progit总结
1 版本控制
1.1 版本控制
版本控制是一种记录一个或若干文件内容变化,以便将来查阅特定版本修订情况的系统。
可以对任何类型的文件进行版本控制。
版本控制系统(Version Control Systems(VCS))分类:
1 本地版本控制系统
大多都是采用某种简单的数据库来记录文件的历次更新差异。如rcs。
2 集中式版本控制系统Centralized Version Control Systems (CVCSs)
都有一个单一的集中管理的服务器,保存所有文件的修订版本。
客户端取出最新的文件或者提交更新。如CVS, SVN等。
3 分布式版本控制系统Distributed Version Control Systems (DVCSs)
客户端并不只提取最新版本的文件快照,而是把代码仓库完整地镜像下来。如git。
1.2 git与其它VCS的区别
git只关心文件数据的整体是否发生变化,而大多数其他系统则只关心文件内容的具体差异。
2 git基础
2.1 git文件状态
工作目录下面的所有文件两种状态:
1 已跟踪:被纳入版本控制管理的文件,在上次快照中有它们的记录
初次git clone某个仓库时,工作目录中的所有文件都属于已跟踪文件,且状态为未修改。
已跟踪的任何一个文件,在 git 内主要有三种状态:
已提交(committed):表示该文件已经被安全地保存在本地数据库中了,git commit后文件状态为commited
已修改(modified):表示修改了某个文件,但还没有提交保存到本地数据库中
已暂存(staged):表示把已修改的文件标记在下次提交快照中,git add之后的文件状态为staged
2 未跟踪:所有其他文件,git不会自动将之纳入跟踪范围
git add添加所有目标文件到index暂存区,同时未跟踪过的文件标记为已跟踪。
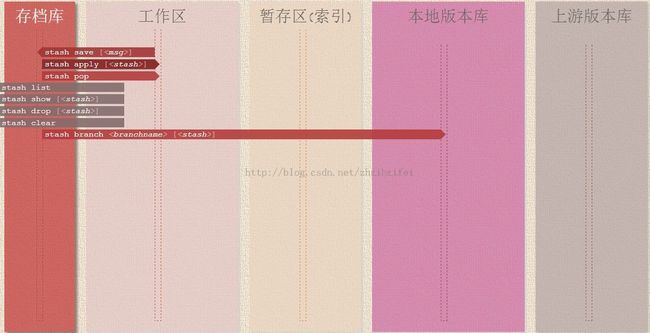
git项目的三个工作区域:
1 本地版本库(.git目录)
保存元数据和对象数据库等版本库需要的全部信息(Git 版本库的骨架),一般包括分支master。
git init初始化空版本库。
git commit保存.git/index的内容到仓库。
git clone此目录
2 工作区(工作目录)
存放从.git目录的压缩对象数据库中提取出来的文件,git clone到此目录
3 暂存区(索引)
保存了一份工作(树)的快照,作为下次提交内容的文件.git/index。
git add保存快照到index。
基本的git工作流程如下:
1 在工作目录中修改某些文件。
2 对修改后的文件进行快照,然后保存到暂存区域。
3 提交更新,将保存在暂存区域的文件快照永久转储到git目录中。
参考:http://ndpsoftware.com/git-cheatsheet.html
2.2 git安装
linux上安装:
$ yum install git-core #Fedora $ apt-get install git #Debian
其它平台参考:http://git-scm.com/book/zh/v1/%E8%B5%B7%E6%AD%A5-%E5%AE%89%E8%A3%85-Git
2.3 环境配置
初次运行前,需要先配置下git工作环境。git config用来配置或读取相应的配置变量。配置文件及目录:
1 /etc/gitconfig:系统中对所有用户都适用的配置。
若使用 git config 时用 --system 选项,读写的就是这个文件。
2 ~/.gitconfig或~/.config/git/config:用户目录下的配置文件,只适用于该用户。
若使用 git config 时用 --global 选项,读写的就是这个文件。
3 .git/config:当前项目git目录中的配置文件,仅针对当前项目有效。
注意:每一个级别的配置都会覆盖上层的相同配置。
在Windows系统上,.gitconfig 文件位于C:\Users\$USER主目录
用户信息:用户名称和电子邮件地址。每次git提交时都会引用这两条信息:
$ git config --global user.name "zhaihaifei" $ git config --global user.email "[email protected]"文本编辑器:默认编辑器,一般可能会是 Vi 或者 Vim。可以重新设置:
$ git config --global core.editor emacs差异分析工具
$ git config --global merge.tool vimdiff查看配置信息
$ git config --list user.name=zhaihaifei [email protected] $ git config user.name zhaihaifei
3 git
CONFIGURE TOOLING Configure user information for all local repositories $ git config --global user.name "[name]" #Sets the name you want atached to your commit transactions $ git config --global user.email "[email address]" #Sets the email you want atached to your commit transactions $ git config --global color.ui auto #Enables helpful colorization of command line output CREATE REPOSITORIES Start a new repository or obtain one from an existing URL $ git init [project-name] #Creates a new local repository with the specified name $ git clone [url] #Downloads a project and its entire version history MAKE CHANGES Review edits and crafa commit transaction $ git status #Lists