前缀
uri="" 设置被引入的标签库的路径
%>
3.include指令
<%@include file="" 设置被包涵的页面的路径 %>
Jsp中的内置对象
request 请求对象 封装请求信息
response 响应对象
封装响应信息
1.设置HTTP标头的方法
void addCookie(Cookie cookie)
Adds the specified cookie to the response.
void addDateHeader(java.lang.String name, long date)
Adds a response header with the given name and date-value.
void addHeader(java.lang.String name, java.lang.String value)
Adds a response header with the given name and value.
void addIntHeader(java.lang.String name, int value)
Adds a response header with the given name and integer value.
boolean containsHeader(java.lang.String name)
Returns a boolean indicating whether the named response header has already been set.
void setDateHeader(java.lang.String name, long date)
Sets a response header with the given name and date-value.
void setHeader(java.lang.String name, java.lang.String value)
Sets a response header with the given name and value. 例如设置浏览器无缓冲:setHeader("pragma"."no-cache");或者setHeader("cache-control"."no-cache");
注:
60秒重新加载本页面
setIntHeader("refresh",60);
3秒后浏览器加载新的页面
setHeader("referesh","3;URL=http://www.baidu.com");
void setIntHeader(java.lang.String name, int value)
Sets a response header with the given name and integer value.
java.lang.String encodeURL(java.lang.String url)
Encodes the specified URL by including the session ID in it, or, if encoding is not needed, returns the URL unchanged.
2.重定向解析
void sendRedirect(java.lang.String location)
Sends a temporary redirect response to the client using the specified redirect location URL and clears the buffer.
java.lang.String encodeRedirectURL(java.lang.String url)
Encodes the specified URL for use in the sendRedirect method or, if encoding is not needed, returns the URL unchanged.
3.设定数据内容的类型和长度
void setContentType(java.lang.String type)
Sets the content type of the response being sent to the client, if the response has not been committed yet.这是实现ServletResponse接口的方法。
4.设定状态吗的方法
void sendError(int sc)
Sends an error response to the client using the specified status code and clears the buffer.
void sendError(int sc, java.lang.String msg)
Sends an error response to the client using the specified status and clears the buffer.
void setStatus(int sc)
Sets the status code for this response.
注:状态码常数
static int SC_ACCEPTED
Status code (202) indicating that a request was accepted for processing, but was not completed.
static int SC_BAD_GATEWAY
Status code (502) indicating that the HTTP server received an invalid response from a server it consulted when acting as a proxy or gateway.
static int SC_BAD_REQUEST
Status code (400) indicating the request sent by the client was syntactically incorrect.
static int SC_CONFLICT
Status code (409) indicating that the request could not be completed due to a conflict with the current state of the resource.
static int SC_CONTINUE
Status code (100) indicating the client can continue.
static int SC_CREATED
Status code (201) indicating the request succeeded and created a new resource on the server.
static int SC_EXPECTATION_FAILED
Status code (417) indicating that the server could not meet the expectation given in the Expect request header.
static int SC_FORBIDDEN
Status code (403) indicating the server understood the request but refused to fulfill it.
static int SC_FOUND
Status code (302) indicating that the resource reside temporarily under a different URI.
static int SC_GATEWAY_TIMEOUT
Status code (504) indicating that the server did not receive a timely response from the upstream server while acting as a gateway or proxy.
static int SC_GONE
Status code (410) indicating that the resource is no longer available at the server and no forwarding address is known.
static int SC_HTTP_VERSION_NOT_SUPPORTED
Status code (505) indicating that the server does not support or refuses to support the HTTP protocol version that was used in the request message.
static int SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR
Status code (500) indicating an error inside the HTTP server which prevented it from fulfilling the request.
static int SC_LENGTH_REQUIRED
Status code (411) indicating that the request cannot be handled without a defined Content-Length.
static int SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED
Status code (405) indicating that the method specified in the Request-Line is not allowed for the resource identified by the Request-URI.
static int SC_MOVED_PERMANENTLY
Status code (301) indicating that the resource has permanently moved to a new location, and that future references should use a new URI with their requests.
static int SC_MOVED_TEMPORARILY
Status code (302) indicating that the resource has temporarily moved to another location, but that future references should still use the original URI to access the resource.
static int SC_MULTIPLE_CHOICES
Status code (300) indicating that the requested resource corresponds to any one of a set of representations, each with its own specific location.
static int SC_NO_CONTENT
Status code (204) indicating that the request succeeded but that there was no new information to return.
static int SC_NON_AUTHORITATIVE_INFORMATION
Status code (203) indicating that the meta information presented by the client did not originate from the server.
static int SC_NOT_ACCEPTABLE
Status code (406) indicating that the resource identified by the request is only capable of generating response entities which have content characteristics not acceptable according to the accept headers sent in the request.
static int SC_NOT_FOUND
Status code (404) indicating that the requested resource is not available.
static int SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED
Status code (501) indicating the HTTP server does not support the functionality needed to fulfill the request.
static int SC_NOT_MODIFIED
Status code (304) indicating that a conditional GET operation found that the resource was available and not modified.
static int SC_OK
Status code (200) indicating the request succeeded normally.
static int SC_PARTIAL_CONTENT
Status code (206) indicating that the server has fulfilled the partial GET request for the resource.
static int SC_PAYMENT_REQUIRED
Status code (402) reserved for future use.
static int SC_PRECONDITION_FAILED
Status code (412) indicating that the precondition given in one or more of the request-header fields evaluated to false when it was tested on the server.
