Core Java (四) Java文件操作
下面介绍几个在OCJP中要求的io中的类的使用:
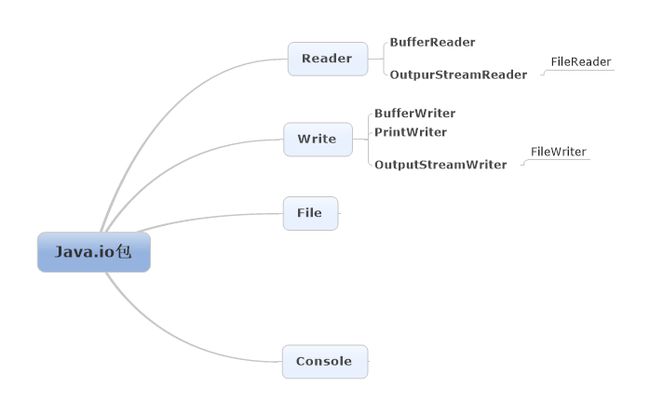
java.io:
BufferedReader, BufferedWriter, File, FileReader, FileWriter, PrintWriter, and Console.
OCJP要求的几个文件操作类的层次关系:
左边的类是右边类的supercalss
PrintWriter类
pw.printf();
pw.write();等
测试程序,实现将in.txt中的数据一行一行复制到file.txt中,并添加了一些内容。:
package cn.xujin;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
Scanner in = new Scanner(new File("G:\\in.txt"));
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new File("G:\\file.txt"));
String name = "GinSmile";
pw.write(name);//把字符串添加到文件末尾
pw.append('w');//直接把字符添加到文件末尾
pw.println();//仅仅打印一个换行符
while(in.hasNext()){
String s = in.nextLine();
pw.println(s);
}
pw.println();
pw.printf("%x", 100);
pw.println();
char[] buf = {'a','b','c','d','e','f'};
pw.write(buf, 0, 4);//把字符数组的一部分添加到文件末尾
pw.close();
}
}
PrintWriter类实现写入操作,write(),与print()两个函数意义相同,最后一定要记得close()这个函数。
close()在JDK的doc中是这样解释的:
-
Closes the stream and releases any system resources associated with it.
注意:可能出现找不到文件的情况,所以要在main上有throws子句标记。
BufferedReader, BufferedWriter, File,FileReader,FIleWriter
BufferedReader
创建一个BufferedReader 类型的对象:
| Constructor and Description |
|---|
BufferedReader(Reader in)
Creates a buffering character-input stream that uses a default-sized input buffer.
|
BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz)
Creates a buffering character-input stream that uses an input buffer of the specified size.
|
例如:BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
FileReader类继承自Reader类,所以用它可以。
重要的函数:
int |
read()
Reads a single character.
|
int |
read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
Reads characters into a portion of an array.
|
String |
readLine()
Reads a line of text.
|
BufferedWriter
创建一个BufferedWriter 类型的对象:
BufferedWriter(Writer out)
Creates a buffered character-output stream that uses a default-sized output buffer.
|
BufferedWriter(Writer out, int sz)
Creates a new buffered character-output stream that uses an output buffer of the given size.
|
FileWriter类继承自Writer类。
全部函数:
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
void |
close()
Closes the stream, flushing it first.
|
void |
flush()
Flushes the stream.
|
void |
newLine()
Writes a line separator.
|
void |
write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
Writes a portion of an array of characters.
|
void |
write(int c)
Writes a single character.
|
void |
write(String s, int off, int len)
Writes a portion of a String.
|
File
创建一个File 类型的对象:
| Constructor and Description |
|---|
File(File parent, String child)
Creates a new
File instance from a parent abstract pathname and a child pathname string.
|
File(String pathname)
Creates a new
File instance by converting the given pathname string into an abstract pathname.
|
File(String parent, String child)
Creates a new
File instance from a parent pathname string and a child pathname string.
|
File(URI uri)
Creates a new File instance by converting the given file: URI into an abstract pathname.
|
FileReader
构造函数:
| Constructor and Description |
|---|
FileReader(File file)
Creates a new FileReader, given the File to read from.
|
FileReader(FileDescriptor fd)
Creates a new FileReader, given the FileDescriptor to read from.
|
FileReader(String fileName)
Creates a new FileReader, given the name of the file to read from.
|
FileWriter
构造函数:
| Constructor and Description |
|---|
FileWriter(File file)
Constructs a FileWriter object given a File object.
|
FileWriter(File file, boolean append)
Constructs a FileWriter object given a File object.
|
FileWriter(FileDescriptor fd)
Constructs a FileWriter object associated with a file descriptor.
|
FileWriter(String fileName)
Constructs a FileWriter object given a file name.
|
FileWriter(String fileName, boolean append)
Constructs a FileWriter object given a file name with a boolean indicating whether or not to append the data written.
|
测试程序,从一个文件in.txt中读取数据,再把数据写入到file.txt中:
package cn.xujin;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
File file = new File("G:\\in.txt");
String s;
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
try {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("G:\\file.txt"));
while((s = br.readLine())!= null){
bw.write(s);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
bw.write("GinSmile");
bw.newLine();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Console
这个类用来和控制台打交道,
创建一个Console变量:Console cons = System.console();
读取一个字符串:String username = cons.readLine("%s", "User name:");就是输出一个User name: 在之后输入的内容(String类型)将存到username里面。
读取一个密码:char[] passwd = cons.readPassword("%s", "Password:");就是输出一个Password: 在之后输入的内容(char[]类型)将存到passwd里面。
输出:
public Console printf(String format,
Object... args) 这个方法和c语言一样,和System.out.printf也一样,就是把内容送到输出流。
测试程序,读入用户名和密码,并显示出来,在读密码的时候不会在屏幕上显示。
package cn.xujin;
import java.io.Console;
public class TestConsole {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Console cons;
char[] passwd = null;
String username = null;
if((cons = System.console()) != null &&
(username = cons.readLine("%s", "User name:")) != null &&
(passwd = cons.readPassword("%s", "Password:")) != null)
{
System.out.println("User name:" + username);
String password = new String(passwd);
System.out.println("Password:" + password);
}
else System.out.println("The console is unavailable ");
}
}
结果:

创建一个BufferedWriter 类型的对象:
BufferedWriter(Writer out)
Creates a buffered character-output stream that uses a default-sized output buffer.
|
BufferedWriter(Writer out, int sz)
Creates a new buffered character-output stream that uses an output buffer of the given size.
|
FileWriter类继承自Writer类。