Studying note of GCC-3.4.6 source (56)
4.3.1.7.5. Create nodes of builtins
GCC offers a facility name builtin functions. They just act as functions from library we usually used in coding. In fact you can use these builtins in you program as library function, and you even needn’t include header files.
Obvioulsy, these functions can not be in form of function declaration we see from header file. They can’t appear in any header file. These functions are processed within GCC internal, they must be in form of rtx object. Some builtin functions just indicate the expected operation, and they will be replaced by lines of codes after expansion (for example, the famous and commonly seen in Linux code builtin – builtin_const); some even need invoke function defined in libiberty within itself – the library used by GCC. As a step of system startup, the internal presentation of the builtin functions should be created and pushed into the right namespace – it is done by c_common_nodes_and_builtins.
cxx_init_decl_processing (continue)
3000 c_common_nodes_and_builtins ();
4.3.1.7.5.1. Nodes of builtin integer types
c_common_nodes_and_builtins first creates builtin types. As a common approach, GCC likes to use file to describe the detail. Here again for those builtin types a file “builtin-types.def” is used, which provides a declarative way of describing the types that are used when declaring builtin functions. Before including this file, you must define the following macros:
DEF_PRIMITIVE_TYPE (ENUM, TYPE)
The ENUM is an identifier indicating which type is being defined. TYPE is an expression for a `tree' that represents the type.
DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_0 (ENUM, RETURN)
DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_1 (ENUM, RETURN, ARG1)
DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_2 (ENUM, RETURN, ARG1, ARG2)
DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_3 (ENUM, RETURN, ARG1, ARG2, ARG3)
DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_4 (ENUM, RETURN, ARG1, ARG2, ARG3, ARG4)
These macros describe function types. ENUM is as above. The RETURN type is one of the enumerals already defined. ARG1, ARG2, and ARG3 give the types of the arguments, similarly.
DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_VAR_0 (ENUM, RETURN)
DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_VAR_1 (ENUM, RETURN, ARG1)
DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_VAR_2 (ENUM, RETURN, ARG1, ARG2)
DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_VAR_3 (ENUM, RETURN, ARG1, ARG2, ARG3)
Similar, but for function types that take variable arguments, for example:
DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_1 (BT_INT_DOUBLE, BT_INT, BT_DOUBLE)
describes the type `int ()(double)', using the enumeral BT_INT_DOUBLE, whereas:
DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_VAR_1 (BT_INT_DOUBLE_VAR, BT_INT, BT_DOUBLE)
describes the type `int ()(double, ...)'.
DEF_POINTER_TYPE (ENUM, TYPE)
This macro describes a pointer type. ENUM is as above; TYPE is the type pointed to.
3057 void
3058 c_common_nodes_and_builtins (void) in c-common.c
3059 {
3060 enum builtin_type
3061 {
3062 #define DEF_PRIMITIVE_TYPE(NAME, VALUE) NAME,
3063 #define DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_0(NAME, RETURN) NAME,
3064 #define DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_1(NAME, RETURN, ARG1) NAME,
3065 #define DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_2(NAME, RETURN, ARG1, ARG2) NAME,
3066 #define DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_3(NAME, RETURN, ARG1, ARG2, ARG3) NAME,
3067 #define DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_4(NAME, RETURN, ARG1, ARG2, ARG3, ARG4) NAME,
3068 #define DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_VAR_0(NAME, RETURN) NAME,
3069 #define DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_VAR_1(NAME, RETURN, ARG1) NAME,
3070 #define DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_VAR_2(NAME, RETURN, ARG1, ARG2) NAME,
3071 #define DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_VAR_3(NAME, RETURN, ARG1, ARG2, ARG3) NAME,
3072 #define DEF_POINTER_TYPE(NAME, TYPE) NAME,
3073 #include "builtin-types.def"
3074 #undef DEF_PRIMITIVE_TYPE
