蚁群算法浅谈
本文参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/biaoyu/archive/2012/09/26/2704456.html
http://blog.163.com/ykn_2010/blog/static/1420333362012111411258466/
简介
蚁群算法(ant colony optimization, ACO),又称蚂蚁算法,是一种用来在图中寻找优化路径的机率型算法。它由Marco Dorigo于1992年在他的博士论文中提出,其灵感来源于蚂蚁在寻找食物过程中发现路径的行为。蚁群算法是一种模拟进化算法,初步的研究表明该算法具有许多优良的性质。针对PID控制器参数优化设计问题,将蚁群算法设计的结果与遗传算法设计的结果进行了比较,数值仿真结果表明,蚁群算法具有一种新的模拟进化优化方法的有效性和应用价值。
定义
各个蚂蚁在没有事先告诉他们食物在什么地方的前提下开始寻找食物。当一只找到食物以后,它会向环境释放一种挥发性分泌物pheromone (称为信息素,该物质随着时间的推移会逐渐挥发消失,信息素浓度的大小表征路径的远近)来实现的,吸引其他的蚂蚁过来,这样越来越多的蚂蚁会找到食物。有些蚂蚁并没有像其它蚂蚁一样总重复同样的路,他们会另辟蹊径,如果另开辟的道路比原来的其他道路更短,那么,渐渐地,更多的蚂蚁被吸引到这条较短的路上来。最后,经过一段时间运行,可能会出现一条最短的路径被大多数蚂蚁重复着。
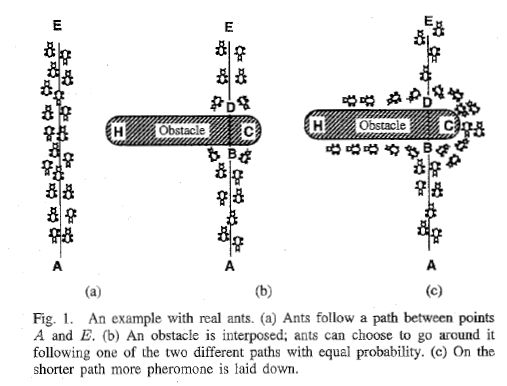
蚁群算法是一种仿生学算法,是由自然界中蚂蚁觅食的行为而启发的。在自然界中,蚂蚁觅食过程中,蚁群总能够按照寻找到一条从蚁巢和食物源的最优路径。图(1)显示了这样一个觅食的过程。
在图1(a)中,有一群蚂蚁,假如A是蚁巢,E是食物源(反之亦然)。这群蚂蚁将沿着蚁巢和食物源之间的直线路径行驶。假如在A和E之间突然出现了一个障碍物(图1(b)),那么,在B点(或D点)的蚂蚁将要做出决策,到底是向左行驶还是向右行驶?由于一开始路上没有前面蚂蚁留下的信息素(pheromone),蚂蚁朝着两个方向行进的概率是相等的。但是当有蚂蚁走过时,它将会在它行进的路上释放出信息素,并且这种信息素会议一定的速率散发掉。信息素是蚂蚁之间交流的工具之一。它后面的蚂蚁通过路上信息素的浓度,做出决策,往左还是往右。很明显,沿着短边的的路径上信息素将会越来越浓(图1(c)),从而吸引了越来越多的蚂蚁沿着这条路径行驶。
蚁群算法原理
假如蚁群中所有蚂蚁的数量为m,所有城市之间的信息素用矩阵pheromone表示,最短路径为bestLength,最佳路径为bestTour。每只蚂蚁都有自己的内存,内存中用一个禁忌表(Tabu)来存储该蚂蚁已经访问过的城市,表示其在以后的搜索中将不能访问这些城市;还有用另外一个允许访问的城市表(Allowed)来存储它还可以访问的城市;另外还用一个矩阵(Delta)来存储它在一个循环(或者迭代)中给所经过的路径释放的信息素;还有另外一些数据,例如一些控制参数(α,β,ρ,Q)(α,β,ρ,Q),该蚂蚁行走玩全程的总成本或距离(tourLength),等等。假定算法总共运行MAX_GEN次,运行时间为t。
蚁群算法计算过程如下:
(1)初始化
设t=0,初始化bestLength为一个非常大的数(正无穷),bestTour为空。初始化所有的蚂蚁的Delt矩阵所有元素初始化为0,Tabu表清空,Allowed表中加入所有的城市节点。随机选择它们的起始位置(也可以人工指定)。在Tabu中加入起始节点,Allowed中去掉该起始节点。
(2)为每只蚂蚁选择下一个节点。
为每只蚂蚁选择下一个节点,该节点只能从Allowed中以某种概率(公式1)搜索到,每搜到一个,就将该节点加入到Tabu中,并且从Allowed中删除该节点。该过程重复n-1次,直到所有的城市都遍历过一次。遍历完所有节点后,将起始节点加入到Tabu中。此时Tabu表元素数量为n+1(n为城市数量),Allowed元素数量为0。接下来按照(公式2)计算每个蚂蚁的Delta矩阵值。最后计算最佳路径,比较每个蚂蚁的路径成本,然后和bestLength比较,若它的路径成本比bestLength小,则将该值赋予bestLength,并且将其Tabu赋予BestTour。
(3)更新信息素矩阵
(4)检查终止条件
(5)输出最优值
Java实现
在该java实现中我们选择使用tsplib上的数据att48,这是一个对称tsp问题,城市规模为48,其最优值为10628.其距离计算方法如图(2)所示:
att48距离计算方法
实现中,使用了两个java类,一个Ant类,一个ACO类。
具体实现代码如下(此代码借鉴了蚁群优化算法的JAVA实现):
Ant类:
1: import java.util.Random;
2: import java.util.Vector;
3:
4: /**
5: *
6: * @author BIAO YU
7: *
8: */
9: public class Ant implements Cloneable {
10:
11: private Vector<Integer> tabu; //禁忌表
12: private Vector<Integer> allowedCities; //允许搜索的城市
13: private float[][] delta; //信息数变化矩阵
14: private int[][] distance; //距离矩阵
15:
16: private float alpha;
17: private float beta;
18:
19: private int tourLength; //路径长度
20: private int cityNum; //城市数量
21:
22: private int firstCity; //起始城市
23: private int currentCity; //当前城市
24:
25: public Ant(){
26: cityNum = 30;
27: tourLength = 0;
28:
29: }
30:
31: /**
32: * Constructor of Ant
33: * @param num 蚂蚁数量
34: */
35: public Ant(int num){
36: cityNum = num;
37: tourLength = 0;
38:
39: }
40:
41: /**
42: * 初始化蚂蚁,随机选择起始位置
43: * @param distance 距离矩阵
44: * @param a alpha
45: * @param b beta
46: */
47: public void init(int[][] distance, float a, float b){
48: alpha = a;
49: beta = b;
50: allowedCities = new Vector<Integer>();
51: tabu = new Vector<Integer>();
52: this.distance = distance;
53: delta = new float[cityNum][cityNum];
54: for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
55: Integer integer = new Integer(i);
56: allowedCities.add(integer);
57: for (int j = 0; j < cityNum; j++) {
58: delta[i][j] = 0.f;
59: }
60: }
61:
62: Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
63: firstCity = random.nextInt(cityNum);
64: for (Integer i:allowedCities) {
65: if (i.intValue() == firstCity) {
66: allowedCities.remove(i);
67: break;
68: }
69: }
70:
71: tabu.add(Integer.valueOf(firstCity));
72: currentCity = firstCity;
73: }
74:
75: /**
76: * 选择下一个城市
77: * @param pheromone 信息素矩阵
78: */
79: public void selectNextCity(float[][] pheromone){
80: float[] p = new float[cityNum];
81: float sum = 0.0f;
82: //计算分母部分
83: for (Integer i:allowedCities) {
84: sum += Math.pow(pheromone[currentCity][i.intValue()], alpha)*Math.pow(1.0/distance[currentCity][i.intValue()], beta);
85: }
86: //计算概率矩阵
87: for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
88: boolean flag = false;
89: for (Integer j:allowedCities) {
90:
91: if (i == j.intValue()) {
92: p[i] = (float) (Math.pow(pheromone[currentCity][i], alpha)*Math.pow(1.0/distance[currentCity][i], beta))/sum;
93: flag = true;
94: break;
95: }
96: }
97:
98: if (flag == false) {
99: p[i] = 0.f;
100: }
101: }
102:
103: //轮盘赌选择下一个城市
104: Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
105: float sleectP = random.nextFloat();
106: int selectCity = 0;
107: float sum1 = 0.f;
108: for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
109: sum1 += p[i];
110: if (sum1 >= sleectP) {
111: selectCity = i;
112: break;
113: }
114: }
115:
116: //从允许选择的城市中去除select city
117: for (Integer i:allowedCities) {
118: if (i.intValue() == selectCity) {
119: allowedCities.remove(i);
120: break;
121: }
122: }
123: //在禁忌表中添加select city
124: tabu.add(Integer.valueOf(selectCity));
125: //将当前城市改为选择的城市
126: currentCity = selectCity;
127:
128: }
129:
130: /**
131: * 计算路径长度
132: * @return 路径长度
133: */
134: private int calculateTourLength(){
135: int len = 0;
136: for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
137: len += distance[this.tabu.get(i).intValue()][this.tabu.get(i+1).intValue()];
138: }
139: return len;
140: }
141:
142:
143:
144: public Vector<Integer> getAllowedCities() {
145: return allowedCities;
146: }
147:
148: public void setAllowedCities(Vector<Integer> allowedCities) {
149: this.allowedCities = allowedCities;
150: }
151:
152: public int getTourLength() {
153: tourLength = calculateTourLength();
154: return tourLength;
155: }
156: public void setTourLength(int tourLength) {
157: this.tourLength = tourLength;
158: }
159: public int getCityNum() {
160: return cityNum;
161: }
162: public void setCityNum(int cityNum) {
163: this.cityNum = cityNum;
164: }
165:
166: public Vector<Integer> getTabu() {
167: return tabu;
168: }
169:
170: public void setTabu(Vector<Integer> tabu) {
171: this.tabu = tabu;
172: }
173:
174: public float[][] getDelta() {
175: return delta;
176: }
177:
178: public void setDelta(float[][] delta) {
179: this.delta = delta;
180: }
181:
182: public int getFirstCity() {
183: return firstCity;
184: }
185:
186: public void setFirstCity(int firstCity) {
187: this.firstCity = firstCity;
188: }
189:
190: }
191:
ACO类:
1: import java.io.BufferedReader;
2: import java.io.FileInputStream;
3: import java.io.IOException;
4: import java.io.InputStreamReader;
5:
6: /**
7: *
8: * @author BIAO YU
9: *
10: *
11: */
12: public class ACO {
13:
14: private Ant[] ants; //蚂蚁
15: private int antNum; //蚂蚁数量
16: private int cityNum; //城市数量
17: private int MAX_GEN; //运行代数
18: private float[][] pheromone; //信息素矩阵
19: private int[][] distance; //距离矩阵
20: private int bestLength; //最佳长度
21: private int[] bestTour; //最佳路径
22:
23: //三个参数
24: private float alpha;
25: private float beta;
26: private float rho;
27:
28:
29: public ACO(){
30:
31: }
32: /** constructor of ACO
33: * @param n 城市数量
34: * @param m 蚂蚁数量
35: * @param g 运行代数
36: * @param a alpha
37: * @param b beta
38: * @param r rho
39: *
40: **/
41: public ACO(int n, int m, int g, float a, float b, float r) {
42: cityNum = n;
43: antNum = m;
44: ants = new Ant[antNum];
45: MAX_GEN = g;
46: alpha = a;
47: beta = b;
48: rho = r;
49:
50: }
51:
52: @SuppressWarnings("resource")
53: /**
54: * 初始化ACO算法类
55: * @param filename 数据文件名,该文件存储所有城市节点坐标数据
56: * @throws IOException
57: */
58: private void init(String filename) throws IOException{
59: //读取数据
60: int[] x;
61: int[] y;
62: String strbuff;
63: BufferedReader data = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(filename)));
64:
65: distance = new int[cityNum][cityNum];
66: x = new int[cityNum];
67: y = new int[cityNum];
68: for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
69: strbuff = data.readLine();
70: String[] strcol = strbuff.split("");
71: x[i] = Integer.valueOf(strcol[1]);
72: y[i] = Integer.valueOf(strcol[2]);
73: }
74: //计算距离矩阵 ,针对具体问题,距离计算方法也不一样,此处用的是att48作为案例,它有48个城市,距离计算方法为伪欧氏距离,最优值为10628
75: for (int i = 0; i < cityNum - 1; i++) {
76: distance[i][i] = 0; //对角线为0
77: for (int j = i + 1; j < cityNum; j++) {
