全文检索引擎Solr系列——入门篇
Solr采用Lucene搜索库为核心,提供全文索引和搜索开源企业平台,提供REST的HTTP/XML和JSON的API,如果你是Solr新手,那么就和我一起来入门吧!本教程以solr4.8作为测试环境,jdk版本需要1.7及以上版本。
准备
本文假设你对Java有初中级以上水平,因此不再介绍Java相关环境的配置。下载解压缩solr,在example目录有start.jar文件,启动:
|
1
|
java -jar start.jar
|
浏览器访问:http://localhost:8983/solr/,你看到的就是solr的管理界面
索引数据
服务启动后,目前你看到的界面没有任何数据,你可以通过POSTing命令向Solr中添加(更新)文档,删除文档,在exampledocs目录包含一些示例文件,运行命令:
|
1
|
java -jar post.jar solr.xml monitor.xml
|
上面的命令是向solr添加了两份文档,打开这两个文件看看里面是什么内容,solr.xml里面的内容是:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<add>
<doc>
<field name="id">SOLR1000</field>
<field name="name">Solr, the Enterprise Search Server</field>
<field name="manu">Apache Software Foundation</field>
<field name="cat">software</field>
<field name="cat">search</field>
<field name="features">Advanced Full-Text Search Capabilities using Lucene</field>
<field name="features">OptimizedforHigh Volume Web Traffic</field>
<field name="features">Standards Based Open Interfaces - XML and HTTP</field>
<field name="features">Comprehensive HTML Administration Interfaces</field>
<field name="features">Scalability - Efficient Replication to other Solr Search Servers</field>
<field name="features">Flexible and Adaptable with XML configuration and Schema</field>
<field name="features">Good unicode support: héllo (hello with an accent over the e)</field>
<field name="price">0</field>
<field name="popularity">10</field>
<field name="inStock">true</field>
<field name="incubationdate_dt">2006-01-17T00:00:00.000Z</field>
</doc>
</add>
|
表示向索引中添加一个文档,文档就是用来搜索的数据源,现在就可以通过管理界面搜索关键字”solr”,具体步骤是:
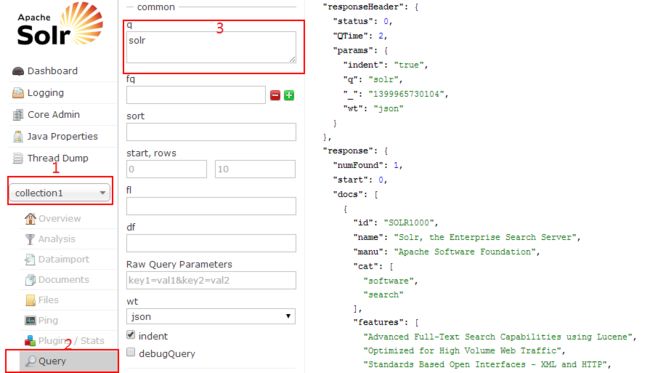
点击页面下的Execute Query按钮后右侧就会显示查询结果,这个结果就是刚才导入进去的solr.xml的json格式的展示结果。solr支持丰富的查询语法,比如:现在想搜索字段name里面的关键字”Search”就可以用语法name:search,当然如果你搜索name:xxx就没有返回结果了,因为文档中没有这样的内容。
数据导入
导入数据到Solr的方式也是多种多样的:
- 可以使用DIH(DataImportHandler)从数据库导入数据
- 支持CSV文件导入,因此Excel数据也能轻松导入
- 支持JSON格式文档
- 二进制文档比如:Word、PDF
- 还能以编程的方式来自定义导入
更新数据
如果同一份文档solr.xml重复导入会出现什么情况呢?实际上solr会根据文档的字段id来唯一标识文档,如果导入的文档的id已经存在solr中,那么这份文档就被最新导入的同id的文档自动替换。你可以自己尝试试验一下,观察替换前后管理界面的几个参数:Num Docs,Max Doc,Deleted Docs的变化。
- numDocs:当前系统中的文档数量,它有可能大于xml文件个数,因为一个xml文件可能有多个<doc>标签。