static int SC_PROXY_AUTHENTICATION_REQUIRED
Status code (407) indicating that the client MUST first authenticate itself with the proxy.
static int SC_REQUEST_ENTITY_TOO_LARGE
Status code (413) indicating that the server is refusing to process the request because the request entity is larger than the server is willing or able to process.
static int SC_REQUEST_TIMEOUT
Status code (408) indicating that the client did not produce a request within the time that the server was prepared to wait.
static int SC_REQUEST_URI_TOO_LONG
Status code (414) indicating that the server is refusing to service the request because the Request-URI is longer than the server is willing to interpret.
static int SC_REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE
Status code (416) indicating that the server cannot serve the requested byte range.
static int SC_RESET_CONTENT
Status code (205) indicating that the agent SHOULD reset the document view which caused the request to be sent.
static int SC_SEE_OTHER
Status code (303) indicating that the response to the request can be found under a different URI.
static int SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE
Status code (503) indicating that the HTTP server is temporarily overloaded, and unable to handle the request.
static int SC_SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS
Status code (101) indicating the server is switching protocols according to Upgrade header.
static int SC_TEMPORARY_REDIRECT
Status code (307) indicating that the requested resource resides temporarily under a different URI.
static int SC_UNAUTHORIZED
Status code (401) indicating that the request requires HTTP authentication.
static int SC_UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE
Status code (415) indicating that the server is refusing to service the request because the entity of the request is in a format not supported by the requested resource for the requested method.
static int SC_USE_PROXY
Status code (305) indicating that the requested resource MUST be accessed through the proxy given by the Location field.
page 当前页面对象
如同java中的this
pageContext 当前页面的上下文环境对象
session 会话对象
可用于实现购物车功能
application 当前应用的配置环境对象
可用于实现网站的计数器功能
application对象被所有的客户共享。
config 当前页面的配置对象
手动配置一个jsp页面
使用Servlet标签的子标签<jsp-file>来指定jsp页面文件和Servlet-mapping标签将该jsp页面映射到指定的URL。
exception 异常对象
封装异常处理信息;只有在%@page isErrorPage="true"%的页面才可以使用exception对象。
out 输出流对象
HTML的标准输出;out对象对应的类为javax.servlet.jsp
Class JspWriter
Class JspWriter的类结构
java.lang.Object
java.io.Writer
javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter
All Implemented Interfaces:
java.io.Closeable, java.io.Flushable, java.lang.Appendable
Direct Known Subclasses:
BodyContent
Class JspWriter的常用API
out 对象的主要方法分为两类
1.向浏览器输出数据的常用方法如下
abstract void close()
Close the stream, flushing it first 关闭输出流
abstract void print(java.lang.String s)
Print a string.
abstract void println()
Terminate the current line by writing the line separator string.
abstract void println(boolean x)
Print a boolean value and then terminate the line.
2.对缓冲区进行操作的常用方法如下
abstract void clear()
Clear the contents of the buffer.
abstract void clearBuffer()
Clears the current contents of the buffer.
int getBufferSize()
This method returns the size of the buffer used by the JspWriter.
abstract int getRemaining()
This method returns the number of unused bytes in the buffer.
abstract void flush()
Flush the stream.
boolean isAutoFlush()
This method indicates whether the JspWriter is autoFlushing
四大作用域
能够存储一些临时数据
pageContext 当前页面有效
request 同一个请求
session 同一个会话
application 同一个web应用
setAttribute("key",);
getAttribute("key");
JSP常用动作
<jsp:名称 ></jsp:名称>
1.在某个作用域范围创建对象
<jsp:useBean id="uid" class="com.zhongx.jsp.User" scope="page"></jsp:useBean>
id属性:表示创建的对应对象的引用,不能重复
class属性:表示需要创建的对象的类路径
scope属性:生成对象的作用域范围; page 当前页面范围; request 当前请求范围; session 当前会话范围; application 当前应用范围
2.设置对象的属性
<jsp:setProperty property="name" name="uid" value="hello"/>
name属性:设置需要取值的对象
property属性 :设置需要设值的属性名
value属性 :属性的取值
3.获得对象属性值
<jsp:getProperty property="name" name="uid"/>
name属性:设置需要取值的对象
property属性 :设置需要设值的属性名
4.页面跳转
类似servlet中的forward转发
<jsp:forward page="testAction2.jsp"></jsp:forward>
page属性: 目标页面的地址
forward之后不能写代码
5.设置参数
作为跳转的子标签,在两个页面转发过程中设置参数