all new or modified files to be commited $ git add [file] #Snapshots the file in preparation for versioning $ git reset [file] #Unstages the file, but preserve its contents $ git diff #Shows file differences not yet staged $ git diff --staged #Shows file differences between staging and the last file version $ git commit -m "[descriptive message]" #Records file snapshots permanently in version history GROUP CHANGES Name a series of commits and combine completed efforts $ git branch #Lists all local branches in the current repository $ git branch [branch-name] #Creates a new branch $ git checkout [branch-name] #Switches to the specified branch and updates the working directory $ git merge [branch] #Combines the specified branch’s history into the current branch $ git branch -d [branch-name] #Deletes the specified branch REFACTOR FILENAMES Relocate and remove versioned files $ git rm [file] #Deletes the file from the working directory and stages the deletion $ git rm --cached [file] #Removes the file from version control but preserves the file locally $ git mv [file-original] [file-renamed] #Changes the file name and prepares it for commit SUPPRESS TRACKING Exclude temporary files and paths *.log build/ temp-* A text file named .gitignoresuppresses accidental versioning of files and paths matching the specified paterns $ git ls-files --other --ignored --exclude-standard #Lists all ignored files in this project SAVE FRAGMENTS Shelve and restore incomplete changes $ git stash #Temporarily stores all modified tracked files $ git stash list #Lists all stashed changesets $ git stash pop #Restores the most recently stashed files $ git stash drop #Discards the most recently stashed changeset REVIEW HISTORY Browse and inspect the evolution of project files $ git log #Lists version history for the current branch $ git log --follow [file] #Lists version history for a file, including renames $ git diff [first-branch]...[second-branch] #Shows content differences between two branches $ git show [commit] #Outputs metadata and content changes of the specified commit REDO COMMITS Erase mistakes and crafreplacement history $ git reset [commit] #Undoes all commits afer [commit], preserving changes locally $ git reset --hard [commit] #Discards all history and changes back to the specified commit SYNCHRONIZE CHANGES Register a repository bookmark and exchange version history $ git fetch [bookmark] #Downloads all history from the repository bookmark $ git merge [bookmark]/[branch] #Combines bookmark’s branch into current local branch $ git push [alias] [branch] #Uploads all local branch commits to GitHub $ git pull #Downloads bookmark history and incorporates changes
git操作实例
#先在本地创建一个项目,并为它绑定一个本地Git仓库
~$ mkdir hellogit; cd hellogit/
~/hellogit$ ls -a
. ..