- maxDoc:maxDoc有可能比numDocs的值要大,比如重复post同一份文件后,maxDoc值就增大了。
- deletedDocs:重复post的文件会替换掉老的文档,同时deltedDocs的值也会加1,不过这只是逻辑上的删除,并没有真正从索引中移除掉
删除数据
通过id删除指定的文档,或者通过一个查询来删除匹配的文档
|
1
2
|
java -Ddata=args -jar post.jar"<delete><id>SOLR1000</id></delete>"
java -Ddata=args -jar post.jar"<delete><query>name:DDR</query></delete>"
|
此时solr.xml文档从索引中删除了,再次搜”solr”时不再返回结果。当然solr也有数据库中的事务,执行删除命令的时候事务自动提交了,文档就会立即从索引中删除。你也可以把commit设置为false,手动提交事务。
|
1
|
java -Ddata=args -Dcommit=false-jar post.jar"<delete><id>3007WFP</id></delete>"
|
执行完上面的命令时文档并没有真正删除,还是可以继续搜索相关结果,最后可以通过命令:
|
1
|
java -jar post.jar -
|
提交事务,文档就彻底删除了。现在把刚刚删除的文件重新导入Solr中来,继续我们的学习。
删除所有数据:
|
1
|
http://localhost:8983/solr/collection1/update?stream.body=<delete><query>*:*</query></delete>&commit=true
|
删除指定数据
|
1
|
http://localhost:8983/solr/collection1/update?stream.body=<delete><query>title:abc</query></delete>&commit=true
|
多条件删除
|
1
|
http://localhost:8983/solr/collection1/update?stream.body=<delete><query>title:abc AND name:zhang</query></delete>&commit=true
|
查询数据
查询数据都是通过HTTP的GET请求获取的,搜索关键字用参数q指定,另外还可以指定很多可选的参数来控制信息的返回,例如:用fl指定返回的字段,比如f1=name,那么返回的数据就只包括name字段的内容
|
1
|
http://localhost:8983/solr/collection1/select?q=solr&fl=name&wt=json&indent=true
|
- 排序
Solr提供排序的功能,通过参数sort来指定,它支持正序、倒序,或者多个字段排序
- q=video&sort=price desc
- q=video&sort=price asc
- q=video&sort=inStock asc, price desc
默认条件下,Solr根据socre 倒序排列,socre是一条搜索记录根据相关度计算出来的一个分数。
- 高亮
网页搜索中,为了突出搜索结果,可能会对匹配的关键字高亮出来,Solr提供了很好的支持,只要指定参数:
- hl=true #开启高亮功能
- hl.fl=name #指定需要高亮的字段
|
1
|
http://localhost:8983/solr/collection1/select?q=Search&wt=json&indent=true&hl=true&hl.fl=features
|
返回的内容中包含:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
"highlighting":{
"SOLR1000":{
"features":["Advanced Full-Text <em>Search</em> Capabilities using Lucene"]
}
}
|
文本分析
文本字段通过把文本分割成单词以及运用各种转换方法(如:小写转换、复数移除、词干提取)后被索引,schema.xml文件中定义了字段在索引中,这些字段将作用于其中.
默认情况下搜索”power-shot”是不能匹配”powershot”的,通过修改schema.xml文件(solr/example/solr/collection1/conf目录),把features和text字段替换成”text_en_splitting”类型,就能索引到了。
|
1
2
3
|
<field name="features"type="text_en_splitting"indexed="true"stored="true"multiValued="true"/>
...