<jsp:param value="test" name="key"/>
name属性:参数的名称
vlaue属性:参数的取值
获得传递的参数
request.getParameter("key");
<jsp:forward page="testAction2.jsp">
<jsp:param value="test" name="key"/>
</jsp:forward>
6.包涵页面
动态包涵
<jsp:include page="testIncludeAction.jsp"></jsp:include>
page属性:设置被包涵的页面
通过JspRuntimeLibrary.include方法将被包涵的页面动态的包涵
动态包涵与静态包涵
动态包涵是通过JSP的include动作来实现,
他在转换之后的servlet代码中通过JspRuntimeLibrary.include方法实现
在work目录中会将包涵的页面与被包涵的页面都生成对应的转换文件和字节码文件
静态包涵是通过JSP的include指令来实现
在转换后的servlet中直接将被包涵的页面的源码包涵进来,然后一同编译执行输出
在work目录中被包涵的页面不会有单独的转换servlet和字节码文件
传递参数
<jsp:include page="testIncludeAction.jsp">
<jsp:param value="test" name="test"/>
</jsp:include>
获得参数
request.getParameter("test");
EL(Expression Language,表达式语言)
帮助程序员更加灵活方便快捷的获得对应的值
语法:${}
<h1>EL</h1>
<h2>简单计算</h2>
<h2>1+1=${1+1 }</h2>
<h2>"1"+1=${"1"+1 }</h2>
<h2>4>3=${4>3 }</h2>
<h2>true&&false=${true&&false }</h2>
<h2>1>3?"好大":"好小"=${1>3?"好大":"好小" }</h2>
<h2>从作用域获得对象</h2>
<h2>page:${pageScope.user1 }</h2>
<h2>request:${requestScope.user2 }</h2>
<h2>session:${sessionScope.user3 }</h2>
<h2>application:${applicationScope.user4 }</h2>
<!-- 直接获得会从pageContext---request---session---application 按照从小到大范围查找 -->
<h2>直接获得 :${user1 }</h2>
<h2>直接使用pageContext内置对象调用API</h2>
<h2>url:${pageContext.request.serverPort}</h2>
<h2>接收页面参数</h2>
<h2>参数name=${param.name }</h2>
<h2>参数name是否为空${empty param.name }</h2>
<h2>cookie=${cookie.JSESSIONID.value}</h2>
JSTL(Java standard tag library,java标准标签库)
标签:通过标签这种形式来实现一组java类所表现的功能
1.引入标签库的实现类以及配置文件(.tld)
JSTL1.1.jar Standard.jar
JSTL1.2
2.在JSP页面引入标签库
向作用域中设置键值对
<c:set var="name" value="hello" scope="application"></c:set>
<c:set var="tag" scope="session">
<h1>hello</h1>
<h1>hello</h1>
<h2>hello</h2>
<h1>hello</h1>
<h3>hello</h3>
</c:set>
移除键值对
<c:remove var="name"/>
输出值
<c:out value="${name}"></c:out>
设置url
<c:url value="${url }"></c:url>
页面重定向
<c:redirect url="http://localhost:8899/helloJSP129/testEL.jsp"></c:redirect>
分支流程控制
<c:if test="${5>param.num}">
<h1>你真好</h1>
</c:if>
类似java中的switch/case
<c:choose>
<c:when test="${param.age<18}">
<h1>你未成年</h1>
</c:when>
<c:when test="${param.age>=18 && param.age<60}">
<h1>小青年</h1>
</c:when>
<c:when test="${param.age>=60 && param.age<100}">
<h1>你该享受生活了</h1>
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>
<h1>你成仙了</h1>
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
自定义标签
标签功能---->实现类
----->配置文件 .tld
//标签库的属性和描述信息
标签库的描述
<description>JSTL 1.1 core library</description>
标签库显示的名称
<display-name>JSTL core</display-name>
标签库的版本
<tlib-version>1.1</tlib-version>
标签库的别名
<short-name>c</short-name>
表示当前标签库的引用路径
*不能重复
<uri>http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core</uri>
验证
<validator>
<description>
Provides core validation features for JSTL tags.
</description>
<validator-class>
org.apache.taglibs.standard.tlv.JstlCoreTLV
</validator-class>
</validator>
//配置标签
<tag>
对当前标签的描述
<description>
Catches any Throwable that occurs in its body and optionally
exposes it.
</description>
标签名称,不能重复
<name>catch</name>
表示标签对应的功能实现类
<tag-class>org.apache.taglibs.standard.tag.common.core.CatchTag</tag-class>
表示当前标签体的约束
JSP 表示标签体中可以是jsp中的任何内容
scriptless 表示标签体中不能包涵脚本
tagdependent 当前标签体是否依赖标签本身
empty 表示没有标签体
<body-content>JSP</body-content>
在当前标签中配置属性
<attribute>
属性的描述信息
<description>
Name of the exported scoped variable for the
exception thrown from a nested action. The type of the
scoped variable is the type of the exception thrown.
</description>
属性名称
<name>var</name>
配置属性的特性(是否必须出现)
<required>false</required>
表示是否支持EL动态取值
(Runtime Expression Value)
<rtexprvalue>false</rtexprvalue>
</attribute>
</tag>
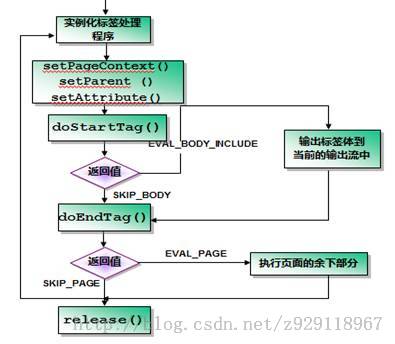
1.书写功能实现类
方法:
doStartTag()
doEndTag()
常数:
SKIP_BODY 忽略标签体
SKIP_PAGE 忽略结束标签之后的其他标签
EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE 显示标签体内容
EVAL_BODY_BUFFERED 缓存标签体内容
EVAL_BODY_AGAIN 重复执行标签体
EVAL_PAGE 标签结束后其他标签继续执行
2.配置配置文件
定义tld文件参照myTag.tld
3.自定义分页标签的代码示例
1)page.tld配置文件
2)com.zhongxin.backstage.bodyTag.TestPage 分页标签的处理类
3)在页面使用自定义标签
4)属性的参数的实体类Page
在tld配置文件中对应的属性:
<attribute>
MVC
M---Model 模型层
V---View 视图层
C---Controller 控制层
模型层:JavaBean实现 封装数据对象,处理业务逻辑实现
视图层:Jsp实现 获取数据,将数据显示
控制层:Servlet实现 接收视图层参数,调用业务逻辑,将返回结果传递给视图层
总结
jsp
(1)jsp是什么?
java server page,java服务器端页面技术。其主要作用在服务器端动态生成页面,其组成java代码和html.