~/hellogit$ git status #检查当前文件状态
fatal: Not a git repository (or any of the parent directories): .git
~/hellogit$ <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">git init</span> #在当前目录下创建一个.git文件夹,即git仓库</span>
Initialized empty Git repository in /home/localadmin/hellogit/.git/
~/hellogit$ ls -a
. .. .git
~/hellogit$ echo "hello git readme" > README.md
~/hellogit$ ls -a
. .. .git README.md
~/hellogit$ git status
On branch master
Initial commit
<span style="background-color: rgb(153, 51, 153);">Untracked files</span>: #未跟踪的文件,意味着git在之前的快照(提交)中没有这些文件;git不会自动将之纳入跟踪范围</span>
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
README.md
nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
~/hellogit$ git add . #git add添加所有目标文件到index暂存区,状态为staged,同时未跟踪过的文件标记为已跟踪。</span>
~/hellogit$ git status
On branch master
Initial commit
<span style="background-color: rgb(51, 153, 153);">Changes to be committed</span>: #说明是已暂存状态。如果此时git commit提交,版本将被留存在历史记录中,使得README.md状态由staged状态变为commited</span>
(use "git rm --cached <file>..." to unstage)
new file: README.md
~/hellogit$ <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">git commit -m 'readme file'</span>
[master (root-commit) 60c0223] readme file
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
create mode 100644 README.md
#提交时记录的是放在暂存区域的快照,任何还未暂存的仍然保持已修改状态,可以在下次提交时纳入版本管理。</span>
#每一次运行提交操作,都是对你项目作一次快照,以后可以回到这个状态,或者进行比较。</span>
~/hellogit$ git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working directory clean
~/hellogit$ echo "edit again" >> README.md #修改文件
~/hellogit$ git status
On branch master
<span style="background-color: rgb(153, 153, 0);">Changes not staged for commit</span>: #已跟踪文件的内容发生了变化,但还没有放到暂存区。要暂存需要运行git add命令
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: README.md
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
~/hellogit$ git add README.md
~/hellogit$ echo "edit more" >> README.md #修改文件
~/hellogit$ git status
On branch master
Changes to be committed: #运行 git add 命令前的版本</span>
(use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
modified: README.md
<span style="background-color: rgb(0, 153, 0);">Changes not staged for commit</span>: #echo "edit more"后的版本,如果现在提交,那么提交的是运行git add命令前的版本</span>
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: README.md
~/hellogit$ <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">git diff</span> #查看尚未暂存的文件更新了哪些部分,不加参数直接输入git diff
#此命令比较的是工作目录中当前文件和暂存区域快照之间的差异,也就是修改之后还没有暂存起来的变化内容。</span>
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 9e46238..95075d5 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -1,2 +1,3 @@
hello git readme
edit again
+edit more
~/hellogit$ git add README.md
~/hellogit$ git status
On branch master
Changes to be committed:
(use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
modified: README.md
~/hellogit$ echo "*.[oa]" > .gitignore #指定要忽略某些文件
*.[oa]
*~
~/hellogit$ <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">git mv README.md README</span>
~/hellogit$ git status
On branch master
Changes to be committed:
(use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
renamed: README.md -> README #重命名
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
.gitignore
~/hellogit$ ls -a
. .. .git .gitignore README
~/hellogit$ <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">git rm README</span> #从git中移除某个文件,就必须要从已跟踪文件清单中移除(确切地说,是从暂存区域移除),然后提交</span>
error: the following file has changes staged in the index:
README
(use --cached to keep the file, or -f to force removal)
~/hellogit$ git commit -m 'rename'
[master 77e1213] rename
