git不同于类似SVN这种版本管理系统,虽然熟悉常用的操作就可以满足大部分需求,但为了在遇到麻烦时不至于靠蛮力去尝试,了解git的原理还是很有必要。
文件
通过git管理的文件版本信息全部存放在根目录.git下,稍微看下:
$ ls .git COMMIT_EDITMSG HEAD branches description index logs packed-refs FETCH_HEAD ORIG_HEAD config hooks info objects refs
git除了提供给我们平时常用的一些命令之外,还有很多底层命令,可以用于查看以上部分文件表示的东西。
三个区域/三类对象
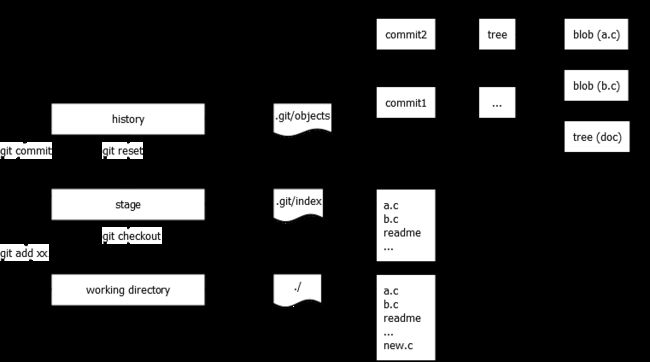
理解git里的三个区域概念非常重要。git里很多常用的命令都是围绕着这三个区域来做的。它们分别为:
- working directory,也就是你所操作的那些文件
- history,你所提交的所有记录,文件历史内容等等。git是个分布式版本管理系统,在你本地有项目的所有历史提交记录;文件历史记录;提交日志等等。
- stage(index),暂存区域,本质上是个文件,也就是
.git/index
git中还有三类常用对象(实际不止三种),理解这三类对象也很重要。分别为:
- blob,用于表示一个文件
- tree,用于表示一个目录,索引到若干文件或子目录
- commit,用于表示一次提交(commit)
所有对象都会以文件的形式保存在.git/objects目录,一个对象一个文件。
接下来把上面所有的内容关联起来。做以下操作:
$ mkdir test && cd test $ git init $ ls -a .git/objects # 没有文件 . .. info pack $ touch readme # working directory里增加了一个readme文件 $ git add readme # 添加一个文件到stage区域 $ git ls-files --stage # 这个命令可以查看stage区域里的内容,可以看到有readme 100644 e69de29bb2d1d6434b8b29ae775ad8c2e48c5391 0 readme $ ls -a .git/objects # 同时.git/objects增加了一个e6的目录 . .. e6 info pack $ ls -a .git/objects/e6/ # e6目录下增加了一个文件 . .. 9de29bb2d1d6434b8b29ae775ad8c2e48c5391
上面的操作展示了git中三个区域三个对象的部分关联关系。git中每个对象都以一个40个字符长度的SHA-1哈希值为标识,以这40个字符的前2个字符作为文件夹,以后38个字符为文件名。
基于以上继续操作:
$ git commit -m 'first commit' # commit会将stage里标识的文件提交到history区域 [master (root-commit) 8bf6969] first commit 0 files changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-) create mode 100644 readme $ ls -a .git/objects # 增加了2个文件,也就是2个对象 . .. 8b e6 e8 info pack $ git ls-files --stage # stage仅表示当前被版本管理的文件,所以内容不变 100644 e69de29bb2d1d6434b8b29ae775ad8c2e48c5391 0 readme # git cat-file 命令可以用于查看.git/objects下的文件,意即可用于查看对象 $ git cat-file -t e69de29bb2d1d6434b8b29ae775ad8c2e48c5391 # 这个是之前git add readme产生的文件对象 blob blob # 同样我们来查看git commit -m后新增的两个对象 $ ls .git/objects/8b/ f696927c17526eb8f0c6dae8badb968a001ed0 $ git cat-file -t 8bf696927c17526eb8f0c6dae8badb968a001ed0 # 记得带上8b这个文件夹名,才算一个完整的对象ID。这是一个commit对象 commit $ ls .git/objects/e8 0ad49ace82167de62e498622d70377d913c79e $ git cat-file -t e80ad49ace82167de62e498622d70377d913c79e # tree对象 tree
区域和对象如何交互的可以用下图描述:
通过git cat-file -p可以查看对象的更多描述,git cat-file -t仅获取对象的类型。做以下操作获得更深的认识:
# 这个commit对象记录了提交者的信息,还包括指向的tree对象 $ git cat-file -p 8bf696927c17526eb8f0c6dae8badb968a001ed0 tree e80ad49ace82167de62e498622d70377d913c79e author Kevin Lynx <[email protected]> 1410090424 +0800 committer Kevin Lynx <[email protected]> 1410090424 +0800 first commit # 查看tree对象可以看出tree指向的blob对象 $ git cat-file -p e80ad49ace82167de62e498622d70377d913c79e 100644 blob e69de29bb2d1d6434b8b29ae775ad8c2e48c5391 readme
即使是已经被版本管理的文件,发生改动后(正常改动或合并)都使用git add来重新mark它。创建第二次提交进一步认识:
$ echo 'hello git' > readme $ touch install $ git ls-files --stage # 不使用git add,暂存区域内容没变 100644 e69de29bb2d1d6434b8b29ae775ad8c2e48c5391 0 readme # 此时stage里内容未变,提示no changes added to commit $ git commit # On branch master # Changed but not updated: # (use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed) # (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory) # # modified: readme # # Untracked files: # (use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed) # # install no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a") $ git add readme $ ls .git/objects/ # git add之后.git/objects下新增文件 8b 8d e6 e8 info pack $ ls .git/objects/8d/ 0e41234f24b6da002d962a26c2495ea16a425f $ git cat-file -p 8d0e41234f24b6da002d962a26c2495ea16a425f # 查看该新增对象 hello git # 这个时候还可以在提交前撤销git add readme $ git reset readme # 从history到stage Unstaged changes after reset: M readme $ cat readme hello git $ git checkout readme # 从stage到working directory $ cat readme # 没有内容,回到第一个版本 $ git add install # 添加新创建的文件 $ git ls-files --stage # stage中的内容是最新的readme和新添加的install 100644 e69de29bb2d1d6434b8b29ae775ad8c2e48c5391 0 install 100644 8d0e41234f24b6da002d962a26c2495ea16a425f 0 readme $ ls .git/objects/ 8b 8d e6 e8 info pack
以上,发现一个有趣的现象:新加的install文件的SHA-1哈希值和之前的readme相同,这是因为这2个文件都是空的,内容相同。继续:
$ git commit -m 'second commit' $ ls .git/objects/ # 提交后新增2个对象 45 72 8b 8d e6 e8 info pack $ ls .git/objects/72/ b94e949c5fca6092cc74c751a7bb35ee71c283 $ git cat-file -p 72b94e949c5fca6092cc74c751a7bb35ee71c283 tree 45cf0bd049d7eea4558b14f33a894db27c7c1130 # 新创建的tree对象 parent 8bf696927c17526eb8f0c6dae8badb968a001ed0 # commit对象有parent,正是上一次提交 author Kevin Lynx <[email protected]> 1410094456 +0800 committer Kevin Lynx <[email protected]> 1410094456 +0800 second commit # 新创建的tree对象指向了2个文件 $ git cat-file -p 45cf0bd049d7eea4558b14f33a894db27c7c1130 100644 blob e69de29bb2d1d6434b8b29ae775ad8c2e48c5391 install 100644 blob 8d0e41234f24b6da002d962a26c2495ea16a425f readme
需要注意,有时候我们使用git commit -a,它会直接将已经加入版本管理的文件一起提交,从而跳过了git add这个过程。同git很多操作一样,它只是一个快捷操作。
总结
从上面的内容其实已经可以看出git的优势所在,它可以完全不需要服务器就完成一个版本控制系统的所有事情。在.git文件中它记录了所有的文件的所有历史提交,记录了每一次提交的信息。
git的常用操作中还会涉及到分支、远端仓库等,空了再写。
参考文档
- Git的思想和基本工作原理
- 图解Git
- Git详解之九:Git内部原理
- Git 少用 Pull 多用 Fetch 和 Merge