(2)jsp的组成?
A. html:包括css/js
B.java代码
java代码段 <%java代码%>
表达式 <%=%>
jsp声明:<%! %>
C.jsp隐含对象
对象不需要创建,可以直接调用。 out、 request、 response、 session、 application、 config: ServletConfig实例 、 pageContext:( PageContext实例 jsp引擎会为每一个jsp实例分配唯一的一个PageContext实例; 可以放置数据: PageContext.setAttribute(String,Object) Object PageContext.getAttribute(String) ; 访问其它八个隐含对象)
page 表示jsp实例本身
exception jsp在运行过程当中,产生的错误会封装到该对象上。
D、指令
servelt引擎在将.jsp文件转换成servelt源文件时,所做的一些额外的处理。
语法:
<%@指令名 属性%>
常用的一些指令
<%@page import="java.util.*"%>
<%@page pageEncoding="utf-8" contentType="text/html;charset=utf-8"%>
pageEncoding: jsp文件在保存的时候需要按照什么样的编码格式来保存。
contentType:等同于response 的setContentType()
errorPage:指定错误处理页面
isErrorPage:当前页面是否为错误处理页面,缺省值是false
session:true(缺省)/false,当前页面是否支持session。
isELIgnored:true(缺省)/false,是否忽略el表达式。
<%@include file=""%>
<%@taglib prefix="" uri=""%>:引入标签。
E、活动元素
在jsp已经运行时,让jsp引擎做一些额外的处理。
<jsp:include/>:一个jsp在运行过程当中,去调用 另外一个jsp。
F、注释:
<!--
注释内容
-->
注释内容如果是java代码,会执行,不会
在浏览器端输出。
<%--
注释内容
--%>
注释内容如果是java代码,不会执行,不会
在浏览器端输出。
(3)jsp如何执行的?
jsp引擎会将jsp文件转换为一个servelt源文件,再去 调用其service方法
(4)如何转换成servlet源文件
A、html --->放到service()方法里,使用out.write()输出。
B、java代码-->放到service()方法里,照搬。
C、jsp表达式--->放到serivce()方法里,使用print()输出。
servlet线程安全问题?
当请求到达服务后,服务求就会创建一个新的线程来处理请求,有可能出现 多个请求访问同一个servlet实例,如果操作servelt属性,就有可能出现 线程安全问题。
1.加锁
加上synchronized的代码块。
2.让servlet实现SingleThreadModel接口
SingleThreadModel 是一个标识接口,实现SingleThreadModel接口的作用, 服务器会给每一个请求都创建一个servlet的实例。(不建议使用)
3.尽量避免操作修改servlet的属性。
mvc
(1)什么是mvc?
model view controller
是一种软件架构思想,将一个软件的组成部分划分成 三种不同类型的模块,分别是模型、视图和控制器。
模型:
封装了业务逻辑:
业务逻辑:包括业务逻辑本身的处理,还有 为保证业务逻辑能够正确处理所需要的事务 、安全、日志、审核等等基础服务。 封装:业务逻辑实现以及对外提供的接口。
视图:
实现了表示逻辑:将模型中的数据以合适的方式 展现出来,另外,也提供合适的界面,用于输入。
控制器:
视图将请求交给控制器,控制器依据请求的不同, 调用合适的模型来处理;模型处理之后的结果给 控制器,控制器依据结果,选择合适的视图展现 给用户。
这样做的目的,是使得模型可以方便地 多个视图复用。
(2)在web应用当中,如何使用mvc?
model: 使用java类来实现,或者是ejb,spring等容器 管理的javabean来实现(容器会提供部分 基础服务)。
view: 使用jsp(html,css,js)
controller: 使用servlet(或者filter)
(3)mvc的优势与缺点:
优点:
A.使得模型可以方便地 多个视图复用
B.模型方便测试(比如 servlet中包含的业务逻辑, 要测试的话,需要部署,启动服务器,通过浏览器 发送请求。将业务逻辑写在java类,只需要测试java类。 )
C.方便分工协作。
缺点:
mvc是一种思想,在做具体产品或者项目时, 需要设计(开发的复杂度增加)。 开发的周期变长,代码的维护量增加了。
总结:
如果产品或者项目需要代码的良好的可维护性、 可测试性、方便分工协作(一般是比较大型的项目)。 反之,没有必要用。
注释
html <!---->
css //单行 /**/ 多行注释
js //单行 /**/ 多行注释
jsp <%----%>隐含注释,即开发人员专用的注释
java //单行 /**/ 多行注释 /** */ 文档注释
JSP
一、JSP介绍
JSP:页面文件,动态页面。
JSP:JAVA Server Page,是服务器端一种基于JAVA语言的网页技术,所有程序操作都是在服务端执行,网络上传送的仅仅是运行的结果。运行的结果与浏览器无关,但是发送的结果在不同浏览器展示的效果有差别。
HTML+CSS+JAVASCRIPT+JAVA+JSP标签==JSP
二、JSP原理
假如目前浏览器发送一个请求,
http://localhost:9000/project_123_0010_cookie/login.jsp。
如果是第一次向该JSP发送请求,如果页面地址不正确,将会报404错误。如果页面地址正确,那边会将该JSP转换为Servlet,然后对其进行编译。【因此第一次加载该页面会相对较慢,但是以后打开会很快。】
转换的Servlet将会对请求的信息进行响应,响应的结果为HTML文本。
JSP和Servlet区别:
唯一区别是JSP在第一次请求会编译为Servlet,其实JSP实质上就是一个Servlet。
JSP页面文件,Servlet是一个JAVA类。
三、JSP页面构成
v 静态内容
HTML文本、CSS样式、JAVASCRIPT客户端验证脚本
v 指令
指令不会再客户端产生任何的输出,是在服务器解释并执行的。最要用于对JSP页面进行转换,它只在当前页面设置有效。
J2EE API
<%@ page language="java"%>
<%@指令名称 属性=属性值 .... %>
指令名称:
page、include、taglib[JSTL]
① Page
Page指令通常称为页面指令,可以定义在当前整个JSP页面范围的有效属性。
ü Language
当前编写JSP所使用的语句,目前只能为JAVA
ü Import
用于向当前JSP页面导入所需要的包和类名【类的路径】
格式:
import="java.util.*":表示util包下的所有类
import="java.util.*,java.a.A":表示util包下的所有类,以及A类
默认导入包:
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.jsp.*;
import java.lang.*;
【从Work文件夹下查找到对应的类文件。】
ü pageEncoding
用来设置JSP页面的字符编码
ü contentType
设置页面响应的MIME
| <%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" contentType="application/msword; charset=utf-8"%> <table> <tr> <td>123</td> <td>123</td> </tr> </table> |
ü Session
设置当前页面是否支持Session,默认是true。
ü isThreadSafe
是否线程安全,默认为true。表示会已多线程的方式处理用户请求。
如果设置为false,会阻塞其它浏览器打开页面。
ü isELIgnored
表示EL表达式是否禁止,默认为false。
ü isErrorPage
表示是否为错误页面。
ü errorPage
表示错误页面,当当前页面有错误的时候跳转到指定的错误页面。
| <%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8" errorPage="word.jsp"%> <% int i = 5/0 ; %>