78: double rij = Math.sqrt(((x[i] - x[j]) * (x[i] - x[j])+ (y[i] - y[j]) * (y[i] - y[j]))/10.0);
79: int tij = (int) Math.round(rij);
80: if (tij < rij) {
81: distance[i][j] = tij + 1;
82: distance[j][i] = distance[i][j];
83: }else {
84: distance[i][j] = tij;
85: distance[j][i] = distance[i][j];
86: }
87: }
88: }
89: distance[cityNum - 1][cityNum - 1] = 0;
90:
91: //初始化信息素矩阵
92: pheromone=new float[cityNum][cityNum];
93: for(int i=0;i<cityNum;i++)
94: {
95: for(int j=0;j<cityNum;j++){
96: pheromone[i][j]=0.1f; //初始化为0.1
97: }
98: }
99: bestLength=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
100: bestTour=new int[cityNum+1];
101: //随机放置蚂蚁
102: for(int i=0;i<antNum;i++){
103: ants[i]=new Ant(cityNum);
104: ants[i].init(distance, alpha, beta);
105: }
106: }
107:
108: public void solve(){
109:
110: for (int g = 0; g < MAX_GEN; g++) {
111: for (int i = 0; i < antNum; i++) {
112: for (int j = 1; j < cityNum; j++) {
113: ants[i].selectNextCity(pheromone);
114: }
115: ants[i].getTabu().add(ants[i].getFirstCity());
116: if (ants[i].getTourLength() < bestLength) {
117: bestLength = ants[i].getTourLength();
118: for (int k = 0; k < cityNum + 1; k++) {
119: bestTour[k] = ants[i].getTabu().get(k).intValue();
120: }
121: }
122: for (int j = 0; j < cityNum; j++) {
123: ants[i].getDelta()[ants[i].getTabu().get(j).intValue()][ants[i].getTabu().get(j+1).intValue()] = (float) (1./ants[i].getTourLength());
124: ants[i].getDelta()[ants[i].getTabu().get(j+1).intValue()][ants[i].getTabu().get(j).intValue()] = (float) (1./ants[i].getTourLength());
125: }
126: }
127:
128: //更新信息素
129: updatePheromone();
130:
131: //重新初始化蚂蚁
132: for(int i=0;i<antNum;i++){
133:
134: ants[i].init(distance, alpha, beta);
135: }
136: }
137:
138: //打印最佳结果
139: printOptimal();
140: }
141:
142: //更新信息素
143: private void updatePheromone(){
144: //信息素挥发
145: for(int i=0;i<cityNum;i++)
146: for(int j=0;j<cityNum;j++)
147: pheromone[i][j]=pheromone[i][j]*(1-rho);
148: //信息素更新
149: for(int i=0;i<cityNum;i++){
150: for(int j=0;j<cityNum;j++){
151: for (int k = 0; k < antNum; k++) {
152: pheromone[i][j] += ants[k].getDelta()[i][j];
153: }
154: }
155: }
156: }
157:
158: private void printOptimal(){
159: System.out.println("The optimal length is: " + bestLength);
160: System.out.println("The optimal tour is: ");
161: for (int i = 0; i < cityNum + 1; i++) {
162: System.out.println(bestTour[i]);
163: }
164: }
165:
166: public Ant[] getAnts() {
167: return ants;
168: }
169:
170: public void setAnts(Ant[] ants) {
171: this.ants = ants;
172: }
173:
174: public int getAntNum() {
175: return antNum;
176: }
177:
178: public void setAntNum(int m) {
179: this.antNum = m;
180: }
181:
182: public int getCityNum() {
