Spark Python 快速体验
Spark是2015年最受热捧大数据开源平台,我们花一点时间来快速体验一下Spark。
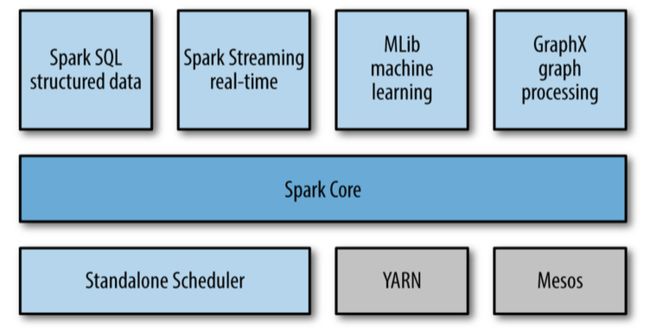
Spark 技术栈
如上图所示,Spark的技术栈包括了这些模块:
核心模块 :Spark Core
集群管理
Standalone Scheduler
YARN
Mesos
Spark SQL
Spark 流 Streaming
Spark 机器学习 MLLib
GraphX 图处理模块
安装和启动Spark
Spark Python Shell
> bin/pyspark
Spark Ipython Shell
> IPYTHON=1 ./bin/pyspark > IPYTHON_OPTS="notebook" ./bin/pyspark
Spark 架构
初始化 Spark Context
在使用Spark的功能之前首先要初始化Spark的context,Context包含了Spark的连接和配置信息。
Spark Context,Driver和Worker节点之间的关系如下图:
# Construct a conf
conf = new SparkConf()
conf.set("spark.app.name", "My Spark App")conf.set("spark.master", "local[4]")conf.set("spark.ui.port", "36000") # Override the default port
# Create a SparkContext with this configuration
sc = SparkContext(conf)
创建 RDD
RDD是Spark的基本数据模型,所有的操作都是基于RDD。RDD是inmutable(不可改变)的。
lines = sc.textFile("README.md")
pythonLines = lines.filter(lambda line: "Python" in line)
pythonLines.first()
pythonLines.count()
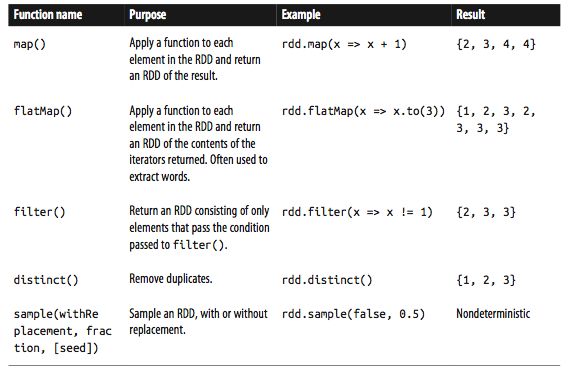
RDD 操作:
下面是一些对RDD的变形操作
RDD Transformation on {1,2,3,4}
两个RDD之间的操作, Transformation on {1,2,3} and {3,4,5}
RDD actions on {1,2,3,3}
Transformation on pair RDD {(1,2),(3,4),(3,6)}
Transform on two pair RDDs {(1,2),(3,4),(3,6)}, {(3,9)}
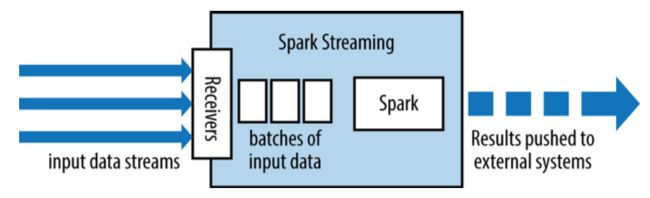
Spark 流 stream
Spark流基于RDD,可以理解对小的时间片段上的RDD操作。
SparkSQL
Spark SQL可以用于操作和查询结构化和半结构化的数据。包括Hive,JSON, CSV等。
# Import Spark SQL
from pyspark.sql import HiveContext, Row
# Or if you can't include the hive requirements
from pyspark.sql import SQLContext, Row
input = hiveCtx.jsonFile(inputFile)
# Register the input schema RDDinput.registerTempTable("tweets")
# Select tweets based on the retweetCount
topTweets = hiveCtx.sql("SELECT text, retweetCount FROM tweets ORDER BY retweetCount LIMIT 10")
Spark SQL支持JDBC
SparkML
机器学习的基本流程如下:
获得数据
从数据中提取特征
对数据进行有监督的或者无监督的学习,训练机器学习的模型
对模型进行评估,找出最佳模型
由于Spark的架构特点,Spark支持的机器学习算法是哪些可以并行的算法。
from pyspark.mllib.regression import LabeledPoint
from pyspark.mllib.feature import HashingTF
from pyspark.mllib.classification import LogisticRegressionWithSGD
spam = sc.textFile("spam.txt")normal = sc.textFile("normal.txt")
# Create a HashingTF instance to map email text to vectors of 10,000 features.
tf = HashingTF(numFeatures = 10000)
# Each email is split into words, and each word is mapped to one feature.
spamFeatures = spam.map(lambda email: tf.transform(email.split(" ")))
normalFeatures = normal.map(lambda email: tf.transform(email.split(" ")))
# Create LabeledPoint datasets for positive (spam) and negative (normal) examples.
positiveExamples = spamFeatures.map(lambda features: LabeledPoint(1, features))
negativeExamples = normalFeatures.map(lambda features: LabeledPoint(0, features))
trainingData = positiveExamples.union(negativeExamples)
trainingData.cache() # Cache since Logistic Regression is an iterative algorithm.
# Run Logistic Regression using the SGD algorithm.
model = LogisticRegressionWithSGD.train(trainingData)
# Test on a positive example (spam) and a negative one (normal). We first apply
# the same HashingTF feature transformation to get vectors, then apply the model.
posTest = tf.transform("O M G GET cheap stuff by sending money to ...".split(" "))
negTest = tf.transform("Hi Dad, I started studying Spark the other ...".split(" "))
print "Prediction for positive test example: %g" % model.predict(posTest)
print "Prediction for negative test example: %g" % model.predict(negTest)