<%@ page isErrorPage="true" language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="utf-8"%> 有错误 <%=exception.getMessage() %> 注意:如果要使用exception对象,需要设置isErrorPage为true。 |
② Include
用于页面包含。
<%@ includefile="head.html"%>
该指令放置在JSP页面哪个位置,就在哪个位置进行展示。
其实质将两个页面合并为一个Servlet。
与动作方式的包含本质区别在于是否合并为一个Servlet。
<jsp:include page="head.html"></jsp:include>
另外包含的文件可以为HTML、JSP、文本文档等。
另外file属性对应的路径可以为绝对路径以及相对路径。
③ Tablib
后面讲述,JSTL
v 表达式
<%= %>
百分号和等于符号必须挨在一起。
另外中间不能带分号。
v 注释
<%----%> 该注释方式为JAVA注释方式,页面源代码看不到,展示页面看不到
<!-- 你好-->该注释方式为HTML注释方式,页面源代码能看到,展示页面看不到
v 声明
格式:<%!int i = 6 ; %>
通过声明定义的属性和方法都是全局,而在java代码段中定义的属性和方法是局部的。
定义属性:
定义方法:
| <%! int i = 6 ;
String hello(String person){ return "你好"+person; } %> <%=hello("120") %> |
v 动作
后面讲述
四、JSP内置对象
pageContext在JSTL中使用。能找到任何的内置对象。
Page相当于this对象,反映的是当前JSP转换为Servlet的对象。
Exception需要在页面中定义了指令的属性isErrorPage属性为true。
Config获取配置信息。
| <%=config.getServletContext().getInitParameter("as") %> |
| <servlet> <servlet-name>test</servlet-name> <jsp-file>/sjx.jsp</jsp-file> <init-param> <param-name>ss</param-name> <param-value>123</param-value> </init-param> </servlet>
<servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>test</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/sjx1.jsp</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <%=config.getInitParameter("ss") %> <%=this.getServletContext().getInitParameter("b") %> <%=this.getInitParameter("ss") %> <%=this.getServletConfig().getInitParameter("ss") %> |
五、JSP动作JAVABEAN
JAVABEAN是一个封装了业务逻辑的可重用组件,包括可视化组件以及封装业务逻辑的组件。例如:分页
Model 1: JSP +JAVABEAN [JSP --- > JSP]
Model 2: JSP + SERVLET + Service + Servlet + JSP 【MVC】
v JAVABEAN构造
1.构造对象
<jsp:useBean
id="em" class="com.csu.edu.vo.EmpVo"></jsp:useBean>
|
EmpVo em = new EmpVo();
2.设置属性值
<jsp:setProperty property="empName"name="em"value="B"/>
|
em.setEmpName(“B”)
<jsp:setProperty property="empName"name="em" param="a"/>
--->em.setEmpName(request.getParameter(“a”))
3.获取属性值
<jsp:getProperty property="empName"name="em"/>
----> em.getEmpName()
4.设置scope
值可以为:pageContext、request、session、application
<jsp:useBean id="em"class="com.csu.edu.vo.EmpVo"
scope="session" ></jsp:useBean>
----》session.setAttribute(“em”,new com.csu.edu.vo.EmpVo())
验证:
<%=((EmpVo)session.getAttribute("em")).getEmpName() %>
原则:
1.JAVABEAN类必须得有一个空的构造方法。
2.属性一定记得带上set/get方法。
3.最好实现序列化接口。
六、JSP其它动作
1.转发
<jsp:forward page=""></jsp:forward>
<jsp:forwardpage="index.jsp?id=1"></jsp:forward>
<jsp:forward page="index.jsp">
<jsp:param value="1" name="id"/>
</jsp:forward>
2.页面包含
<jsp:include page="404.html"></jsp:include>
动作方式和指令方式区别:
| 动作方式 |
指令方式 |
| 只是内容合并,页面代码并未合并为一个Servlet |
将两个页面合并为一个Servlet |
| 两个页面使用两个request对象 |
两个页面共享同一个request对象 |
|
|
效率更高 |
| 可以传递参数值,采用以下方式 <jsp:include page="404.html"> <jsp:param value="1" name="id"/> </jsp:include> |
不能传递参数值 |
| 不要求 |
包含页面和被包含页面编码必须一致 |
七、SVN版本控制
版本控制工具。CVS、SVN
https://liuwei-123fba4f/svn/123/
SVN服务器
目的:保证代码都是最新的。
版本号如果比当前服务器中该页面的版本低,那么无法进行提交。
八、EL表达式
v 介绍
EL:ExpressionLanguage。
表现形式: ${ }
表现结构: ${user.name} ----》<%= user.getName() %>
v EL作用范围
能使用在JSP中,另外可以在JAVASCRIPT中和JSTL标签中。
alert('${requestScope.u.username }')
v EL表达式运算
① 算数运算符
${1+1 }
${"a" }${"b" } 不要使用${“a”+”b” }
② 关系运算
等于 == eq
| ${1==1 } ${1 eq 1 } |
不等于 != ne
大于 > gt
小于 < lt
大于等于 >= ge
小于等于 <= le
③ 逻辑运算
与 and
或 or
使用短路方式
④ Empty运算符
判断对象是否为空,或者是否为空字符串
${empty requestScope.i }
⑤ EL隐式对象
param、paramValues、pageScope、requestScope、sessionScope、applicationScope
param获取参数值
| ${param.id } ${param["id"] } |
paramValues 哪个参数的所有值
| http://localhost:8080/project_123_00011_el/el2.jsp?id=234&psw=a&psw=b ${paramValues.psw[0] } |
| User u = new User(); u.setUsername("A"); u.setPassword("1"); request.setAttribute("u",u);
${requestScope.u.username } ${requestScope.u["username"] } |
⑥ pageContext
${pageContext.request.requestURL}