2 files changed, 3 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 .gitignore
rename README.md => README (79%)
~/hellogit$ git rm README #如果删除之前修改过并且已经放到暂存区域的话,则必须要用强制删除选项 -f(译注:即 force 的首字母),以防误删除文件后丢失修改的内容。</span>
rm 'README'
~/hellogit$ ls -a
. .. .git .gitignore
~/hellogit$ git status
On branch master
<span style="background-color: rgb(102, 51, 255);">Changes to be committed</span>:
(use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
<span style="background-color: rgb(51, 102, 102);">deleted: README</span>
~/hellogit$ git commit -m 'del readme'
[master a25275d] del readme
1 file changed, 4 deletions(-)
delete mode 100644 README
~/hellogit$ git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working directory clean
~/hellogit$ <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">git remote add origin [email protected]:zhaihaifei/hellogit.git</span> #添加remote仓库,并设置它的别名为origin(remote仓库默认名称)</span>
~/hellogit$ git remote -v
<span style="background-color: rgb(102, 255, 153);">origin [email protected]:zhaihaifei/hellogit.git (fetch)
origin [email protected]:zhaihaifei/hellogit.git (push)</span>
~/hellogit$ echo 'print 1 + 1' >hellpgit.py
~/hellogit$ git commit -m 'add py'
~/hellogit$ git push -u origin master #push出错
To [email protected]:zhaihaifei/hellogit.git
! [rejected] master -> master (fetch first)
error: failed to push some refs to '[email protected]:zhaihaifei/hellogit.git'
hint: Updates were rejected because the remote contains work that you do
hint: not have locally. This is usually caused by another repository pushing
hint: to the same ref. You may want to first integrate the remote changes
hint: (e.g., 'git pull ...') before pushing again.
hint: See the 'Note about fast-forwards' in 'git push --help' for details.
~/hellogit$ <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">git fetch origin</span> #取得远程更新
warning: no common commits
remote: Counting objects: 3, done.
remote: Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
Unpacking objects: 100% (3/3), done.
From github.com:zhaihaifei/hellogit
* [new branch] master -> origin/master
~/hellogit$ <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">git merge origin/master</span> #把更新的内容合并到本地分支/master
Already up-to-date.
~/hellogit$ <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">git push origin master</span> #push成功
Counting objects: 21, done.
Delta compression using up to 12 threads.
Compressing objects: 100% (10/10), done.
Writing objects: 100% (19/19), 1.55 KiB | 0 bytes/s, done.
Total 19 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0)
To [email protected]:zhaihaifei/hellogit.git
474d5a1..5c1277d master -> master
4 git深入
5 远程服务器上的git
合作开发需要创建git远程仓库,也称为git服务器,有两种实现方式:
1 架设git服务器
参考http://git-scm.com/book/zh/v1
2 git托管服务(git hosting)
托管服务网站列表:https://git.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/GitHosting
其中 github是目前为止最大的开源git托管服务
注:远程仓库通常只是一个 裸仓库(bare repository) , 即一个没有当前工作目录的仓库。
因为该仓库只是一个合作媒介,所以不需要从硬盘上取出最新版本的快照;
仓库里存放的仅仅是工作目录中.git子目录内的内容。
6 github
6.1 简介
github是git项目托管网站,提供一个web界面。也可以是指Git客户端工具
术语:https://help.github.com/articles/github-glossary/
注册及设置帐户:https://help.github.com/categories/setup/
6.2 从git连接github
https://help.github.com/articles/set-up-git/#platform-linux
1 配置git
$git config --global user.name "YOUR NAME" $git config user.name $git config --global user.email "YOUR EMAIL ADDRESS" $git config user.email参考:https://help.github.com/categories/setup/
https://help.github.com/articles/setting-your-username-in-git/
2 连接认证
从git连接github需要认证,有两种连接认证方式:1 https(推荐)