<field name="text"type="text_en_splitting"indexed="true"stored="false"multiValued="true"/>
|
修改完后重启solr,然后重新导入文档
|
1
|
java -jar post.jar *.xml
|
现在就可以匹配了
- power-shot—>Powershot
- features:recharing—>Rechargeable
- 1 gigabyte –> 1G
场景:小时候我们都使用过新华字典,妈妈叫你翻开第38页,找到“坑爹”所在的位置,此时你会怎么查呢?毫无疑问,你的眼睛会从38页的第一个字开始从头至尾地扫描,直到找到“坑爹”二字为止。这种搜索方法叫做顺序扫描法。对于少量的数据,使用顺序扫描是够用的。但是妈妈叫你查出坑爹的“坑”字在哪一页时,你要是从第一页的第一个字逐个的扫描下去,那你真的是被坑了。此时你就需要用到索引。索引记录了“坑”字在哪一页,你只需在索引中找到“坑”字,然后找到对应的页码,答案就出来了。因为在索引中查找“坑”字是非常快的,因为你知道它的偏旁,因此也就可迅速定位到这个字。
那么新华字典的目录(索引表)是怎么编写而成的呢?首先对于新华字典这本书来说,除去目录后,这本书就是一堆没有结构的数据集。但是聪明的人类善于思考总结,发现每个字都会对应到一个页码,比如“坑”字就在第38页,“爹”字在第90页。于是他们就从中提取这些信息,构造成一个有结构的数据。类似数据库中的表结构:
word page_no --------------- 坑 38 爹 90 ... ...
这样就形成了一个完整的目录(索引库),查找的时候就非常方便了。对于全文检索也是类似的原理,它可以归结为两个过程:1.索引创建(Indexing)2. 搜索索引(Search)。那么索引到底是如何创建的呢?索引里面存放的又是什么东西呢?搜索的的时候又是如何去查找索引的呢?带着这一系列问题继续往下看。
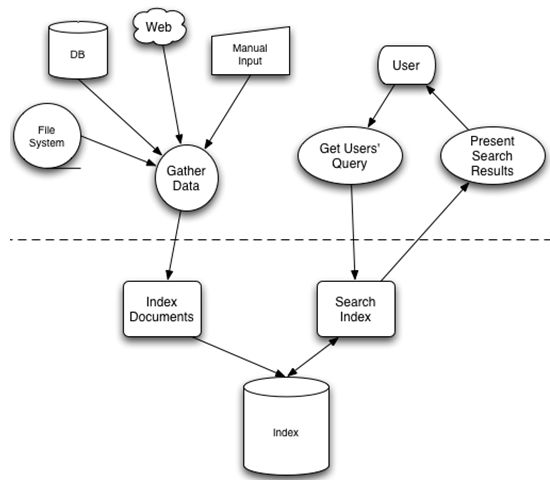
索引
Solr/Lucene采用的是一种反向索引,所谓反向索引:就是从关键字到文档的映射过程,保存这种映射这种信息的索引称为反向索引
- 左边保存的是字符串序列
- 右边是字符串的文档(Document)编号链表,称为倒排表(Posting List)
字段串列表和文档编号链表两者构成了一个字典。现在想搜索”lucene”,那么索引直接告诉我们,包含有”lucene”的文档有:2,3,10,35,92,而无需在整个文档库中逐个查找。如果是想搜既包含”lucene”又包含”solr”的文档,那么与之对应的两个倒排表去交集即可获得:3、10、35、92。
索引创建
假设有如下两个原始文档:
文档一:Students should be allowed to go out with their friends, but not allowed to drink beer.
文档二:My friend Jerry went to school to see his students but found them drunk which is not allowed.