${pageContext.request.scheme}
九、JSTL标签库
1.JSTL介绍
JSTL:Java Server Page Standard TagLibrary。JSP标准标签库。
目的:实现JSP页面无JAVA代码。
tld文件用于描述标签库的配置文件。
2.使用JSTL
① 导JAR包
② 指令的配置
<%@ taglibprefix="c"uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
查找JSTL JAR包中META-INF文件中对应的tld文件。
③ 使用标签库
v 设置值
<c:set var="i" value="1" scope="request"></c:set>
----> request.setAttribute(“i”,1)
v 获取值
<c:out value="${requestScope.i }"></c:out>
v 移除值
<c:remove var="i" scope="request"/>
v 捕获异常
| <c:catch var="execp"> <% int i = 4/0 ; %> </c:catch> ${execp } ${execp.message } |
v 切割
| <c:forTokens items="${split }" delims=":" var="sp"> ${sp }<br/> </c:forTokens> |
v For循环
| <c:forEach var="j" begin="1" end="${param.index }" step="1"> <c:forEach var="k" begin="${j }" end="${param.index }" step="1"> * </c:forEach> <br/> </c:forEach> |
v 判断
| List<EmpVo> emps = new ArrayList<EmpVo>(); request.setAttribute("emps",emps); <c:if test="${empty emps}"> <td colspan="2">当前行无记录!</td> </c:if> empty包括用于验证对象是否为空,字符串是否为空字符串,集合中是否有对象数据。 |
v IF.。。ELSE
| <c:choose> <c:when test="${empty emps}"> <td colspan="2"> 当前行无记录! </td> </c:when> <c:otherwise> <td> 姓名 </td> <td> 年龄 </td> </c:otherwise> </c:choose>
<c:choose> <c:when test="${1+1 lt 2}"> 1 </c:when> <c:when test="${1+1 eq 2}"> 2 </c:when> <c:otherwise> 3 </c:otherwise> </c:choose> |
v 循环遍历集合中的值
| List<EmpVo> emps = new ArrayList<EmpVo>(); emps.add(new EmpVo("1","A","Manager")); emps.add(new EmpVo("2","B","Manager")); request.setAttribute("emps", emps); <c:forEach var="emp" items="${emps }"> <tr> <td> ${emp.empName } </td> <td> ${emp.job } </td> </tr> </c:forEach> |
v 格式化标签
Fmt
| <fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date() %>" type="time"/> <fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date() %>" type="both"/> <fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date() %>" pattern="yyyy/MM/dd"/> <fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date() %>" timeStyle="full" type="both"/> <fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date() %>" timeStyle="short" type="both"/> <fmt:formatNumber value="12.235" pattern=".00"></fmt:formatNumber> <fmt:formatNumber value="0.125" pattern=".00%"></fmt:formatNumber> |
v 函数标签
Fn:
Ø fn:contains判断在某一字符串中是否包含指定的子字符串
Example:${fn:contains("Hello","H")}
Ø fn:containsIgnoreCase依上,只是不再区分大小写
Ø fn:startsWith是否已某字符串开头
Ø fn:endsWith
Ø fn:indexOf判断子字符串在原字符串中出现的位置
Ø fn:split用于将一个字符串分割
Ø fn:join已某字符连接
Ø fn:replace使用新字符串替换原有字符串中的某一段子字符串
Ø fn:trim
Ø fn:substring用于从原有字符串截取一个子字符串
Ø fn:substringAfter获取截取指定字符串之后的所有字符
Ø fn:substringBefore与上相反
Ø fn:toUpperCase将所有字母转为大写
Ø fn:length
${fn:length("abc")} =====3
v 自定义标签
自定义标签是显示设计的,用于在JSP页面中添加功能。
| 配置tld文件路径 <jsp-config> <taglib> <taglib-uri>http://www.csu.com</taglib-uri> <taglib-location>CLASSPATH:</taglib-location> </taglib> </jsp-config> |
步骤:
1.创建tld文件,用于配置标签库的元素、属性等特征。
| <taglib xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-jsptaglibrary_2_1.xsd" version="2.1">
<description>JSTL 1.1 core library</description> <display-name>JSTL core</display-name> <tlib-version>1.1</tlib-version> <short-name>my</short-name> <uri>http://www.csu.com</uri>
<tag> <description> Catches any Throwable that occurs in its body and optionally exposes it. </description> <name>hello</name> <tag-class>com.csu.edu.tag.HelloTag</tag-class> <body-content>JSP</body-content> <attribute> <name>name</name> <required>true</required> <rtexprvalue>false</rtexprvalue> </attribute> </tag>
</taglib> body-content值为JSP,表示标签中可以包含文本内容 为empty,表示标签中不可以包含文本内容 Rtexprvalue用于设置JSTL标签是否支持表达式语言。False表示禁止表达式语言。 |
2.创建解释标签元素属性的类,继承TagSupport
| public class HelloTag extends TagSupport{
} |
3.页面引用
| <%@ taglib prefix="my" uri="http://www.csu.com" %> <my:hello name="123"></my:hello> |
4.写实现
| public class HelloTag extends TagSupport{