$ git clone https://github.com/zhaihaifei/Hello.git使用https的好处是任何场景都可以工作, 能穿越防火墙。
使用https时,每次git fetch, git pull或git push跟远程仓库交互时要输入用户名和密码,两种方法避免:
1 使用credential helper记住用户名和密码(参考man 7 gitcredentials)
git当前包括两个helper:
cache: 缓存credential在内存中,
store: 保存credential在硬盘中,
过程:
1 查找helper
~$ git help -a | grep credential- credential-cache remote-ext credential-cache--daemon remote-fd credential-store remote-ftp2. 查看helper
$ git help credential-store3. 使用
<pre name="code" class="python">$ git config credential.helper store #保存于.git/config或.gitconfig
$ cat ../.gitconfig
[credential]
helper = store
$ git push https://github.com/zhaihaifei/Hello.git
Username: <type your username>
Password: <type your password>
[several days later]
$ git push https://github.com/zhaihaifei/Hello.git
[your credentials are used automatically]
$ git config --list
remote.origin.url=https://github.com/zhaihaifei/Hello.git
credential.helper=store
2 参考https://help.github.com/articles/which-remote-url-should-i-use/#cloning-with-https-recommended
2 ssh连接
参考:https://help.github.com/categories/ssh/
要使用ssh,必须在本机生成ssh keypair, 再把public key加入github帐户,过程如下:
1检查是否已经存在KEY
$ls -al ~/.ssh # Lists the files in your .ssh directory, if they exist默认的文件名: id_dsa.pub,id_ecdsa.pub,id_ed25519.pub,id_rsa.pub
2 生成ssh key
$ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "[email protected]" # Creates a new ssh key, using the provided email as a label # Generating public/private rsa key pair.3 把ssh key加入ssh agent(这一步也可以省略)
保证ssh-agent运行状态:$ ssh-agent -s
添加生成的ssh key,$ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa
4 将public key添加到github
登录github,点设置按钮,在侧边栏中找到SSH keys,进入设置
5 测试连接
ssh -T [email protected]
过程参考:https://help.github.com/articles/generating-ssh-keys/
实例操作:
~$ cat .gitconfig cat: .gitconfig: No such file or directory localadmin@openstack2:~$ git config --global user.name "zhaihaifei" localadmin@openstack2:~$ git config --global user.email "[email protected]" localadmin@openstack2:~$ cat .gitconfig [user] name = zhaihaifei email = [email protected] ~$ git clone https://github.com/tengqm/senlin.git Cloning into 'senlin'... Checking connectivity... done. ~$ cd senlin ~/senlin$ git remote -v origin https://github.com/tengqm/senlin.git (fetch) origin https://github.com/tengqm/senlin.git (push) ~/senlin$ git remote add github [email protected]:tengqm/senlin.git ~/senlin$ git fetch github Permission denied (publickey). fatal: Could not read from remote repository. Please make sure you have the correct access rights and the repository exists. ~$ cd .ssh ~/.ssh$ ls -al ~/.ssh ~/.ssh$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "[email protected]" Generating public/private rsa key pair. Enter file in which to save the key (/home/localadmin/.ssh/id_rsa): Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again: Your identification has been saved in /home/localadmin/.ssh/id_rsa. Your public key has been saved in /home/localadmin/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. ... ~/.ssh$ ls id_rsa id_rsa.pub ~/.ssh$ cat id_rsa.pub ... ~/.ssh$ ssh-agent -s SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/tmp/ssh-Ea7YQrFb0CrN/agent.12332; export SSH_AUTH_SOCK; SSH_AGENT_PID=12333; export SSH_AGENT_PID; echo Agent pid 12333; ~/.ssh$ ssh -T [email protected] Hi zhaihaifei! You've successfully authenticated, but...注意:在Windows安装的GitHub会自动处理ssh keypair,位于windows7在C:\Users\ADMIN\.ssh目录下
6.3 操作
创建远程仓库,参考https://help.github.com/articles/create-a-repo/
其它:https://help.github.com/
7 git本地仓库与github远程仓库
建立二者之间的连接:
1 在github上创建远程仓库
2 在本地创建git仓库
3 使用命令git remote add建立本地仓库与远程仓库的联系。