java NIO-Channel
基本简介
Java NIO(New IO)是一个可以替代标准Java IO API的IO API(从Java 1.4开始),Java NIO提供了与标准IO不同的IO工作方式。
Java NIO: Channels and Buffers(通道和缓冲区)
标准的IO基于字节流和字符流进行操作的,而NIO是基于通道(Channel)和缓冲区(Buffer)进行操作,数据总是从通道读取到缓冲区中,或者从缓冲区写入到通道中。
Java NIO: Non-blocking IO(非阻塞IO)
Java NIO可以让你非阻塞的使用IO,例如:当线程从通道读取数据到缓冲区时,线程还是可以进行其他事情。当数据被写入到缓冲区时,线程可以继续处理它。从缓冲区写入通道也类似。
Java NIO: Selectors(选择器)
Java NIO引入了选择器的概念,选择器用于监听多个通道的事件(比如:连接打开,数据到达)。因此,单个的线程可以监听多个数据通道。
Channel
Java NIO的通道类似流,但又有些不同:
- 既可以从通道中读取数据,又可以写数据到通道。但流的读写通常是单向的。
- 通道可以异步地读写。
- 通道中的数据总是要先读到一个Buffer,或者总是要从一个Buffer中写入。
正如上面所说,从通道读取数据到缓冲区,从缓冲区写入数据到通道。如下图所示:
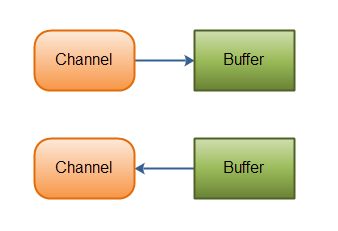
Channel的实现
- 通道表示到实体,如硬件设备、文件、网络套接字或可以执行一个或多个不同 I/O 操作(如读取或写入)的程序组件的开放的连接。
- 通道可处于打开或关闭状态。创建通道时它处于打开状态,一旦将其关闭,则保持关闭状态。一旦关闭了某个通道,试图对其调用 I/O 操作就会导致 ClosedChannelException 被抛出。通过调用通道的 isOpen 方法可测试通道是否处于打开状态。
void close();关闭此通道。
booleanisOpen(); 判断此通道是否处于打开状态这些是Java NIO中最重要的通道的实现:
- FileChannel
- DatagramChannel
- SocketChannel
- ServerSocketChannel
1:FileChannel
- 用于读取、写入、映射和操作文件的通道。
- 文件通道在其文件中有一个当前 position,可对其进行查询和修改。该文件本身包含一个可读写的长度可变的字节序列,并且可以查询该文件的当前大小。写入的字节超出文件的当前大小时,则增加文件的大小;截取 该文件时,则减小文件的大小。文件可能还有某个相关联的元数据,如访问权限、内容类型和最后的修改时间;此类未定义访问元数据的方法。
- 以不影响通道当前位置的方式,对文件中绝对位置的字节进行读取或写入。
- 将文件中的某个区域直接映射到内存中;对于较大的文件,这通常比调用普通的 read 或 write 方法更为高效。
- 强制对底层存储设备进行文件的更新,确保在系统崩溃时不丢失数据。
- 以一种可被很多操作系统优化为直接向文件系统缓存发送或从中读取的高速传输方法,将字节从文件传输到某个其他通道中,反之亦然。
- 可以锁定某个文件区域,以阻止其他程序对其进行访问。
此类没有定义打开现有文件或创建新文件的方法,以后的版本中可能添加这些方法。在此版本中,可从现有的 FileInputStream、FileOutputStream 或 RandomAccessFile 对象获得文件通道,方法是调用该对象的 getChannel 方法,这会返回一个连接到相同底层文件的文件通道。
实例:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class FileChannelTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
File inPut=new File("filechannel.txt");
File outPut=new File("filechannel.txt");
if(!inPut.exists())
{
inPut.createNewFile();
}
if(!outPut.exists())
{
outPut.createNewFile();
}
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(inPut);
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(outPut);
FileChannel inputChannel=fis.getChannel();
FileChannel outputChannel=fos.getChannel();
String testdata="You can combine streams into chains to achieve "
+ "more advanced input and output operations. For instance, "
+ "reading every byte one at a time from a file is slow. It is faster "
+ "to read a larger block of data from the disk and then iterate through "
+ "that block byte for byte afterwards.";
ByteBuffer outbuffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
for(int j=0;j<testdata.length();j+=48)
{
for (int i = j; i < j + 48&&i<testdata.length(); i++)
{
outbuffer.put(testdata.getBytes()[i]);
}
outbuffer.flip();
outputChannel.write(outbuffer);
outbuffer.clear();
}
outputChannel.close();
fos.close();
ByteBuffer inBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
int i= inputChannel.read(inBuffer);
while(i!=-1)
{
inBuffer.flip();
while (inBuffer.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.print((char) inBuffer.get());
}
inBuffer.clear();
i=inputChannel.read(inBuffer);
}
inputChannel.close();