private String name ;
private JspWriter out ;
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
@Override public int doEndTag() throws JspException { return EVAL_PAGE; }
@Override public int doStartTag() throws JspException { try { out.print("<font color=\"red\">hello,"+ name +"</font>"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE; }
@Override public void setPageContext(PageContext pageContext) { this.out = pageContext.getOut() ; }
} |
doStartTag方法的返回值:
SKIP_BODY:标签内的文本忽略不输出
EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE:标签内的文本内容能输出
doEndTag方法返回值
SKIP_PAGE:跳过整个JSP页面后面的输出,后面的输出会被截断
EVAL_PAGE:继续执行页面剩下的部分。
5.
十、反射
v 反射概念
Reflect,反射就是指在程序运行时获取自身的信息【自省】。在JAVA中,只需要提供类所在的路径,即可获得类的相关信息【类、属性、方法、类的父类及父接口】
v 获取类的属性
获取对象所属类:
User u = new User();
System.out.println(u.getClass());
System.out.println(User.class);
获取类中的属性
getFields():需要要求类中的属性权限设置为public
getDeclaredFields():获取类中声明过的属性,返回Field的数组
field.getName():获取类中属性名字
| public static void main(String[] args) { User u = new User(); System.out.println(u.getClass()); System.out.println(User.class); Class clazz = u.getClass() ; Field [] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field : fields) { System.out.println(field.getName()+" " +Modifier.toString(field.getModifiers())+" " +field.getType().getName()); } } |
v 构造方法
① 无参构造方法
| User u = (User)Class.forName("com.csu.edu.vo.User").newInstance(); System.out.println(u); u.setUsername("A"); System.out.println(u.getUsername()); |
② 有参构造方法
| try { Constructor<User>[] cons= (Constructor<User>[])Class.forName("com.csu.edu.vo.User") .getConstructors(); System.out.println(cons.length); for (Constructor<User> constructor : cons) { System.out.println(constructor.getParameterTypes().length); Class [] clazz = constructor.getParameterTypes(); int length = clazz.length ; if(length == 3){ for (Class class1 : clazz) { System.out.println(class1.getSimpleName()); } User u = constructor.newInstance("A","1",20); System.out.println(u.getAge()); } } } catch (SecurityException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } |
③ 获取父类及父接口
| try { System.out.println(Class.forName("com.csu.edu.vo.User").getSuperclass().getName()); Class.forName("com.csu.edu.vo.User").getInterfaces(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } |
v 方法动态调用
| try { Method[] methods = Class.forName("com.csu.edu.vo.User").getMethods(); for (Method method : methods) { System.out.println(method.getName()); // System.out.println(method.getParameterTypes()); } } catch (SecurityException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } |
无参函数
| try { Method m = Class.forName("com.csu.edu.vo.User").getMethod("hello"); m.invoke(Class.forName("com.csu.edu.vo.User").newInstance()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } |
有参函数
| try { Method m = Class.forName("com.csu.edu.vo.User") .getMethod("hello",String.class); m.invoke( Class.forName("com.csu.edu.vo.User").newInstance(),"123"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } |
作业:
利用上述知识,做Hibernate的模拟
最终效果:
insert into country(id,contry) values('1','中国')
Hibernate配置文件如下:
Insert into country(id,name) values(getId(),getCountry())
<hibernate-mapping >
<class name="com.csu.edu.pojo.Country"
table="country" dynamic-update="true" >
<idname="id" column="id">
<generator class="sequence">
<paramname="sequence">sales</param>
</generator>
</id>
<propertyname="contry" column="name"></property>
<property name="asd"column="name"></property>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
Insert into country(id,name) values(getId(),getCountry())
要求:不要求配置配置文件,只需要将该配置文件用java语言模拟,将其可设置为:
tableName="saless";
map.put("id","id");
map.put("name","contry");
注意:hashMap中第一个字符为数据库对应的字段,第二个字符为pojo中对应的字段。
十一、数据池
数据池:数据库连接池 DBCP DataBase Connection Pool。
Tomcat数据库连接池。JNDI:JAVA命名和目录服务