创建过程大概分为如下步骤:
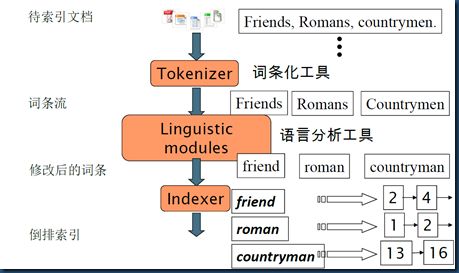
一:把原始文档交给分词组件(Tokenizer)
分词组件(Tokenizer)会做以下几件事情(这个过程称为:Tokenize),处理得到的结果是词汇单元(Token)
- 将文档分成一个一个单独的单词
- 去除标点符号
- 去除停词(stop word)
- 所谓停词(Stop word)就是一种语言中没有具体含义,因而大多数情况下不会作为搜索的关键词,这样一来创建索引时能减少索引的大小。英语中停词(Stop word)如:”the”、”a”、”this”,中文有:”的,得”等。不同语种的分词组件(Tokenizer),都有自己的停词(stop word)集合。经过分词(Tokenizer)后得到的结果称为词汇单元(Token)。上例子中,便得到以下词汇单元(Token):
"Students","allowed","go","their","friends","allowed","drink","beer","My","friend","Jerry","went","school","see","his","students","found","them","drunk","allowed"
- 所谓停词(Stop word)就是一种语言中没有具体含义,因而大多数情况下不会作为搜索的关键词,这样一来创建索引时能减少索引的大小。英语中停词(Stop word)如:”the”、”a”、”this”,中文有:”的,得”等。不同语种的分词组件(Tokenizer),都有自己的停词(stop word)集合。经过分词(Tokenizer)后得到的结果称为词汇单元(Token)。上例子中,便得到以下词汇单元(Token):
二:词汇单元(Token)传给语言处理组件(Linguistic Processor)
语言处理组件(linguistic processor)主要是对得到的词元(Token)做一些语言相关的处理。对于英语,语言处理组件(Linguistic Processor)一般做以下几点:
- 变为小写(Lowercase)。
- 将单词缩减为词根形式,如”cars”到”car”等。这种操作称为:stemming。
- 将单词转变为词根形式,如”drove”到”drive”等。这种操作称为:lemmatization。
语言处理组件(linguistic processor)处理得到的结果称为词(Term),例子中经过语言处理后得到的词(Term)如下:
"student","allow","go","their","friend","allow","drink","beer","my","friend","jerry","go","school","see","his","student","find","them","drink","allow"。
经过语言处理后,搜索drive时drove也能被搜索出来。Stemming 和 lemmatization的异同:
- 相同之处:
- Stemming和lemmatization都要使词汇成为词根形式。
- 两者的方式不同:
- Stemming采用的是”缩减”的方式:”cars”到”car”,”driving”到”drive”。
- Lemmatization采用的是”转变”的方式:”drove”到”drove”,”driving”到”drive”。
- 两者的算法不同:
- Stemming主要是采取某种固定的算法来做这种缩减,如去除”s”,去除”ing”加”e”,将”ational”变为”ate”,将”tional”变为”tion”。
- Lemmatization主要是采用事先约定的格式保存某种字典中。比如字典中有”driving”到”drive”,”drove”到”drive”,”am, is, are”到”be”的映射,做转变时,按照字典中约定的方式转换就可以了。
- Stemming和lemmatization不是互斥关系,是有交集的,有的词利用这两种方式都能达到相同的转换。
三:得到的词(Term)传递给索引组件(Indexer)
- 利用得到的词(Term)创建一个字典
Term Document ID student 1 allow 1 go 1 their 1 friend 1 allow 1 drink 1 beer 1 my 2 friend 2 jerry 2 go 2 school 2 see 2 his 2 student 2 find 2 them 2 drink 2 allow 2
- 对字典按字母顺序排序:
Term Document ID allow 1 allow 1 allow 2 beer 1 drink 1 drink 2 find 2 friend 1 friend 2 go 1 go 2 his 2 jerry 2 my 2 school 2 see 2 student 1 student 2 their 1 them 2
- 合并相同的词(Term)成为文档倒排(Posting List)链表
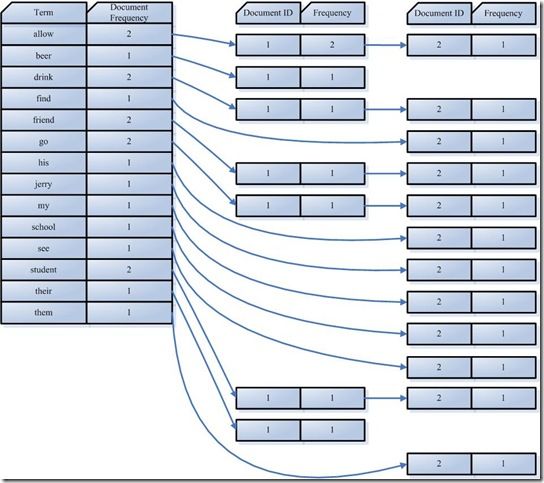
- Document Frequency:文档频次,表示多少文档出现过此词(Term)
- Frequency:词频,表示某个文档中该词(Term)出现过几次
