使用POI读写word docx文件
来自:http://haohaoxuexi.iteye.com/blog/2049110
POI在读写word docx文件时是通过xwpf模块来进行的,其核心是XWPFDocument。一个XWPFDocument代表一个docx文档,其可以用来读docx文档,也可以用来写docx文档。XWPFDocument中主要包含下面这几种对象:
XWPFParagraph:代表一个段落。
XWPFRun:代表具有相同属性的一段文本。
XWPFTable:代表一个表格。
XWPFTableRow:表格的一行。
XWPFTableCell:表格对应的一个单元格。
1 读docx文件
跟读doc文件一样,POI在读docx文件的时候也有两种方式,通过XWPFWordExtractor和通过XWPFDocument。在XWPFWordExtractor读取信息时其内部还是通过XWPFDocument来获取的。
1.1 通过XWPFWordExtractor读
在使用XWPFWordExtractor读取docx文档的内容时,我们只能获取到其文本,而不能获取到其文本对应的属性值。下面是一段使用XWPFWordExtractor来读取docx文档内容的示例代码:
public class XwpfTest {
/**
* 通过XWPFWordExtractor访问XWPFDocument的内容
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testReadByExtractor() throws Exception {
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("D:\\test.docx");
XWPFDocument doc = new XWPFDocument(is);
XWPFWordExtractor extractor = new XWPFWordExtractor(doc);
String text = extractor.getText();
System.out.println(text);
CoreProperties coreProps = extractor.getCoreProperties();
this.printCoreProperties(coreProps);
this.close(is);
}
/**
* 输出CoreProperties信息
* @param coreProps
*/
private void printCoreProperties(CoreProperties coreProps) {
System.out.println(coreProps.getCategory()); //分类
System.out.println(coreProps.getCreator()); //创建者
System.out.println(coreProps.getCreated()); //创建时间
System.out.println(coreProps.getTitle()); //标题
}
/**
* 关闭输入流
* @param is
*/
private void close(InputStream is) {
if (is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
1.2 通过XWPFDocument读
在通过XWPFDocument读取docx文档时,我们就可以获取到文本比较精确的属性信息了。比如我们可以获取到某一个XWPFParagraph、XWPFRun或者是某一个XWPFTable,包括它们对应的属性信息。下面是一个使用XWPFDocument读取docx文档的示例:
public class XwpfTest {
/**
* 通过XWPFDocument对内容进行访问。对于XWPF文档而言,用这种方式进行读操作更佳。
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testReadByDoc() throws Exception {
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("D:\\table.docx");
XWPFDocument doc = new XWPFDocument(is);
List<XWPFParagraph> paras = doc.getParagraphs();
for (XWPFParagraph para : paras) {
//当前段落的属性
// CTPPr pr = para.getCTP().getPPr();
System.out.println(para.getText());
}
//获取文档中所有的表格
List<XWPFTable> tables = doc.getTables();
List<XWPFTableRow> rows;
List<XWPFTableCell> cells;
for (XWPFTable table : tables) {
//表格属性
// CTTblPr pr = table.getCTTbl().getTblPr();
//获取表格对应的行
rows = table.getRows();
for (XWPFTableRow row : rows) {
//获取行对应的单元格
cells = row.getTableCells();
for (XWPFTableCell cell : cells) {
System.out.println(cell.getText());;
}
}
}
this.close(is);
}
/**
* 关闭输入流
* @param is
*/
private void close(InputStream is) {
if (is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2 写docx文件
2.1 直接通过XWPFDocument生成
在使用XWPFDocument写docx文件时不需要像使用HWPFDocument写doc文件那样必须从一个doc文件开始,我们可以直接new一个空的XWPFDocument,之后再往这个XWPFDocument里面填充内容,然后再把它写入到对应的输出流中。下面是使用XWPFDocument生成docx文件的示例代码:
public class XwpfTest {
/**
* 基本的写操作
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testSimpleWrite() throws Exception {
//新建一个文档
XWPFDocument doc = new XWPFDocument();
//创建一个段落
XWPFParagraph para = doc.createParagraph();
//一个XWPFRun代表具有相同属性的一个区域。
XWPFRun run = para.createRun();
run.setBold(true); //加粗
run.setText("加粗的内容");
run = para.createRun();
run.setColor("FF0000");
run.setText("红色的字。");
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("D:\\simpleWrite.docx");
//把doc输出到输出流
doc.write(os);
this.close(os);
}
/***
* 写一个表格
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testWriteTable() throws Exception {
XWPFDocument doc = new XWPFDocument();
//创建一个5行5列的表格
XWPFTable table = doc.createTable(5, 5);
//这里增加的列原本初始化创建的那5行在通过getTableCells()方法获取时获取不到,但通过row新增的就可以。
// table.addNewCol(); //给表格增加一列,变成6列
table.createRow(); //给表格新增一行,变成6行
List<XWPFTableRow> rows = table.getRows();
//表格属性
CTTblPr tablePr = table.getCTTbl().addNewTblPr();
//表格宽度
CTTblWidth width = tablePr.addNewTblW();
width.setW(BigInteger.valueOf(8000));
XWPFTableRow row;
List<XWPFTableCell> cells;
XWPFTableCell cell;
int rowSize = rows.size();
int cellSize;
for (int i=0; i<rowSize; i++) {
row = rows.get(i);
//新增单元格
row.addNewTableCell();
//设置行的高度
row.setHeight(500);
//行属性
// CTTrPr rowPr = row.getCtRow().addNewTrPr();
//这种方式是可以获取到新增的cell的。
// List<CTTc> list = row.getCtRow().getTcList();
