android之Http协议编程01
今天,我来粗略的讲解下Http协议,并实现,以Android为客服端,Web为服务端,在Android上读取Web服务上一段简单的字符串。
Http协议是应用层端的协议,Http的英文名称为HyperText Transfer Protocol,意思就是超为文本传输协议。Http可以通过传输层的Tcp协议在客服端和服务端进行数据的传输。它在Java Web开发运用上最为常见。在以Jsp/Servelet的Java Web开发中,我们在Jsp界面数据和Servelet数据传输采用的就是这种http协议编程,使用三大框架进行J2EE开发过程中,在Jsp界面和ActionServelet中的数据传输也是采用的Http协议编程的。
我们平时做的web项目,当我们部署到tomcat服务器上,这时我们一般都是在浏览器输入我们要访问的地址(URL(Uniform Resource Locator统一资源定位符),这个请读者自己参考相关知识,了解URL各部分的相关含义),浏览器得到这个地址后,会把这个地址发送到DNS进行域名解析,解析成其相对应的ip地址,然后由ip地址就可以连接到相对应的地方,当然其底层是通过Tcp/Ip协议的,当两者建立连接时,我们在两者之间可以采用流的方式在两者之间进行数据的传输。
在Java(android)中进行Http编程,我们一般有两种方式:
1. 标准的Java接口(path->URL->HttpConnection->inputStream)。
2. 采用Apache接口来实现两者之间的通信(这个下次介绍,这里先采用第一种方法);
当然,还可以采用主拼Http协议的编程来实现,就是利用某些工具得到http协议中请求体的信息和回复体的信息,然后我们主拼这段信息来实现,当然这个实现起来很麻烦,也很容易出错,一般都不建议。
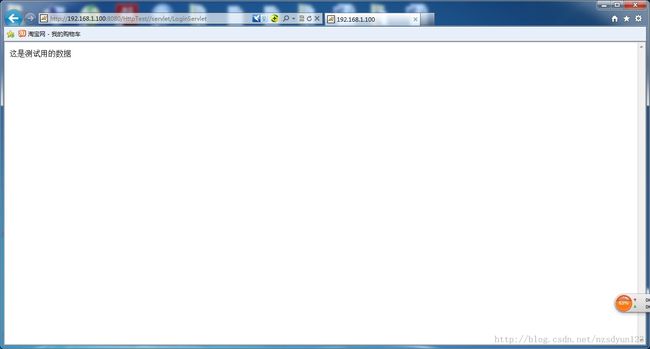
现在,我们要首先在MyElipse中建立一个web项目,并将其部署到Tomcat服务器中,其通过URL(http://192.168.1.100:8080/HttpTest//servlet/LoginServlet)访问后的效果图如下。
图 1
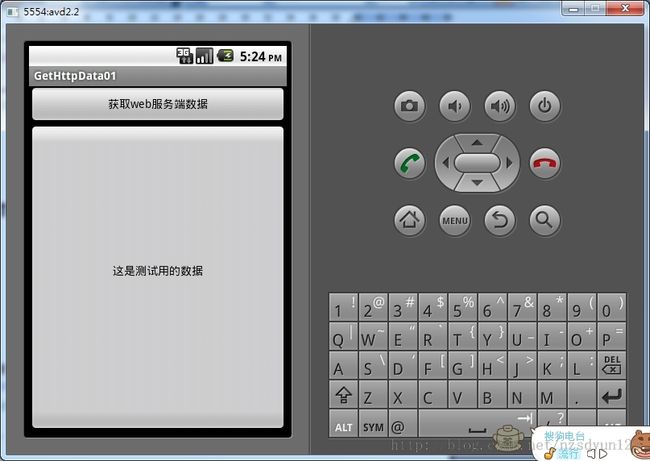
然后我们要在elipse中建立一个Android项目,其运行后的截图如下
图2
我们要做的就是把图1上的数据‘这时测试用的数据’显示在图2上,这也就达到了在android中获取服务端的数据。
现在贴出代码:
MyElipse的Web项目的部分代码,因为我们只是简单的加条数据,所以只需再Servelet中加入如下代码即可
Servelet代码:
package com.kun.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
importjavax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class LoginServlet extendsHttpServlet {
/**
* The doGet method of the servlet. <br>
*
* This method is called when a form has itstag value method equals to get.