对词(Term) “allow”来讲,总共有两篇文档包含此词(Term),词(Term)后面的文档链表总共有两个,第一个表示包含”allow”的第一篇文档,即1号文档,此文档中,”allow”出现了2次,第二个表示包含”allow”的第二个文档,是2号文档,此文档中,”allow”出现了1次
至此索引创建完成,搜索”drive”时,”driving”,”drove”,”driven”也能够被搜到。因为在索引中,”driving”,”drove”,”driven”都会经过语言处理而变成”drive”,在搜索时,如果您输入”driving”,输入的查询语句同样经过分词组件和语言处理组件处理的步骤,变为查询”drive”,从而可以搜索到想要的文档。
搜索步骤
搜索”microsoft job”,用户的目的是希望在微软找一份工作,如果搜出来的结果是:”Microsoft does a good job at software industry…”,这就与用户的期望偏离太远了。如何进行合理有效的搜索,搜索出用户最想要得结果呢?搜索主要有如下步骤:
一:对查询内容进行词法分析、语法分析、语言处理
- 词法分析:区分查询内容中单词和关键字,比如:english and janpan,”and”就是关键字,”english”和”janpan”是普通单词。
- 根据查询语法的语法规则形成一棵树
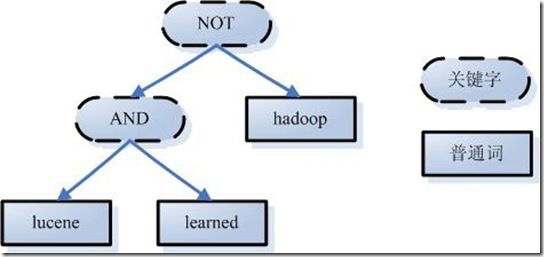
- 语言处理,和创建索引时处理方式是一样的。比如:leaned–>lean,driven–>drive
二:搜索索引,得到符合语法树的文档集合
三:根据查询语句与文档的相关性,对结果进行排序
我们把查询语句也看作是一个文档,对文档与文档之间的相关性(relevance)进行打分(scoring),分数高比较越相关,排名就越靠前。当然还可以人工影响打分,比如百度搜索,就不一定完全按照相关性来排名的。
如何评判文档之间的相关性?一个文档由多个(或者一个)词(Term)组成,比如:”solr”, “toturial”,不同的词可能重要性不一样,比如solr就比toturial重要,如果一个文档出现了10次toturial,但只出现了一次solr,而另一文档solr出现了4次,toturial出现一次,那么后者很有可能就是我们想要的搜的结果。这就引申出权重(Term weight)的概念。
权重表示该词在文档中的重要程度,越重要的词当然权重越高,因此在计算文档相关性时影响力就更大。通过词之间的权重得到文档相关性的过程叫做空间向量模型算法(Vector Space Model)
影响一个词在文档中的重要性主要有两个方面:
- Term Frequencey(tf),Term在此文档中出现的频率,ft越大表示越重要
- Document Frequency(df),表示有多少文档中出现过这个Trem,df越大表示越不重要
物以希为贵,大家都有的东西,自然就不那么贵重了,只有你专有的东西表示这个东西很珍贵,权重的公式:

空间向量模型
文档中词的权重看作一个向量
Document = {term1, term2, …… ,term N}
Document Vector = {weight1, weight2, …… ,weight N}
把欲要查询的语句看作一个简单的文档,也用向量表示:
Query = {term1, term 2, …… , term N}
Query Vector = {weight1, weight2, …… , weight N}
把搜索出的文档向量及查询向量放入N维度的空间中,每个词表示一维:
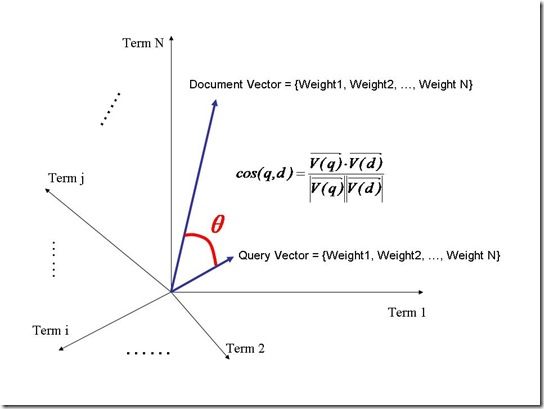
夹角越小,表示越相似,相关性越大
Document
Document是Solr索引(动词,indexing)和搜索的最基本单元,它类似于关系数据库表中的一条记录,可以包含一个或多个字段(Field),每个字段包含一个name和文本值。字段在被索引的同时可以存储在索引中,搜索时就能返回该字段的值,通常文档都应该包含一个能唯一表示该文档的id字段。例如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
<doc>
<field name="id">company123</field>
<field name="companycity">Atlanta</field>
<field name="companystate">Georgia</field>
<field name="companyname">Code Monkeys R Us, LLC</field>
<field name="companydescription">we write lots of code</field>
<field name="lastmodified">2013-06-01T15:26:37Z</field>
</doc>
|
Schema
Solr中的Schema类似于关系数据库中的表结构,它以schema.xml的文本形式存在在conf目录下,在添加文当到索引中时需要指定Schema,Schema文件主要包含三部分:字段(Field)、字段类型(FieldType)、唯一键(uniqueKey)
- 字段类型(FieldType):用来定义添加到索引中的xml文件字段(Field)中的类型,如:int,String,date,
- 字段(Field):添加到索引文件中时的字段名称
- 唯一键(uniqueKey):uniqueKey是用来标识文档唯一性的一个字段(Feild),在更新和删除时用到