3075 #undef DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_0
3076 #undef DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_1
3077 #undef DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_2
3078 #undef DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_3
3079 #undef DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_4
3080 #undef DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_VAR_0
3081 #undef DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_VAR_1
3082 #undef DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_VAR_2
3083 #undef DEF_FUNCTION_TYPE_VAR_3
3084 #undef DEF_POINTER_TYPE
3085 BT_LAST
3086 };
3087
3088 typedef enum builtin_type builtin_type;
3089
3090 tree builtin_types[(int) BT_LAST];
3091 int wchar_type_size;
3092 tree array_domain_type;
3093 tree va_list_ref_type_node;
3094 tree va_list_arg_type_node;
3095
3096 /* Define `int' and `char' first so that dbx will output them first. */
3097 record_builtin_type (RID_INT, NULL, integer_type_node);
3098 record_builtin_type (RID_CHAR, "char", char_type_node);
3099
3100 /* `signed' is the same as `int'. FIXME: the declarations of "signed",
3101 "unsigned long", "long long unsigned" and "unsigned short" were in C++
3102 but not C. Are the conditionals here needed? */
3103 if (c_dialect_cxx ())
3104 record_builtin_type (RID_SIGNED, NULL, integer_type_node);
3105 record_builtin_type (RID_LONG, "long int", long_integer_type_node);
3106 record_builtin_type (RID_UNSIGNED, "unsigned int", unsigned_type_node);
3107 record_builtin_type (RID_MAX, "long unsigned int",
3108 long_unsigned_type_node);
3109 if (c_dialect_cxx ())
3110 record_builtin_type (RID_MAX, "unsigned long", long_unsigned_type_node);
3111 record_builtin_type (RID_MAX, "long long int",
3112 long_long_integer_type_node);
3113 record_builtin_type (RID_MAX, "long long unsigned int",
3114 long_long_unsigned_type_node);
3115 if (c_dialect_cxx ())
3116 record_builtin_type (RID_MAX, "long long unsigned",
3117 long_long_unsigned_type_node);
3118 record_builtin_type (RID_SHORT, "short int", short_integer_type_node);
3119 record_builtin_type (RID_MAX, "short unsigned int",
3120 short_unsigned_type_node);
3121 if (c_dialect_cxx ())
3122 record_builtin_type (RID_MAX, "unsigned short",
3123 short_unsigned_type_node);
3124
3125 /* Define both `signed char' and `unsigned char'. */
3126 record_builtin_type (RID_MAX, "signed char", signed_char_type_node);
3127 record_builtin_type (RID_MAX, "unsigned char", unsigned_char_type_node);
record_builtin_type pushes the declarations of builtin types into global namespace. Parameter rid_index is the index of the builtin type in the array RID_POINTERS; name is the name used when looking up the builtin type; type is the *_TYPE node of the builtin type. See that, type node is created in build_common_tree_nodes.
2729 void
2730 record_builtin_type (enum rid rid_index, in decl.c
2731 const char* name,
2732 tree type)
2733 {
2734 tree rname = NULL_TREE, tname = NULL_TREE;
2735 tree tdecl = NULL_TREE;
2736
2737 if ((int) rid_index < (int) RID_MAX)
2738 rname = ridpointers[(int) rid_index];
2739 if (name)
2740 tname = get_identifier (name);
2741
2742 /* The calls to SET_IDENTIFIER_GLOBAL_VALUE below should be
2743 eliminated. Built-in types should not be looked up name; their
2744 names are keywords that the parser can recognize. However, there
2745 is code in c-common.c that uses identifier_global_value to look
2746 up built-in types by name. */
2747 if (tname)
2748 {
2749 tdecl = build_decl (TYPE_DECL, tname, type);
2750 DECL_ARTIFICIAL (tdecl) = 1;
2751 SET_IDENTIFIER_GLOBAL_VALUE (tname, tdecl);
2752 }
2753 if (rname)
2754 {
2755 if (!tdecl)
2756 {
2757 tdecl = build_decl (TYPE_DECL, rname, type);
2758 DECL_ARTIFICIAL (tdecl) = 1;
2759 }
2760 SET_IDENTIFIER_GLOBAL_VALUE (rname, tdecl);
2761 }
2762
2763 if (!TYPE_NAME (type))
2764 TYPE_NAME (type) = tdecl;
2765
2766 if (tdecl)
2767 {
2768 TREE_CHAIN (tdecl) = builtin_type_decls;
2769 builtin_type_decls = tdecl;
2770 }
2771 }
By carefully checking reswords, it is interesting to find that, for example, above at line 3105, “long” is the word associates with RID_LONG, but here we expect it should be “long int” – it is the name for programmer; while for those won’t be opened to programmer, NULL will be passed as name.