在WEB工程中,JSP页面或者Servlet可以通过连接池获取到连接,但是JAVA应用程序无法获取。
步骤:
1.配置Tomcat目录下conf/context.xml
| <Resource name="jdbc/myoracle" auth="Container" type="javax.sql.DataSource" driverClassName="oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver" url="jdbc:oracle:thin:@172.16.10.210:1521:orcl" username="scott" password="tiger" maxActive="20" maxIdle="10" maxWait="10000"/> |
maxActive:最大的连接数。
maxIdle:最小连接数。无连接访问时,保证池子最小拥有多少个连接
maxWait:表示等待的最大时间,时间级别为ms。
例子:
有一个要连接,从10个连接中获取一个连接。
有十一个要连接,从10个连接中获取10个连接,再创建1个连接
要二十一个连接,有10个连接,创建10个连接,还有一个连接等待。
假如一段时间之后,没有需要连接,销毁10个连接,保证池子中有10个连接。
2.拷贝class12.jar放置到Tomcat目录lib下面
3.修改工程中的web.xml
| <resource-ref> <description>Oracle Datasource example</description> <res-ref-name>jdbc/myoracle</res-ref-name> <res-type>javax.sql.DataSource</res-type> <res-auth>Container</res-auth> </resource-ref> |
4.测试
| Context initContext = new InitialContext(); Context envContext = (Context)initContext.lookup("java:/comp/env"); DataSource ds = (DataSource)envContext.lookup("jdbc/myoracle"); Connection conn = ds.getConnection(); |
优势:
1. 资源重用
由于数据库连接得到重用,避免了频繁创建、释放连接引起的大量性能开销。在减少系统消耗的基础上,另一方面也增进了系统运行环境的平稳性(减少内存碎片以及数据库临时进程/线程的数量)。
2.更快的系统响应速度
数据库连接池在初始化过程中,往往已经创建了若干数据库连接置于池中备用。此时连接的初始化工作均已完成。对于业务请求处理而言,直接利用现有可用连接,避免了数据库连接初始化和释放过程的时间开销,从而缩减了系统整体响应时间。
3. 新的资源分配手段
对于多应用共享同一数据库的系统而言,可在应用层通过数据库连接的配置,实现数据库连接池技术,几年钱也许还是个新鲜话题,对于目前的业务系统而言,如果设计中还没有考虑到连接池的应用,那么…….快在设计文档中加上这部分的内容吧。某一应用最大可用数据库连接数的限制,避免某一应用独占所有数据库资源。
4. 统一的连接管理,避免数据库连接泄漏
在较为完备的数据库连接池实现中,可根据预先的连接占用超时设定,强制收回被占用连接。从而避免了常规数据库连接操作中可能出现的资源泄漏。
十二、Struts1
Struts1是一个MVC框架,跟Servlet功能类似。Struts1是在Servlet基础上的封装。
步骤:
1.解压缩blank对应的war包
2.修改工程中的web.xml
| <servlet> <servlet-name>action</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.apache.struts.action.ActionServlet </servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>config</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/struts-config.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>2</load-on-startup> </servlet>
<!-- Standard Action Servlet Mapping --> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>action</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> |
3.拷贝struts-config.xml到WEB-INF下
4.拷贝JAR包
5.配置FormBean类
| public class LoginFormBean extends ActionForm{
private String username ;
private String password ;
public String getUsername() { return username; }
public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; }
public String getPassword() { return password; }
public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } }
<form-beans> <form-bean name="loginForm" type="com.csu.edu.formbean.LoginFormBean"/> </form-beans> |
6.配置Action
| <action-mappings> <action path="/login" type="com.csu.edu.action.LoginAction" name="loginForm"> <forward name="success" path="/success.jsp"></forward> <forward name="error" path="/error.jsp"></forward> </action> </action-mappings> public class LoginAction extends Action{
@Override public ActionForward execute(ActionMapping mapping, ActionForm form, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { LoginFormBean lfb = (LoginFormBean)form ; // String username = request.getParameter("username"); String username = lfb.getUsername() ; System.out.println(username);
return mapping.findForward("success"); } } |
使用Struts框架,做加法的运算。
Struts1框架流程:
1.服务器启动时候执行ActionServlet的init方法,将struts-config.xml解析JAVA对象。
2.写ActionServlet中的doGet或者doPost方法。
3.获取请求的路径 localhost:8080/project_123_00015_dbcp1/login.do 截取do之前的相对路径 /login
4.利用/login与struts-config.xml的JAVA对象中的Action中的path进行比较查找到具体的Action。
5.利用该Action中的name属性,看是否进行配置。如果有配置,查找FormBeans中FormBean是否有name属性值进行匹配。如果有那么将获取到的值填充到FormBean类中。如果无,将报500错误。
6.如果Action中无name属性的配置,或者已经将数据封装到FormBean中。那么查找Action中的type属性。如果type属性对应的值通过反射时出现异常,那么将报500错误。如果正常,那么将执行到该Action对应的execute方法。
7.查看该Action返回的值传递的字符串与配置文件中Forward中name属性是否有一致,如果一致,那么将已转发或者转向的方式传递到对应的页面。