例如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
<schema name="example"version="1.5">
<field name="id"type="string"indexed="true"stored="true"required="true"multiValued="false"/>
<field name="title"type="text_general"indexed="true"stored="true"multiValued="true"/>
<uniqueKey>id</uniqueKey>
<fieldType name="string"class="solr.StrField"sortMissingLast="true"/>
<fieldType name="text_general"class="solr.TextField"positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer type="index">
<tokenizerclass="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filterclass="solr.StopFilterFactory"ignoreCase="true"words="stopwords.txt"/>
<!-- inthisexample, we will only use synonyms at query time
<filterclass="solr.SynonymFilterFactory"synonyms="index_synonyms.txt"ignoreCase="true"expand="false"/>
-->
<filterclass="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
<analyzer type="query">
<tokenizerclass="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filterclass="solr.StopFilterFactory"ignoreCase="true"words="stopwords.txt"/>
<filterclass="solr.SynonymFilterFactory"synonyms="synonyms.txt"ignoreCase="true"expand="true"/>
<filterclass="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
</schema>
|
Field
在Solr中,字段(Field)是构成Document的基本单元。对应于数据库表中的某一列。字段是包括了名称,类型以及对字段对应的值如何处理的一种元数据。比如:
<field name="name" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
- Indexed:Indexed=true时,表示字段会加被Sorl处理加入到索引中,只有被索引的字段才能被搜索到。
- Stored:Stored=true,字段值会以保存一份原始内容在在索引中,可以被搜索组件组件返回,考虑到性能问题,对于长文本就不适合存储在索引中。
Field Type
Solr中每个字段都有一个对应的字段类型,比如:float、long、double、date、text,Solr提供了丰富字段类型,同时,我们还可以自定义适合自己的数据类型,例如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
<!-- Ik 分词器 -->
<fieldType name="text_cn_stopword"class="solr.TextField">
<analyzer type="index">
<tokenizerclass="org.wltea.analyzer.lucene.IKAnalyzerSolrFactory"useSmart="false"/>
</analyzer>
<analyzer type="query">
<tokenizerclass="org.wltea.analyzer.lucene.IKAnalyzerSolrFactory"useSmart="true"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Ik 分词器 -->
|
Solrconfig:
如果把Schema定义为Solr的Model的话,那么Solrconfig就是Solr的Configuration,它定义Solr如果处理索引、高亮、搜索等很多请求,同时还指定了缓存策略,用的比较多的元素包括:
- 指定索引数据路径
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<!--
Used to specify an alternate directory to hold all index data
other than thedefault./data under the Solr home.