fis.close();
}
}2:DatagramChannel
- 针对面向数据报套接字的可选择通道。
- 数据报通道不是网络数据报套接字的完整抽象。必须通过调用 socket 所获得的关联 DatagramSocket 对象来完成套接字选项的绑定和操作。不可能为任意的已有数据报套接字创建通道,也不可能指定与数据报通道关联的数据报套接字所使用的 DatagramSocketImpl 对象。
- 通过调用此类的 open 方法创建数据报通道。新创建的数据报通道已打开,但尚未连接。为了使用 send 和 receive 方法,无需连接数据报通道。但是如果为了避免作为每次发送和接收操作的一部分而执行的安全检查开销,也可以通过调用数据报通道的 connect 方法来建立数据报通道连接。为了使用 read 和 write 方法,必须建立数据报通道连接,因为这些方法不接受或返回套接字地址。
- 一旦建立了连接,在断开数据报通道的连接或将其关闭之前,该数据报通道保持连接状态。可通过调用数据报通道的 isConnected 方法来确定它是否已连接。
- 多个并发线程可安全地使用数据报通道。尽管在任意给定时刻最多只能有一个线程进行读取和写入操作,但数据报通道支持并发的读写。
实例:
发送端代码:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.DatagramChannel;
public class DatagramChannelSender {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
send();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void send() throws IOException{
DatagramChannel channel =DatagramChannel.open();
ByteBuffer buffer =ByteBuffer.wrap(" This is UPD test".getBytes("utf-8"));
channel.send(buffer, new InetSocketAddress("localhost",10022));
channel.close();
}
}
接收端代码:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.DatagramChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class DatagramChannelReveiver {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
receive();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void receive() throws IOException{
DatagramChannel channel =DatagramChannel.open();
channel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(10022));
ByteBuffer buffer =ByteBuffer.allocate(60);
while(channel.receive(buffer)==null){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
buffer.flip();
String recStr =Charset.forName("utf-8").newDecoder().decode(buffer).toString();
System.out.println("Service has received data:"+recStr);
channel.close();
}
}3:SocketChannel与ServerSocketChannel
- 针对面向流的连接套接字的可选择通道。
- 套接字通道不是连接网络套接字的完整抽象。必须通过调用 socket 方法所获得的关联 Socket 对象来完成对套接字选项的绑定、关闭和操作。不可能为任意的已有套接字创建通道,也不可能指定与套接字通道关联的套接字所使用的 SocketImpl 对象。
- 通过调用此类的某个 open 方法创建套接字通道。新创建的套接字通道已打开,但尚未连接。试图在未连接的通道上调用 I/O 操作将导致抛出 NotYetConnectedException。可通过调用套接字通道的 connect 方法连接该通道;一旦连接后,关闭套接字通道之前它会一直保持已连接状态。可通过调用套接字通道的 isConnected 方法来确定套接字通道是否已连接。
- 套接字通道支持非阻塞连接:可创建一个套接字通道,并且通过 connect 方法可以发起到远程套接字的连接,之后通过 finishConnect 方法完成该连接。可通过调用 isConnectionPending 方法来确定是否正在进行连接操作。
- 可单独地关闭 套接字通道的输入端和输出端,而无需实际关闭该通道。调用关联套接字对象的 shutdownInput 方法来关闭某个通道的输入端将导致该通道上的后续读取操作返回 -1(指示流的末尾)。调用关联套接字对象的 shutdownOutput 方法来关闭通道的输出端将导致该通道上的后续写入操作抛出 ClosedChannelException。
- 套接字通道支持异步关闭,这与 Channel 类中所指定的异步 close 操作类似。如果一个线程关闭了某个套接字的输入端,而同时另一个线程被阻塞在该套接字通道上的读取操作中,那么处于阻塞线程中的读取操作将完成,而不读取任何字节且返回 -1。I如果一个线程关闭了某个套接字的输出端,而同时另一个线程被阻塞在该套接字通道上的写入操作中,那么阻塞线程将收到 AsynchronousCloseException。
- 多个并发线程可安全地使用套接字通道。尽管在任意给定时刻最多只能有一个线程进行读取和写入操作,但数据报通道支持并发的读写。connect 和 finishConnect 方法是相互同步的,如果正在调用其中某个方法的同时试图发起读取或写入操作,则在该调用完成之前该操作被阻塞。
- 服务器套接字通道不是侦听网络套接字的完整抽象。必须通过调用 socket 方法所获得的关联 ServerSocket 对象来完成对套接字选项的绑定和操作。不可能为任意的已有服务器套接字创建通道,也不可能指定与服务器套接字通道关联的服务器套接字所使用的 SocketImpl 对象。
- 通过调用此类的 open 方法创建服务器套接字通道。新创建的服务器套接字通道已打开,但尚未绑定。试图调用未绑定的服务器套接字通道的 accept 方法会导致抛出 NotYetBoundException。可通过调用相关服务器套接字的某个 bind 方法来绑定服务器套接字通道。
多个并发线程可安全地使用服务器套接字通道。
实例: 来源互联网(原文点击)
package com.csu.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
/** * NIO TCP 客户端 * * @date 2010-2-3 * @time 下午03:33:26 * @version 1.00 */
public class TCPClient{
// 信道选择器
private Selector selector;
// 与服务器通信的信道
SocketChannel socketChannel;
// 要连接的服务器Ip地址
private String hostIp;
// 要连接的远程服务器在监听的端口
private int hostListenningPort;
/** * 构造函数 * @param HostIp * @param HostListenningPort * @throws IOException */
public TCPClient(String HostIp,int HostListenningPort)throws IOException{
this.hostIp=HostIp;
this.hostListenningPort=HostListenningPort;
initialize();
}
/** * 初始化 * @throws IOException */
private void initialize() throws IOException{
// 打开监听信道并设置为非阻塞模式
socketChannel=SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress(hostIp, hostListenningPort));
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 打开并注册选择器到信道
selector = Selector.open();
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
// 启动读取线程
new TCPClientReadThread(selector);
}
/** * 发送字符串到服务器 * @param message * @throws IOException */
public void sendMsg(String message) throws IOException{
ByteBuffer writeBuffer=ByteBuffer.wrap(message.getBytes("UTF-16"));
socketChannel.write(writeBuffer);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
TCPClient client=new TCPClient("localhost",1978);
client.sendMsg("发条消息!"+i++);
}
}import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class TCPClientReadThread implements Runnable{
private Selector selector;
public TCPClientReadThread(Selector selector){
this.selector=selector;
new Thread(this).start();
}
public void run() {
try {
while (selector.select() > 0) {
// 遍历每个有可用IO操作Channel对应的SelectionKey
for (SelectionKey sk : selector.selectedKeys()) {
// 如果该SelectionKey对应的Channel中有可读的数据
if (sk.isReadable()) {
// 使用NIO读取Channel中的数据
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) sk.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
sc.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
// 将字节转化为为UTF-16的字符串
String receivedString=Charset.forName("UTF-16").newDecoder().decode(buffer).toString();
// 控制台打印出来
System.out.println("接收到来自服务器"+sc.socket().getRemoteSocketAddress()+"的信息:"+receivedString);
// 为下一次读取作准备
sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
// 删除正在处理的SelectionKey
selector.selectedKeys().remove(sk);
}
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}/** * TCPServerSelector与特定协议间通信的接口 * * @date 2010-2-3 * @time 上午08:42:42 * @version 1.00 */
public interface TCPProtocol{
/** * 接收一个SocketChannel的处理 * @param key * @throws IOException */
void handleAccept(SelectionKey key) throws IOException;
/** * 从一个SocketChannel读取信息的处理 * @param key * @throws IOException */
void handleRead(SelectionKey key) throws IOException;
/** * 向一个SocketChannel写入信息的处理 * @param key * @throws IOException */
void handleWrite(SelectionKey key) throws IOException;
}import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Date;
/** * TCPProtocol的实现类 * * @date 2010-2-3 * @time 上午08:58:59 * @version 1.00 */
