Huffman编码实现压缩解压缩
这是我们的课程中布置的作业,找一些资料将作业完成,顺便将其写到博客,以后看起来也方便。
原理介绍
什么是Huffman压缩
Huffman( 哈夫曼 ) 算法在上世纪五十年代初提出来了,它是一种无损压缩方法,在压缩过程中不会丢失信息熵,而且可以证明 Huffman 算法在无损压缩算法中是最优的。 Huffman 原理简单,实现起来也不困难,在现在的主流压缩软件得到了广泛的应用。对应用程序、重要资料等绝对不允许信息丢失的压缩场合, Huffman 算法是非常好的选择。
怎么实现Huffman压缩
哈夫曼压缩是个无损的压缩算法,一般用来压缩文本和程序文件。哈夫曼压缩属于可变代码长度算法一族。意思是个体符号(例如,文本文件中的字符)用一个特定长度的位序列替代。因此,在文件中出现频率高的符号,使用短的位序列,而那些很少出现的符号,则用较长的位序列。- Huffman编码生成步骤
- 扫描要压缩的文件,对字符出现的频率进行计算。
- 把字符按出现的频率进行排序,组成一个队列。
- 把出现频率最低(权值)的两个字符作为叶子节点,它们的权值之和为根节点组成一棵树。
- 把上面叶子节点的两个字符从队列中移除,并把它们组成的根节点加入到队列。
- 把队列重新进行排序。重复步骤 3、4、5 直到队列中只有一个节点为止。
- 把这棵树上的根节点定义为 0 (可自行定义 0 或 1 )左边为 0 ,右边为 1 。这样就可以得到每个叶子节点的哈夫曼编码了。
如 (a) 、 (b) 、 (c) 、 (d) 几个图,就可以将离散型的数据转化为树型的了。
如果假设树的左边用0 表示右边用 1 表示,则每一个数可以用一个 01 串表示出来。
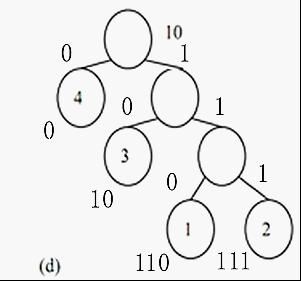
则可以得到对应的编码如下:
1–>110
2–>111
3–>10
4–>0
每一个01 串,既为每一个数字的哈弗曼编码。
- 为什么能压缩
压缩的时候当我们遇到了文本中的1 、 2 、 3 、 4 几个字符的时候,我们不用原来的存储,而是转化为用它们的 01 串来存储不久是能减小了空间占用了吗。(什么 01 串不是比原来的字符还多了吗?怎么减少?)大家应该知道的,计算机中我们存储一个 int 型数据的时候一般式占用了 2^32-1 个 01 位,因为计算机中所有的数据都是最后转化为二进制位去存储的。所以,想想我们的编码不就是只含有 0 和 1 嘛,因此我们就直接将编码按照计算机的存储规则用位的方法写入进去就能实现压缩了。
比如:
1这个数字,用整数写进计算机硬盘去存储,占用了 2^32-1 个二进制位
而如果用它的哈弗曼编码去存储,只有110 三个二进制位。
效果显而易见。
编码实现
- 流程图
编码流程
Created with Raphaël 2.1.0 开始 读入待压缩文件,计算文件中各字符的权重 根据权重构建Huffman树 根据Huffman树获得各个字符的HUffman编码, 并建立Huffman编码的HashTable 将字符总数、字符种数, 以及Huffman树写入压缩文件文件头 再次读入待压缩文件, 根据其内容和coding hash table 将压缩后的数据写入文件 结束
- 数据结构
CharacterWeight:记录字符值,以及其在待压缩文件中的权重。
public class CharacterCode {
private int weight;//字符值
private char character;//字符值
private String code;//其对应huffman编码
} HuffmanNode:huffman树中的节点信息。
public class HuffmanNode {
private int parent;//父节点
private int lChild;//左子
private int rChild;//右子
private int weight;//权重
}- 程序关键步骤
- Huffman树的构建
Huffman树的变量:ArrayList list;
流程图
- Huffman树的构建
Created with Raphaël 2.1.0 开始 i=0 n=字符的种数 循环遍历查找列表中权重最小的两个node 创建一个新的节点作为找到的两个权重最小的节点的父节点, 并将该父节点的权重置为权重最小的两节点的权重和, 将该节点加入数组中。i++ i<n-1 结束 yes no
代码
for(int i=0;i<list.size()-1;i++){
//w1 : the first min weight w2: the second min weight
//i1 : the first min weight index, i2: the second min weight index
int w1 = MAX_VALUE, w2=MAX_VALUE;
int i1 = 0, i2 = 0;
// find the two node with the minimum weight
for(int j=0;j<tree.size();j++){
HuffmanNode node = tree.get(j);
if(node.getWeight()< w1 && node.getParent()==-1){
w2 = w1;
w1 = node.getWeight();
i2 = i1;
i1 = j;
}
else if(node.getWeight()<w2 && node.getParent()==-1){
w2 = node.getWeight();
i2 = j;
}
}
//set the two node to be the children of a new node, and add the new node to the tree
HuffmanNode pNode = new HuffmanNode(w1+w2);
pNode.setlChild(i1);
pNode.setrChild(i2);
tree.add(pNode);
tree.get(i1).setParent(tree.indexOf(pNode));
tree.get(i2).setParent(tree.indexOf(pNode));} - 根据Huffman 树获得Huffman编码
从叶子节点开始网上遍历Huffman树,直到到达根节点,根据当前节点为其父节点的左儿子还是右儿子确定这一位值是0还是1。最后将依次获得的0,1字符串反转获得Huffman编码。
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
HuffmanNode node = tree.get(i);
HuffmanNode pNode = tree.get(node.getParent());
String code ="";
while(true){
if(pNode.getlChild()==tree.indexOf(node)){
code = "0"+code;
}
else if(pNode.getrChild() == tree.indexOf(node)){
code = "1"+code;
}
else {
System.out.println("Tree Node Error!!!");
return null;
}
node=pNode;
if(node.getParent()!=-1)
pNode=tree.get(node.getParent());
else
break;
}
list.get(i).setCode(new String(code));
} 头文件设计
编码 类型 字节数 字符总数 Int 4 字符种类数 Short 2 叶子节点 char字符 short 父节点 3 非叶子节点 Short 左儿子 short 右儿子 short父节点 6 文件头长度(单位: byte)
l= 9n
其中n 为字符种类数。- 文件内容的编码和写入