If replication is in use,thisshould match the replication configuration.
-->
<dataDir>${solr.data.dir:./solr/data}</dataDir>
|
- 缓存参数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
<filterCache
class="solr.FastLRUCache"
size="512"
initialSize="512"
autowarmCount="0"/>
<!-- queryResultCache caches results of searches - ordered lists of
document ids (DocList) based on a query, a sort, and the range
of documents requested. -->
<queryResultCache
class="solr.LRUCache"
size="512"
initialSize="512"
autowarmCount="0"/>
<!-- documentCache caches Lucene Document objects (the stored fieldsforeach document).
Since Lucene internal document ids aretransient,thiscache will not be autowarmed. -->
<documentCache
class="solr.LRUCache"
size="512"
initialSize="512"
autowarmCount="0"/>
|
- 请求处理器
请求处理器用于接收HTTP请求,处理搜索后,返回响应结果的处理器。比如:query请求:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<!-- A request handler that returns indented JSON bydefault-->
<requestHandler name="/query"class="solr.SearchHandler">
<lst name="defaults">
<str name="echoParams">explicit</str>
<str name="wt">json</str>
<str name="indent">true</str>
<str name="df">text</str>
</lst>
</requestHandler>
|
每个请求处理器包括一系列可配置的搜索参数,例如:wt,indent,df等等。
- 搜索组件
MySQL
- 拷贝mysql-connector-java-5.1.25-bin.jar到E:\solr-4.8.0\example\solr-webapp\webapp\WEB-INF\lib目录下面
- 配置E:\solr-4.8.0\example\solr\collection1\conf\solrconfig.xml
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<requestHandlername="/dataimport"
class="org.apache.solr.handler.dataimport.DataImportHandler">
<lstname="defaults">
<strname="config">data-config.xml</str>
</lst>
</requestHandler>
|
- 导入依赖库文件:
|
1
|
<lib dir="../../../dist/" regex="solr-dataimporthandler-\d.*\.jar"/>
|
|
1
|
<lib dir="../../../dist/" regex="solr-cell-\d.*\.jar" />
|
- 创建E:\solr-4.8.0\example\solr\collection1\conf\data-config.xml,指定MySQL数据库地址,用户名、密码以及建立索引的数据表
<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?><dataConfig><dataSourcetype="JdbcDataSource"driver="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/django_blog"user="root"password=""/><documentname="blog"><entityname="blog_blog"pk="id"query="select id,title,content from blog_blog"deltaImportQuery="select id,title,content from blog_blog where ID='${dataimporter.delta.id}'"deltaQuery="select id from blog_blog where add_time > '${dataimporter.last_index_time}'"deletedPkQuery="select id from blog_blog where id=0"><fieldcolumn="id"name="id"/><fieldcolumn="title"name="title"/><fieldcolumn="content"name="content"/></entity></document></dataConfig>
- query 用于初次导入到索引的sql语句。
- 考虑到数据表中的数据量非常大,比如千万级,不可能一次索引完,因此需要分批次完成,那么查询语句query要设置两个参数:${dataimporter.request.length} ${dataimporter.request.offset}
- query=”select id,title,content from blog_blog limit ${dataimporter.request.length} offset ${dataimporter.request.offset}”
- 请求:http://localhost:8983/solr/collection2/dataimport?command=full-import&commit=true&clean=false&offset=0&length=10000
- deltaImportQuery 根据ID取得需要进入的索引的单条数据。
- deltaQuery 用于增量索引的sql语句,用于取得需要增量索引的ID。
- deletedPkQuery 用于取出需要从索引中删除文档的的ID
- query 用于初次导入到索引的sql语句。
- 为数据库表字段建立域(field),编辑E:\solr-4.8.0\example\solr\collection1\conf\schema.xml:
|
<!-- mysql -->
<fieldname="id"type="string"indexed="true"stored="true"required="true"/>