public class TCPProtocolImpl implements TCPProtocol{
private int bufferSize;
public TCPProtocolImpl(int bufferSize){
this.bufferSize=bufferSize;
}
public void handleAccept(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel clientChannel=((ServerSocketChannel)key.channel()).accept();
clientChannel.configureBlocking(false);
clientChannel.register(key.selector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ,ByteBuffer.allocate(bufferSize));
}
public void handleRead(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
// 获得与客户端通信的信道
SocketChannel clientChannel=(SocketChannel)key.channel();
// 得到并清空缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer=(ByteBuffer)key.attachment();
buffer.clear();
// 读取信息获得读取的字节数
long bytesRead=clientChannel.read(buffer);
if(bytesRead==-1){
// 没有读取到内容的情况
clientChannel.close();
}
else{
// 将缓冲区准备为数据传出状态
buffer.flip();
// 将字节转化为为UTF-16的字符串
String receivedString=Charset.forName("UTF-16").newDecoder().decode(buffer).toString();
// 控制台打印出来
System.out.println("接收到来自"+clientChannel.socket().getRemoteSocketAddress()+"的信息:"+receivedString);
// 准备发送的文本
String sendString="你好,客户端. @"+new Date().toString()+",已经收到你的信息"+receivedString;
buffer=ByteBuffer.wrap(sendString.getBytes("UTF-16"));
clientChannel.write(buffer);
// 设置为下一次读取或是写入做准备
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
}
public void handleWrite(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
// do nothing
}
}package com.csu.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
/** * TCP服务器端 * * @date 2010-2-3 * @time 上午08:39:48 * @version 1.00 */
public class TCPServer{
// 缓冲区大小
private static final int BufferSize=1024;
// 超时时间,单位毫秒
private static final int TimeOut=3000;
// 本地监听端口
private static final int ListenPort=1978;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
// 创建选择器
Selector selector=Selector.open();
// 打开监听信道
ServerSocketChannel listenerChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 与本地端口绑定
listenerChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(ListenPort));
// 设置为非阻塞模式
listenerChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 将选择器绑定到监听信道,只有非阻塞信道才可以注册选择器.并在注册过程中指出该信道可以进行Accept操作
listenerChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
// 创建一个处理协议的实现类,由它来具体操作
TCPProtocol protocol=new TCPProtocolImpl(BufferSize);
// 反复循环,等待IO
while(true){
// 等待某信道就绪(或超时)
if(selector.select(TimeOut)==0){
System.out.print("独自等待.");
continue;
}
// 取得迭代器.selectedKeys()中包含了每个准备好某一I/O操作的信道的SelectionKey
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIter=selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(keyIter.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key=keyIter.next();
try{
if(key.isAcceptable()){
// 有客户端连接请求时
protocol.handleAccept(key);
}
if(key.isReadable()){
// 从客户端读取数据
protocol.handleRead(key);
}
if(key.isValid() && key.isWritable()){
// 客户端可写时
protocol.handleWrite(key);
}
}
catch(IOException ex){
// 出现IO异常(如客户端断开连接)时移除处理过的键
keyIter.remove();
continue;
}
// 移除处理过的键
keyIter.remove();
}
}
}
}