183: return cityNum;
184: }
185:
186: public void setCityNum(int cityNum) {
187: this.cityNum = cityNum;
188: }
189:
190: public int getMAX_GEN() {
191: return MAX_GEN;
192: }
193:
194: public void setMAX_GEN(int mAX_GEN) {
195: MAX_GEN = mAX_GEN;
196: }
197:
198: public float[][] getPheromone() {
199: return pheromone;
200: }
201:
202: public void setPheromone(float[][] pheromone) {
203: this.pheromone = pheromone;
204: }
205:
206: public int[][] getDistance() {
207: return distance;
208: }
209:
210: public void setDistance(int[][] distance) {
211: this.distance = distance;
212: }
213:
214: public int getBestLength() {
215: return bestLength;
216: }
217:
218: public void setBestLength(int bestLength) {
219: this.bestLength = bestLength;
220: }
221:
222: public int[] getBestTour() {
223: return bestTour;
224: }
225:
226: public void setBestTour(int[] bestTour) {
227: this.bestTour = bestTour;
228: }
229:
230: public float getAlpha() {
231: return alpha;
232: }
233:
234: public void setAlpha(float alpha) {
235: this.alpha = alpha;
236: }
237:
238: public float getBeta() {
239: return beta;
240: }
241:
242: public void setBeta(float beta) {
243: this.beta = beta;
244: }
245:
246: public float getRho() {
247: return rho;
248: }
249:
250: public void setRho(float rho) {
251: this.rho = rho;
252: }
253:
254:
255: /**
256: * @param args
257: * @throws IOException
258: */
259: public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
260: ACO aco = new ACO(48, 100, 1000, 1.f, 5.f, 0.5f);
261: aco.init("c://data.txt");
262: aco.solve();
263: }
264:
265: }
266:
ACO应用进展及发展趋势
应用的进展
自从ACO在一些经典的组合规划问题如TSP和QAP等NP难的组合优化问题上取得成功以来,目前已陆续渗透到许多新的实际的工程领域中。
(1)在各种工程和工业生产中的应用。例如采用ACO的思想来求解大规模集成电路综合布线问题。在布线过程中,各个引脚对蚂蚁的引力可根据引力函数来计算。各个线网agent根据启发策略,像蚁群一样在开关盒网格上爬行,所经之处便布上1条金属线,历经1个线网的所有引脚之后,线网便布通了。
(2) ACO在各种实际规划问题中的应用。例如在机器人路径规划中的应用[6]。机器人作为一种智能体,在复杂工作环境下的路径规划问题、多机器人之间的协作策略问题,在很大程度上类似于蚂蚁觅食优选路径以及蚂蚁群体中个体之间通过信息素形成协作。路径规划算法是实现机器人控制和导航的基础之一,试验证明ACO解决该问题有很大的优越性。
另外,ACO在动态优化组合问题中也有应用,具体是在有向连接的网络路由和无连接网络系统路由中的应用。其他应用还包括蚂蚁人工神经网络、车辆路线问题(Vehicle Routine Prob-lem,VRP)、在图像处理和模式识别领域的应用等等.
存在的问题
蚁群算法的研究成果令人瞩目,但作为一种较新的理论,它依然存在一些问题。
(1)对于大规模组合优化问题,算法的计算时间而且复杂。由于蚁群算法的时间复杂度是,因此在处理较大规模的组合优化问题时,运算量较大,时间较长。
(2)算法容易在某个或某些局部最优解的邻域附近发生停滞现象,造成早熟收敛,即搜索进行到一定程度后,所有蚂蚁发现的解完全一致,不能继续对解空间进一步搜索,不利于发现全局最优解。
(3)不能较好的解决连续域问题。
(4)由于蚁群算法中蚂蚁个体的运动过程的随机性,当群体规模设置较大时,很难在较短时间内从杂乱无章的路径中找出一条较好的路径。
(5)信息素更新策略,路径搜索策略和最优解保留策略都带有经验性,没有经过严格的理论论证。因此基本蚁群算法的求解效率不高、收敛性较差、求解结果具有较大的分散性。
发展趋势
随着蚁群算法在工程实践中应用的深入和系统复杂性的增加,需要处理的数据量也越来越大,这些问题的影响日益突出,使得单纯一到两种智能方法往往不能很好的解决问题。由于蚁群算法易与其他进化算法或者局部搜索算法结合。所以如何根据实际情况融合多种智能方法必将成为今后蚁群算法新的研究热点。目前,蚁群算法的研究大多集中在算法、模型的更新,以及软件的开发上,所处理的数据也都是静态的。硬件的运行速度要高于软件,如何利用硬件的优势,利用DSP,FPGA和PLC等硬件实现蚁群算法,并使它能够应用于实时系统将是以后研究的一个方向。