<fieldname="title"type="text_cn"indexed="true"stored="true"termVectors="true"termPositions="true"termOffsets="true"/>
<fieldname="content"type="text_cn"indexed="true"stored="true"termVectors="true"termPositions="true"termOffsets="true"/>
<!-- mysql -->
|
- 配置增量索引更新文件
参考:
- http://josh-persistence.iteye.com/blog/2017155
- http://wiki.apache.org/solr/DataImportHandler#Using_delta-import_command
Mongodb
- 安装mongo-connector,最好使用手动安装方式:
<code>git clone https://github.com/10gen-labs/mongo-connector.git cd mongo-connector #安装前修改mongo_connector/constants.py的变量:设置DEFAULT_COMMIT_INTERVAL = 0 python setup.py install </code>
默认是不会自动提交了,这里设置成自动提交,否则mongodb数据库更新,索引这边没法同时更新,或者在命令行中可以指定是否自动提交,不过我现在还没发现。
- 配置schema.xml,把mongodb中需要加上索引的字段配置到schema.xml文件中:
<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?><schemaname="example"version="1.5"><fieldname="_version_"type="long"indexed="true"stored="true"/><fieldname="_id"type="string"indexed="true"stored="true"required="true"multiValued="false"/><fieldname="body"type="string"indexed="true"stored="true"/><fieldname="title"type="string"indexed="true"stored="true"multiValued="true"/><fieldname="text"type="text_general"indexed="true"stored="false"multiValued="true"/><uniqueKey>_id</uniqueKey><defaultSearchField>title</defaultSearchField><solrQueryParserdefaultOperator="OR"/><fieldTypename="string"class="solr.StrField"sortMissingLast="true"/><fieldTypename="long"class="solr.TrieLongField"precisionStep="0"positionIncrementGap="0"/><fieldTypename="text_general"class="solr.TextField"positionIncrementGap="100"><analyzertype="index"><tokenizerclass="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/><filterclass="solr.StopFilterFactory"ignoreCase="true"words="stopwords.txt"/><filterclass="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/></analyzer><analyzertype="query"><tokenizerclass="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/><filterclass="solr.StopFilterFactory"ignoreCase="true"words="stopwords.txt"/><filterclass="solr.SynonymFilterFactory"synonyms="synonyms.txt"ignoreCase="true"expand="true"/><filterclass="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/></analyzer></fieldType></schema>
- 启动Mongod:
<code>mongod --replSet myDevReplSet --smallfiles </code>
初始化:rs.initiate()
- 启动mongo-connector:
<code>E:\Users\liuzhijun\workspace\mongo-connector\mongo_connector\doc_managers>mongo-connector -m localhost:27017 -t http://localhost:8983/solr/collection2 -n s_soccer.person -u id -d ./solr_doc_manager.py </code>
- -m:mongod服务
- -t:solr服务
- -n:mongodb命名空间,监听database.collection,多个命名空间逗号分隔
- -u:uniquekey
- -d:处理文档的manager文件
注意:mongodb通常使用_id作为uniquekey,而Solrmore使用id作为uniquekey,如果不做处理,索引文件时将会失败,有两种方式来处理这个问题:
- 指定参数--unique-key=id到mongo-connector,Mongo Connector 就可以翻译把_id转换到id。
- 把schema.xml文件中的:
<code><uniqueKey>id<uniqueKey> </code>
替换成
<code><uniqueKey>_id</uniqueKey> </code>
同时还要定义一个_id的字段:
<code><field name="_id" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" /> </code>
- 启动时如果报错:
<code>2014-06-18 12:30:36,648 - ERROR - OplogThread: Last entry no longer in oplog cannot recover! Collection(Database(MongoClient('localhost', 27017), u'local'), u'oplog.rs') </code>清空E:\Users\liuzhijun\workspace\mongo-connector\mongo_connector\doc_managers\config.txt中的内容,需要删除索引目录下的文件重新启动
- 测试
mongodb中的数据变化都会同步到solr中去。