Created with Raphaël 2.1.0 开始 将待压缩文件读入字符数组 根据coding hash table 获得huffman编码字符串, 并将该字符串添加到buff中 查看buff,如果字符数大于8 则将字符串转换为Short类型变量并写入文件 将写入的字符从buff中删除 是否到达文件尾? 结束 yes no
代码
while((temp=reader.read())!=-1){ //!= EOF
// get the code from the code table
String code = codeTable.get((char)temp);
c++;
if(c>=count/96){
System.out.print("=");
c=0;
}
try{
StringBuilder codeString = new StringBuilder(code);
outputStringBuffer.append(codeString);
while(outputStringBuffer.length()>8){
out.write(Short.parseShort(outputStringBuffer.substring(0, 8),2));
outputStringBuffer.delete(0, 8);
}
} catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
} 解码实现
- 流程图
Created with Raphaël 2.1.0 开始 读压缩文件,读入文件头, 获得字符总数,字符种数以及huffman表信息, 重建huffman树 读入正文, 根据重建得到的huffman树获得原本的字符, 将字符写入解压缩后的文件 是否到达文件尾部? 结束 yes no
- 数据结构
HuffmanNode:huffman树中的节点信息。
public class HuffmanNode {
private int parent;//父节点
private int lChild;//左子
private int rChild;//右子
private int weight;//权重
}程序关键步骤
重建Huffman树。在文件头中存放的原本就是Huffman树的节点信息。
in = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(file)); count = in.readInt(); charNum = in.readShort(); nodeNum = 2*charNum -1; //rebuild the huffman tree for(int i=0;i<charNum;i++){ HuffmanNode node = new HuffmanNode((char)in.readByte()); int parent = in.readShort(); node.setParent(parent); tree.add(node); } for(int i=charNum;i<nodeNum;i++){ HuffmanNode node = new HuffmanNode(' '); int l = in.readShort(); int r = in.readShort(); int p = in.readShort(); node.setlChild(l); node.setrChild(r); node.setParent(p); tree.add(node); }解码
流程图
Created with Raphaël 2.1.0 开始 Buff.length<32 从文件中读入整数 将读入的整数转为二进制字符串,并将其加到buff中 根据buff中的01字符从顶向下遍历huffman树, 得到叶子节点、其对应的解码值,将其写入文件, 从buff中遍历删去已经遍历过的字符 字符数是否达到总数 处理buff中剩余内容 结束 yes no yes no
代码
while(true){
while(buff.length()<32){
temp = in.readInt();
String codeString = Integer.toBinaryString(temp);
while(codeString.length()<32){
codeString='0'+codeString;
}
buff.append(codeString);
}
node = tree.get(tree.size()-1);
dep = 0;
while(!(node.getlChild()==-1&&node.getrChild()==-1)){
if(dep>=buff.length()){
System.out.println( "Buff overflow");
}
if(buff.charAt(dep)=='0'){
node = tree.get(node.getlChild());
}
else if(buff.charAt(dep)=='1'){
node = tree.get(node.getrChild());
}
else{
System.out.println("Coding error");
}
dep++;
}
char c = node.getCH();
num++;
if(num>=n/99){
System.out.print("=");
num=0;
}
count++;
if(count>=n){
break;
}
charBuff+=c;
if(charBuff.length()>256){
writer.write(charBuff);
charBuff="";
}
buff.delete(0, dep);
}
} catch(EOFException e){
//just do nothing
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
//there may be data released in the buff and charbuff, so we need to process them
while(buff.length()>0){
node = tree.get(tree.size()-1);
dep = 0;
while(!(node.getlChild()==-1&&node.getrChild()==-1)){
if(dep>=buff.length()){
break;
}
if(buff.charAt(dep)=='0'){
node = tree.get(node.getlChild());
}
else if(buff.charAt(dep)=='1'){
node = tree.get(node.getrChild());
}
else{
System.out.println("Coding error");
//return;
}
dep++;
}
char c = node.getCH();
num++;
if(num>=n/99){
System.out.print("=");
num=0;
}
count++;
if(count>=n){
break;
}
charBuff+=c;
if(charBuff.length()>256){
try {
writer.write(charBuff);
} catch (IOException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
charBuff="";
}
buff.delete(0, dep);
}
try {
writer.write(charBuff);
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try{
writer.close();
} catch(IOException e){
throw e;
} 项目源码
留坑回头放上
参考文章
http://blog.csdn.net/u010485034/article/details/30750245
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_694448320100nd5v.html