【POJ 1765】 November Rain(离散化+扫描线)
【POJ 1765】 November Rain(离散化+扫描线)
| Time Limit: 5000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 2193 | Accepted: 472 | |
| Case Time Limit: 2000MS | ||
Description
Contemporary buildings can have very complicated roofs. If we take a vertical section of such a roof it results in a number of sloping segments. When it is raining the drops are falling down on the roof straight from the sky above. Some segments are completely exposed to the rain but there may be some segments partially or even completely shielded by other segments. All the water falling onto a segment as a stream straight down from the lower end of the segment on the ground or possibly onto some other segment. In particular, if a stream of water is falling on an end of a segment then we consider it to be collected by this segment.
For the purpose of designing a piping system it is desired to compute how much water is down from each segment of the roof. To be prepared for a heavy November rain you should count one liter of rain water falling on a meter of the horizontal plane during one second.
Task
Write a program that:
reads the description of a roof,
computes the amount of water down in one second from each segment of the roof,
writes the results.

For the purpose of designing a piping system it is desired to compute how much water is down from each segment of the roof. To be prepared for a heavy November rain you should count one liter of rain water falling on a meter of the horizontal plane during one second.
Task
Write a program that:
reads the description of a roof,
computes the amount of water down in one second from each segment of the roof,
writes the results.
Input
The first line of the input contains one integer n (1 <= n < = 40000) being the number of segments of the roof. Each of the next n lines describes one segment of the roof and contains four integers x1, y1, x2, y2 (0 <= x1, y1, x2, y2 < = 1000000, x1 < x2, y1<>y2) separated by single spaces. Integers x1, y1 are respectively the horizontal position and the height of the left end of the segment. Integers x2, y2 are respectively the horizontal position and the height of the right end of the segment. The segments don't have common points and there are no horizontal segments. You can also assume that there are at most 25 segments placed above any point on the ground level.
Output
The output consists of n lines. The i-th line should contain the amount of water (in liters) down from the i-th segment of the roof in one second.
Sample Input
6 13 7 15 6 3 8 7 7 1 7 5 6 5 5 9 3 6 3 8 2 9 6 12 8
Sample Output
2 4 2 11 0 3
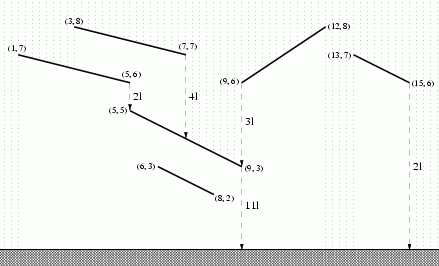
题目大意:有n个屋檐 求积水量
积水量是指横向累计的水流长度(水流在该屋檐上覆盖的横坐标长度)
对于每个屋檐,还要累计上它上面的屋檐流下来的水量。
样例挺友好的,看样例看图应该就能明白
至于写法,我没用线段树维护。
先不考虑上面流下来的水量,从左往右,每当到一个新的横坐标,前一个横坐标到当前累计的水量会统计到当前位置最高的屋檐上。
题目中说同一个横坐标最多25个屋檐,那么就暴力啊……
对于流下来的水。在刚才跑的过程中,建立拓扑图,随便什么方法,建出来就好
然后从最上面流下来就好。。
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define LL long long
#define Pr pair<int,int>
#define fread() freopen("in.in","r",stdin)
#define fwrite() freopen("out.out","w",stdout)
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int msz = 10000;
const int mod = 1e9+7;
const double eps = 1e-8;
struct Point
{
LL x,y,id;
bool ad;
bool operator <(const struct Point a)const
{
return x == a.x? ad == a.ad? ad == 1? y < a.y: y > a.y: ad > a.ad: x < a.x;
}
};
int tmp[233];
bool vis[233];
Point pt[88888];
Point ptc[88888];
int down[88888];
int up[88888];
LL ans[44444];
int tp;
double cal(int pos,LL x)
{
pos <<= 1;
return (pt[pos+1].y-pt[pos].y)*(x-pt[pos].x)*1.0/(pt[pos+1].x-pt[pos].x)+pt[pos].y;
}
int main()
{
//fread();
//fwrite();
int n;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
int tpp = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
scanf("%lld%lld",&pt[tpp].x,&pt[tpp].y);
pt[tpp].id = i;
pt[tpp].ad = 1;
ptc[tpp] = pt[tpp];
tpp++;
scanf("%lld%lld",&pt[tpp].x,&pt[tpp].y);
pt[tpp].id = i;
pt[tpp].ad = 0;
ptc[tpp] = pt[tpp];
tpp++;
}
sort(ptc,ptc+tpp);
memset(ans,0,sizeof(ans));
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
memset(down,-1,sizeof(down));
memset(up,0,sizeof(up));
tp = 0;
int j,mx;
for(int i = 0; i < tpp; ++i)
{
//printf("------Step:%d x:%d y:%d---------\n",i,ptc[i].x,ptc[i].y);
int id = ptc[i].id;
if(i != 0 && ptc[i].x != ptc[i-1].x)
{
mx = -1;
for(j = 0; j < tp; ++j)
{
if(!vis[j]) continue;
if(mx == -1 || cal(tmp[j],ptc[i].x) > cal(mx,ptc[i].x)) mx = tmp[j];
}
//printf("mx:%d\n",mx);
//printf("%d-%d %d-%d\n",pt[mx<<1].x,pt[mx<<1].y,pt[mx<<1|1].x,pt[mx<<1|1].y);
if(mx != -1) ans[mx] += ptc[i].x-ptc[i-1].x;
}
mx = -1;
if(ptc[i].ad)
{
if(pt[id<<1].y < pt[id<<1|1].y)
{
for(j = 0; j < tp; ++j)
{
if(!vis[j]) continue;
//printf("cmp:%f %d\n",cal(tmp[j],ptc[i].x),ptc[i].y);
if(cal(tmp[j],ptc[i].x) < ptc[i].y*1.0 && (mx == -1 || cal(tmp[j],ptc[i].x) > cal(mx,ptc[i].x))) mx = tmp[j];
}
if(mx != -1)
{
//printf("!!!!!!!!!get:%d\n",mx);
down[id] = mx;
up[mx]++;
}
}
for(j = 0; j < tp; ++j)
if(!vis[j]) break;
if(j == tp) tmp[tp++] = id;
else tmp[j] = id;
vis[j] = 1;
}
else
{
for(j = 0; j < tp; ++j)
if(vis[j] && tmp[j] == id) break;
if(j == tp) --tp;
vis[j] = 0;
if(pt[id<<1].y > pt[id<<1|1].y)
{
for(j = 0; j < tp; ++j)
{
if(!vis[j]) continue;
//printf("cmp:%f %d\n",cal(tmp[j],ptc[i].x),ptc[i].y);
if(cal(tmp[j],ptc[i].x) < ptc[i].y*1.0 && (mx == -1 || cal(tmp[j],ptc[i].x) > cal(mx,ptc[i].x))) mx = tmp[j];
}
if(mx != -1)
{
//printf("!!!!!!!!!get:%d\n",mx);
down[id] = mx;
up[mx]++;
}
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
if(!up[i])
{
//printf("ID:%d\n",i);
int id = i;
LL ad = ans[i];
while(down[id] != -1)
{
ans[down[id]] += ad;
up[down[id]]--;
if(up[down[id]] > 0)
{
break;
}else up[down[id]]--;
ad = ans[down[id]];
id = down[id];
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
printf("%lld\n",ans[i]);
}
return 0;
}