In above code snippet, it is obvious that name passed in if non-null has priority over reswords of rid_index to be used as the type name.
262 #define SET_IDENTIFIER_GLOBAL_VALUE(NODE, VAL) / in cp-tree.h
263 set_namespace_binding ((NODE), global_namespace, (VAL))
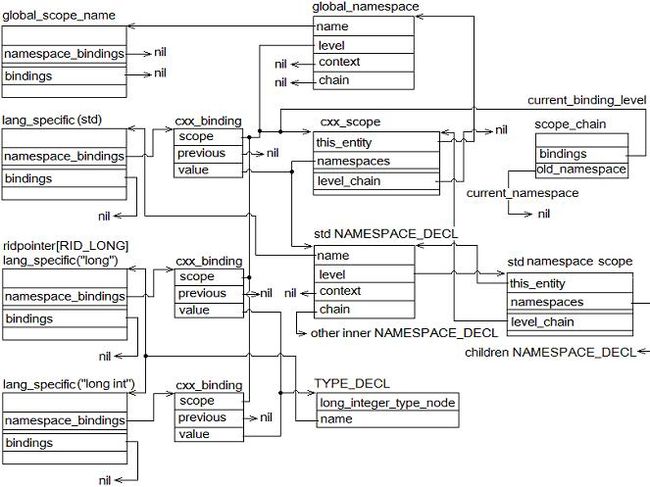
Then SET_IDENTIFIER_GLOBAL_VALUE inserts the NODE into global namespace, and as result, we will get a layout as following figure (only RID_LONG shown).
Figure 35: Nodes for builtin types
See that node pushed by set_namespace_binding is expected to be visited by get_identifier. And along chains of namespace_bindings and bindings, all binding scope defining the identifier can be found out.
4.3.1.7.5.1. Nodes of builtin integer type sizes
In previous, we have seen that, for integer types, such as int, short, have different size upon different platform, so the compiler keeps a set of nodes standing for the standard size. Now it needs to push these nodes into global namespace to make them usable.
c_common_nodes_and_builtins (continue)
3129 /* These are types that c_common_type_for_size and
3130 c_common_type_for_mode use. */
3131 (*lang_hooks.decls.pushdecl) (build_decl (TYPE_DECL, NULL_TREE,
3132 intQI_type_node));
3133 (*lang_hooks.decls.pushdecl) (build_decl (TYPE_DECL, NULL_TREE,
3134 intHI_type_node));
3135 (*lang_hooks.decls.pushdecl) (build_decl (TYPE_DECL, NULL_TREE,
3136 intSI_type_node));
3137 (*lang_hooks.decls.pushdecl) (build_decl (TYPE_DECL, NULL_TREE,
3138 intDI_type_node));
3139 #if HOST_BITS_PER_WIDE_INT >= 64
3140 (*lang_hooks.decls.pushdecl) (build_decl (TYPE_DECL,
3141 get_identifier ("__int128_t"),
3142 intTI_type_node));
3143 #endif
3144 (*lang_hooks.decls.pushdecl) (build_decl (TYPE_DECL, NULL_TREE,
3145 unsigned_intQI_type_node));
3146 (*lang_hooks.decls.pushdecl) (build_decl (TYPE_DECL, NULL_TREE,
3147 unsigned_intHI_type_node));
3148 (*lang_hooks.decls.pushdecl) (build_decl (TYPE_DECL, NULL_TREE,
3149 unsigned_intSI_type_node));
3150 (*lang_hooks.decls.pushdecl) (build_decl (TYPE_DECL, NULL_TREE,
3151 unsigned_intDI_type_node));
3152 #if HOST_BITS_PER_WIDE_INT >= 64
3153 (*lang_hooks.decls.pushdecl) (build_decl (TYPE_DECL,
3154 get_identifier ("__uint128_t"),
3155 unsigned_intTI_type_node));
3156 #endif
int*_type_node are nodes indicating sizes of integer types which are also created in build_common_tree_nodes and are alias of *_type nodes in former section of size no larger than 32 bits. For such nodes, the second parameter passed to build_decl is NULL which will be set in the name field of the TYPE_DECL created as the nodes are NOT associated with identifiers (that is they can’t be visited by user). Hook pushdecl carried by lang_hooks is still pushdecl for C++.