*
* @param request the request send by theclient to the server
* @param response the response send by theserver to the client
* @throws ServletException if an erroroccurred
* @throws IOException if an error occurred
*/
publicvoid doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throwsServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(request,response);
}
/**
* The doPost method of the servlet. <br>
*
* This method is called when a form has itstag value method equals to post.
*
* @param request the request send by theclient to the server
* @param response the response send by theserver to the client
* @throws ServletException if an erroroccurred
* @throws IOException if an error occurred
*/
publicvoid doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throwsServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriterout = response.getWriter();
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
out.println("这是测试用的数据");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}
Elipse中的Android项目代码:
布局文件:main.xml
<?xml version="1.0"encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:text="@string/button_name"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:id="@+id/textView"
/>
</LinearLayout>
主Activity:
package com.kun.gethttp01;
import com.kun.http.HttpUtils;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class GetHttpData01Activity extendsActivity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
Buttonbutton = null;
TextViewtextView = null;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
button = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button);
textView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView);
button.setOnClickListener(new CliclListener());
}
private class CliclListener implements OnClickListener{
@Override
publicvoid onClick(View v) {
Stringpath = "http://192.168.1.100:8080/HttpTest/servlet/LoginServlet";
Stringmsg = HttpUtils.getHttpData(path);
System.out.println(msg);
textView.setText(msg);
}
}
}
HttpUtils代码,将Http操作封装到这个类中,我们最关键的也是这个类:
package com.kun.http;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
publicclass HttpUtils {
/**
* 通过Http协议获取服务端的数据
* @param path 路径
* @return字符串
*/
publicstatic String getHttpData(String path){
String msg = "";
try {
//由地址栏输入的地址生成URL对象
URL url = new URL(path);
//JDK为我们提供的Http协议编程的所封装好的类,我们只需设置几个方法属性就可以进行连接到服务端了
HttpURLConnection connection =(HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection();
//设置连接超时时间,这里5s没有反应就会断开和服务的器的连接请求
System.out.println("444444444444444444444444444");
connection.setConnectTimeout(5000);
//设置这个属性,表示是允许从服务端获取数据
connection.setDoInput(true);
//以GET的方式获取数据
connection.setRequestMethod("GET");
System.out.println("33333333333333333333333");
//服务端返回的结果码
int responseCode = connection.getResponseCode();
System.out.println(responseCode);
if(responseCode==200){//表示连接成功
msg = changeInputStream(connection.getInputStream());//得到输入流,并通过自己写的changeInputStream方法转化成String
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("出错啦");
}
return msg;
}
/**
* 讲输入流转化成字符串
* @param inputStream 输入流
* @return字符串
*/
privatestatic String changeInputStream(InputStream inputStream) {
System.out.println("22222222222222222222222");
//字节数组输出流,可以再内存中缓存一些数据
ByteArrayOutputStream arrayOutputStream = newByteArrayOutputStream();
//下面几行的意思是把输入流的数据读出,并写入到ByteArrayOutputStream中
byte[] data = newbyte[1024];
int len = 0;
try {
while((len = inputStream.read(data))!=-1){
arrayOutputStream.write(data, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generatedcatch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
returnnew String(arrayOutputStream.toByteArray());//讲输出流中的数据转化成String返回
}
}
最后我们需要在清单文件中加入访问网络的权限:
<!-- 添加网络访问权限 -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
最后运行效果图:
Ps:上述文件我们只是简单的http协议编程,在实际开发过程中,我们一般不这么做,因为访问网络获取其中的数据是一件耗时的工作,所以我们一般是采用多线程的方式来做,所以我们下次讲解以多线程的方式获取服务端的数据。