mybatis源码分析之SqlSession的创建过程
mybatis之SqlSessionFactory
mybatis源码分析之Configuration
mybatis源码分析之事务管理器
以上是之前的分析,在mybatis源码分析之事务管理器里分析到了事务管理器
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//DefaultSqlSessionFactory里的openSession
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
//根据配置获取环境
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
//构建事务工厂
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
//通过事务工厂创建事务Transaction对象
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
//创建执行器Executor对象
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
//根据configuration,executor创建DefaultSqlSession对象
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
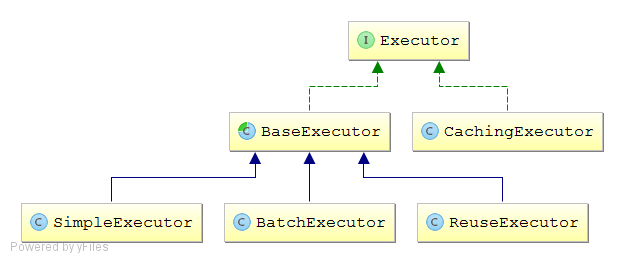
之前已经分析过事务管理器,下面分析执行器Executor
public enum ExecutorType {
SIMPLE, REUSE, BATCH
}
执行器类型只有三种
SIMPLE:普通的执行器;
REUSE:执行器会重用预处理语句(prepared statements);
BATCH:执行器将重用语句并执行批量更新。
configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
//默认执行器类型
protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
//二级缓存的全局开关,默认开启缓存
protected boolean cacheEnabled = true;
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
//executorType为null时executorType=ExecutorType.SIMPLE
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
//根据执行器类型创建执行器
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
//当cacheEnabled为true时创建CachingExecutor对象
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
二级缓存开关配置示例
<settings> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> </settings>
执行器创建后
new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
//DefaultSqlSession构造方法
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor, boolean autoCommit) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.executor = executor;
this.dirty = false;
this.autoCommit = autoCommit;
}
至此SqlSession创建完成,从之前的几篇和这篇能清晰的看到从读取配置文件到SqlSession创建的整个过程.需要注意的是SqlSession 的实例不是线程安全的,是不能被共享的,所以它的最佳的范围是请求或方法范围.每个线程都应该有自己的 SqlSession 实例.