566 tree
567 pushdecl (tree x) in name-lookup.c
568 {
569 tree t;
570 tree name;
571 int need_new_binding;
572
573 timevar_push (TV_NAME_LOOKUP);
574
575 need_new_binding = 1;
…
604 name = DECL_NAME (x);
605 if (name)
606 {
...
1007 }
1008
1009 if (need_new_binding)
1010 add_decl_to_level (x,
1011 DECL_NAMESPACE_SCOPE_P (x)
1012 ? NAMESPACE_LEVEL (CP_DECL_CONTEXT (x))
1013 : current_binding_level);
1014
1015 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, x);
1016 }
For those nodes, name fetched at line 604 is NULL. And the nodes are added in namespace (global here) returned by current_binding_level at line 1013 by add_decl_to_level.
Before executing line 3152 of c_common_nodes_and_builtins, the simplified layout is shown in below figure (nodes related to intTI_type_node are not shown and only the first node linked in names field is given).

Figure 36: Nodes for builtin types 2
Macro HOST_BITS_PER_WIDE_INT has following definition:
47 #if HOST_BITS_PER_LONG >= 64 || !defined NEED_64BIT_HOST_WIDE_INT in hwint.h
48 # define HOST_BITS_PER_WIDE_INT HOST_BITS_PER_LONG
49 # define HOST_WIDE_INT long
50 #else
51 # if HOST_BITS_PER_LONGLONG >= 64
52 # define HOST_BITS_PER_WIDE_INT HOST_BITS_PER_LONGLONG
53 # define HOST_WIDE_INT long long
54 # else
55 # if HOST_BITS_PER___INT64 >= 64
56 # define HOST_BITS_PER_WIDE_INT HOST_BITS_PER___INT64
57 # define HOST_WIDE_INT __int64
58 # else
59 #error "Unable to find a suitable type for HOST_WIDE_INT"
60 # endif
61 # endif
62 #endif
To 32 bits system, NEED_64BIT_HOST_WIDE_INT is not defined. Thus HOST_WIDE_INT is long, and HOST_BITS_PER_WIDE_INT is 32. And from here, it is clearly that for 64 bits system, GCC defines types __int128_t and __uint128_t for programmer.
c_common_nodes_and_builtins (continue)
3158 /* Create the widest literal types. */
3159 widest_integer_literal_type_node
3160 = make_signed_type (HOST_BITS_PER_WIDE_INT * 2);
3161 (*lang_hooks.decls.pushdecl) (build_decl (TYPE_DECL, NULL_TREE,
3162 widest_integer_literal_type_node));
3163
3164 widest_unsigned_literal_type_node
3165 = make_unsigned_type (HOST_BITS_PER_WIDE_INT * 2);
3166 (*lang_hooks.decls.pushdecl) (build_decl (TYPE_DECL, NULL_TREE,
3167 widest_unsigned_literal_type_node));
3168
3169 /* `unsigned long' is the standard type for sizeof.
3170 Note that stddef.h uses `unsigned long',
3171 and this must agree, even if long and int are the same size. */
3172 size_type_node =
3173 TREE_TYPE (identifier_global_value (get_identifier (SIZE_TYPE)));
3174 signed_size_type_node = c_common_signed_type (size_type_node);
3175 set_sizetype (size_type_node);
For 32 bits system, widest_integer_literal_type_node and widest_unsigned_literal_type_node correspond to 64 bits signed/unsigned integer type, they are also hidden from programmer. At line 3172, size_type_node is the type of operator sizeof, it is “unsigned int” for x86/Linux.