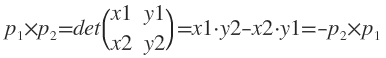HDU 1558 Segment set
A - Segment set
Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u
Description
A segment and all segments which are connected with it compose a segment set. The size of a segment set is the number of segments in it. The problem is to find the size of some segment set.
Input
In the first line there is an integer t - the number of test case. For each test case in first line there is an integer n (n<=1000) - the number of commands.
There are two different commands described in different format shown below:
P x1 y1 x2 y2 - paint a segment whose coordinates of the two endpoints are (x1,y1),(x2,y2).
Q k - query the size of the segment set which contains the k-th segment.
k is between 1 and the number of segments in the moment. There is no segment in the plane at first, so the first command is always a P-command.
There are two different commands described in different format shown below:
P x1 y1 x2 y2 - paint a segment whose coordinates of the two endpoints are (x1,y1),(x2,y2).
Q k - query the size of the segment set which contains the k-th segment.
k is between 1 and the number of segments in the moment. There is no segment in the plane at first, so the first command is always a P-command.
Output
For each Q-command, output the answer. There is a blank line between test cases.
Sample Input
1
10
P 1.00 1.00 4.00 2.00
P 1.00 -2.00 8.00 4.00
Q 1
P 2.00 3.00 3.00 1.00
Q 1
Q 3
P 1.00 4.00 8.00 2.00
Q 2
P 3.00 3.00 6.00 -2.00
Q 5
Sample Output
1
2
2
2
5
并查集的题,加上判断线段相交,可以用数学上向量叉积的方法。
参考大牛的经验后,总结如下
把p0定为原点,p1的坐标是(x1,y1),p2的坐标是(x2,y2)。向量的叉积(cross product)实际上就是矩阵的行列式:
当叉积为正时,说明![]() 在
在![]() 的顺时针方向上;叉积为0说明两向量共线(同向或反向)。
的顺时针方向上;叉积为0说明两向量共线(同向或反向)。
当同时满足:
(1)和![]() 在
在![]() 的两侧(即一个顺时针方向上,一个在逆时针方向上)
的两侧(即一个顺时针方向上,一个在逆时针方向上)
(2)![]() 和
和![]() 在
在![]() 的两侧
的两侧
时可肯定![]() 和
和![]() 相交。
相交。
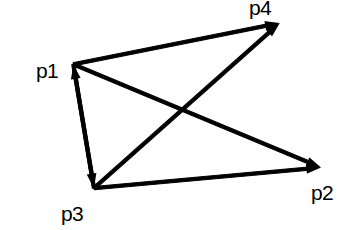
图1
图1是线段相交的一般情形。
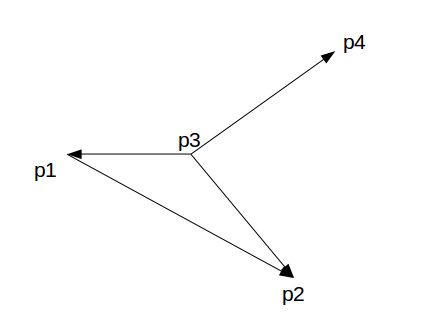
图2只满足第(1)条,不满足第(2)条所以不能证明![]() 和
和![]() 相交。
相交。
图2
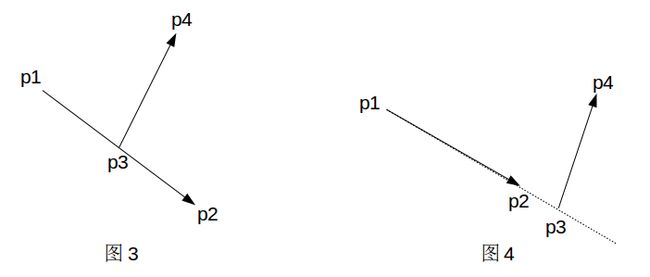
图3和图4是一种特殊情况,它不满足第(2)条,因为![]() 和
和![]() 重合,即
重合,即![]() 和
和![]() 的叉积为0。
的叉积为0。
可见当叉积为0时要分情况讨论,当p3在线段p1p2上时两线段相交;当p3在线段p1p2的延长线上时两线段不相交。
这题其他的就是简单的并查集了。
可以写结构体来记录查询,或者定义点。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef struct{
double x,y;
}Point;
typedef struct{
Point s,e;
}Pquery;
Pquery a[1005];
int fa[1005];
int ans[1005];
int Find(int x) {
return fa[x] == x ? x : fa[x] = Find(fa[x]) ;
}
bool Merge(int u ,int v) {
int fu = Find(u) , fv = Find(v) ;
if(fu != fv)
{
fa[fv] = fu ;
ans[fu]+=ans[fv];
}
return fu != fv ;
}
double mult(Point a, Point b, Point c)
{
return (a.x-c.x)*(b.y-c.y)-(b.x-c.x)*(a.y-c.y);
}
bool IsCross(Point aa, Point bb, Point cc, Point dd)
{
if ( max(aa.x, bb.x)<min(cc.x, dd.x) )
return false;
if ( max(aa.y, bb.y)<min(cc.y, dd.y) )
return false;
if ( max(cc.x, dd.x)<min(aa.x, bb.x) )
return false;
if ( max(cc.y, dd.y)<min(aa.y, bb.y) )
return false;
if ( mult(cc, bb, aa)*mult(bb, dd, aa)<0 )
return false;
if ( mult(aa, dd, cc)*mult(dd, bb, cc)<0 )
return false;
return true;
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
fa[i] = i;
ans[i]=1;
}
int i=0;
while(n--)
{
char type[5];
scanf("%s",type);
if(type[0]=='P')
{
i++;
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&a[i].s.x,&a[i].s.y,&a[i].e.x,&a[i].e.y);
for(int j=1;j<i;j++)
{
if(Find(i)!=Find(j)&&IsCross(a[i].s,a[i].e,a[j].s,a[j].e))
Merge(i,j);
}
}
else
{
int key;
scanf("%d",&key);
printf("%d\n",ans[Find(key)]);
}
}
if(t!=0)
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}