cells = row.getTableCells();
cellSize = cells.size();
for (int j=0; j<cellSize; j++) {
cell = cells.get(j);
if ((i+j)%2==0) {
//设置单元格的颜色
cell.setColor("ff0000"); //红色
} else {
cell.setColor("0000ff"); //蓝色
}
//单元格属性
CTTcPr cellPr = cell.getCTTc().addNewTcPr();
cellPr.addNewVAlign().setVal(STVerticalJc.CENTER);
if (j == 3) {
//设置宽度
cellPr.addNewTcW().setW(BigInteger.valueOf(3000));
}
cell.setText(i + ", " + j);
}
}
//文件不存在时会自动创建
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("D:\\table.docx");
//写入文件
doc.write(os);
this.close(os);
}
/**
* 关闭输出流
* @param os
*/
private void close(OutputStream os) {
if (os != null) {
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.2 以docx文件作为模板
当然,我们也可以像写doc文件那样,先以一个docx文件作为模板,然后建立基于该docx文件的XWPFDocument对象,再把里面一些变化的信息在运行时进行替换,之后将XWPFDocument进行输出就可以了。所不同的是XWPFDocument中没有像HWPFDocument中那样的Range可以用来直接替换内容。而且底层的XWPFParagraph和XWPFRun也不支持直接将文本进行替换。倒是XWPFRun提供了一个设置文本的方法,不过新的文本不会替换旧的文本,而是会追加到原来的文本之后。现在的一个做法是先找出含有需要替换的变量的XWPFRun,然后将其移除,之后在原来的位置新增一个XWPFRun,其对应的文本是替换变量之后的文本。不过你设置的那个的变量的位置不一定就在一个XWPFRun里面,它有可能会被拆分到两个甚至更多的XWPFRun中,所以不是很有必要的话还是不推荐使用这种方式。
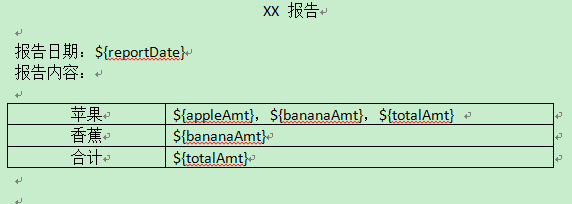
假设我们有一个docx文件,其内容是这样的:
之后我们以该文件作为模板,利用相关数据把里面的变量进行替换,然后把替换后的文档输出到另一个docx文件中。具体做法如下:
public class XwpfTest {
/**
* 用一个docx文档作为模板,然后替换其中的内容,再写入目标文档中。
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testTemplateWrite() throws Exception {
Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<String, Object>();
params.put("reportDate", "2014-02-28");
params.put("appleAmt", "100.00");
params.put("bananaAmt", "200.00");
params.put("totalAmt", "300.00");
String filePath = "D:\\word\\template.docx";
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(filePath);
XWPFDocument doc = new XWPFDocument(is);
//替换段落里面的变量
this.replaceInPara(doc, params);
//替换表格里面的变量
this.replaceInTable(doc, params);
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("D:\\word\\write.docx");
doc.write(os);
this.close(os);
this.close(is);
}
/**
* 替换段落里面的变量
* @param doc 要替换的文档
* @param params 参数
*/
private void replaceInPara(XWPFDocument doc, Map<String, Object> params) {
Iterator<XWPFParagraph> iterator = doc.getParagraphsIterator();
XWPFParagraph para;
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
para = iterator.next();
this.replaceInPara(para, params);
}
}
/**
* 替换段落里面的变量
* @param para 要替换的段落
* @param params 参数
*/
private void replaceInPara(XWPFParagraph para, Map<String, Object> params) {
List<XWPFRun> runs;
Matcher matcher;
if (this.matcher(para.getParagraphText()).find()) {
runs = para.getRuns();
for (int i=0; i<runs.size(); i++) {
XWPFRun run = runs.get(i);
String runText = run.toString();
matcher = this.matcher(runText);
if (matcher.find()) {
while ((matcher = this.matcher(runText)).find()) {
runText = matcher.replaceFirst(String.valueOf(params.get(matcher.group(1))));
}
//直接调用XWPFRun的setText()方法设置文本时,在底层会重新创建一个XWPFRun,把文本附加在当前文本后面,
//所以我们不能直接设值,需要先删除当前run,然后再自己手动插入一个新的run。
para.removeRun(i);
para.insertNewRun(i).setText(runText);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 替换表格里面的变量
* @param doc 要替换的文档
* @param params 参数
*/
private void replaceInTable(XWPFDocument doc, Map<String, Object> params) {
Iterator<XWPFTable> iterator = doc.getTablesIterator();
XWPFTable table;
List<XWPFTableRow> rows;
List<XWPFTableCell> cells;
List<XWPFParagraph> paras;
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
table = iterator.next();
rows = table.getRows();
for (XWPFTableRow row : rows) {
cells = row.getTableCells();
for (XWPFTableCell cell : cells) {
paras = cell.getParagraphs();
for (XWPFParagraph para : paras) {
this.replaceInPara(para, params);
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 正则匹配字符串
* @param str
* @return
*/
private Matcher matcher(String str) {
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("\\$\\{(.+?)\\}", Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(str);
return matcher;
}
/**
* 关闭输入流
* @param is
*/
private void close(InputStream is) {
if (is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 关闭输出流
* @param os
*/
private void close(OutputStream os) {
if (os != null) {
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
经过上面的代码所示的过程处理后,我们替换变量后新输出来的docx文件的内容是这样的: