TensorFlow人工智能引擎入门教程之三 实现一个自创的CNN卷积神经网络
首先回到上一张的google官方的alexnet文件
这是alexnet网络定义的部分 ,我们只需要修改这一部就可以了
def alex_net(_X, _weights, _biases, _dropout):
# Reshape input picture
_X = tf.reshape(_X, shape=[-1, 28, 28, 1])
# Convolution Layer
conv1 = conv2d('conv1', _X, _weights['wc1'], _biases['bc1'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
pool1 = max_pool('pool1', conv1, k=2)
# Apply Normalization
norm1 = norm('norm1', pool1, lsize=4)
# Apply Dropout
norm1 = tf.nn.dropout(norm1, _dropout)
# Convolution Layer
conv2 = conv2d('conv2', norm1, _weights['wc2'], _biases['bc2'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
pool2 = max_pool('pool2', conv2, k=2)
# Apply Normalization
norm2 = norm('norm2', pool2, lsize=4)
# Apply Dropout
norm2 = tf.nn.dropout(norm2, _dropout)
# Convolution Layer
conv3 = conv2d('conv3', norm2, _weights['wc3'], _biases['bc3'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
pool3 = max_pool('pool3', conv3, k=2)
# Apply Normalization
norm3 = norm('norm3', pool3, lsize=4)
# Apply Dropout
norm3 = tf.nn.dropout(norm3, _dropout)
# Fully connected layer
dense1 = tf.reshape(norm3, [-1, _weights['wd1'].get_shape().as_list()[0]]) # Reshape conv3 output to fit dense layer input
dense1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(dense1, _weights['wd1']) + _biases['bd1'], name='fc1') # Relu activation
dense2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(dense1, _weights['wd2']) + _biases['bd2'], name='fc2') # Relu activation
# Output, class prediction
out = tf.matmul(dense2, _weights['out']) + _biases['out']
return out
# Store layers weight & bias
weights = {
'wc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 1, 64])),
'wc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 64, 128])),
'wc3': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 128, 256])),
'wd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4*4*256, 1024])),
'wd2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024, 1024])),
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024, 10]))
}
biases = {
'bc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([64])),
'bc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([128])),
'bc3': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256])),
'bd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024])),
'bd2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024])),
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes]))
}
# Construct model
pred = alex_net(x, weights, biases, keep_prob)
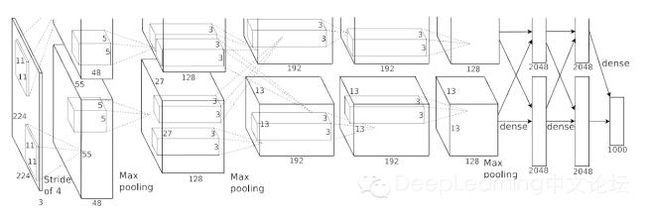
首选要理清他的网络图 这是alexnet论文的 图片 ,这里引用一下 ,每一层与上面对应
下面 我们 做一个实现 ,我们 给conv1 conv2 conv3 后面加上一个conv4 maxpool ,我们看看核心代码区域
Y=wx+b
# Convolution Layer
conv1 = conv2d('conv1', _X, _weights['wc1'], _biases['bc1'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
pool1 = max_pool('pool1', conv1, k=2)
# Apply Normalization
norm1 = norm('norm1', pool1, lsize=4)
# Apply Dropout
norm1 = tf.nn.dropout(norm1, _dropout)
# Convolution Layer
conv2 = conv2d('conv2', norm1, _weights['wc2'], _biases['bc2'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
pool2 = max_pool('pool2', conv2, k=2)
# Apply Normalization
norm2 = norm('norm2', pool2, lsize=4)
# Apply Dropout
norm2 = tf.nn.dropout(norm2, _dropout)
# Convolution Layer
conv3 = conv2d('conv3', norm2, _weights['wc3'], _biases['bc3'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
pool3 = max_pool('pool3', conv3, k=2)
# Apply Normalization
norm3 = norm('norm3', pool3, lsize=4)
# Apply Dropout
norm3 = tf.nn.dropout(norm3, _dropout)
我先往上面我们加上conv4一层
#这后面我们加上部分代码
#convolution layer
conv4 = conv2d('conv4',norm3,tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 2, 256, 512)),tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([512]))
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
pool4 = max_pool('pool4', conv4, k=2)
# Apply Normalization
norm4 = norm('norm4', pool4, lsize=4)
# Apply Dropout
norm4 = tf.nn.dropout(norm4, _dropout)
这样我们 我们加上一层conv2 以2 2的卷积核以及 512输出特征 2x2的pool .我们先不考虑 精度会不会提高的问题,我们只是自定义一个测试看看
根据上面的卷积一层一层 shape 运算 我们得到
最后一层计算(4-2)/2+1=2
也就是说输入为2*2*512
这样我们只需要修改w的矩阵格式 以及 b的矩阵格式即可了
这时候 我们成功在官方alexnet网络上加了一层
形成了 conv1--->conv2----->conv3---->conv4---->full---full---softmax分类 的一个自创的新网络
下面 贴出 修改后的alexnet的代码
import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("/tmp/data/", one_hot=True)
import tensorflow as tf
# Parameters
learning_rate = 0.001
training_iters = 200000
batch_size = 64
display_step = 20
# Network Parameters
n_input = 784 # MNIST data input (img shape: 28*28)
n_classes = 10 # MNIST total classes (0-9 digits)
dropout = 0.8 # Dropout, probability to keep units
# tf Graph input
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_input])
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_classes])
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) # dropout (keep probability)
# Create custom model
def conv2d(name, l_input, w, b):
return tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(tf.nn.conv2d(l_input, w, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME'),b), name=name)
def max_pool(name, l_input, k):
return tf.nn.max_pool(l_input, ksize=[1, k, k, 1], strides=[1, k, k, 1], padding='SAME', name=name)
def norm(name, l_input, lsize=4):
return tf.nn.lrn(l_input, lsize, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75, name=name)
def customnet(_X, _weights, _biases, _dropout):
# Reshape input picture
_X = tf.reshape(_X, shape=[-1, 28, 28, 1])
# Convolution Layer
conv1 = conv2d('conv1', _X, _weights['wc1'], _biases['bc1'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
pool1 = max_pool('pool1', conv1, k=2)
# Apply Normalization
norm1 = norm('norm1', pool1, lsize=4)
# Apply Dropout
norm1 = tf.nn.dropout(norm1, _dropout)
# Convolution Layer
conv2 = conv2d('conv2', norm1, _weights['wc2'], _biases['bc2'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
pool2 = max_pool('pool2', conv2, k=2)
# Apply Normalization
norm2 = norm('norm2', pool2, lsize=4)
# Apply Dropout
norm2 = tf.nn.dropout(norm2, _dropout)
# Convolution Layer
conv3 = conv2d('conv3', norm2, _weights['wc3'], _biases['bc3'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
pool3 = max_pool('pool3', conv3, k=2)
# Apply Normalization
norm3 = norm('norm3', pool3, lsize=4)
# Apply Dropout
norm3 = tf.nn.dropout(norm3, _dropout)
#conv4
conv4 = conv2d('conv4', norm3, _weights['wc4'], _biases['bc4'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
pool4 = max_pool('pool4', conv4, k=2)
# Apply Normalization
norm4 = norm('norm4', pool4, lsize=4)
# Apply Dropout
norm4 = tf.nn.dropout(norm4, _dropout)
# Fully connected layer
dense1 = tf.reshape(norm4, [-1, _weights['wd1'].get_shape().as_list()[0]]) # Reshape conv3 output to fit dense layer input
dense1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(dense1, _weights['wd1']) + _biases['bd1'], name='fc1') # Relu activation
dense2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(dense1, _weights['wd2']) + _biases['bd2'], name='fc2') # Relu activation
# Output, class prediction
out = tf.matmul(dense2, _weights['out']) + _biases['out']
return out
# Store layers weight & bias
weights = {
'wc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 1, 64])),
'wc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 64, 128])),
'wc3': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 128, 256])),
'wc4': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 2, 256, 512])),
'wd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2*2*512, 1024])),
'wd2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024, 1024])),
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024, 10]))
}
biases = {
'bc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([64])),
'bc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([128])),
'bc3': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256])),
'bc4': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([512])),
'bd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024])),
'bd2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024])),
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes]))
}
# Construct model
pred = customnet(x, weights, biases, keep_prob)
# Define loss and optimizer
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(pred, y))
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)
# Evaluate model
correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred,1), tf.argmax(y,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32))
# Initializing the variables
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
# Launch the graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
step = 1
# Keep training until reach max iterations
while step * batch_size < training_iters:
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
# Fit training using batch data
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys, keep_prob: dropout})
if step % display_step == 0:
# Calculate batch accuracy
acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys, keep_prob: 1.})
# Calculate batch loss
loss = sess.run(cost, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys, keep_prob: 1.})
print "Iter " + str(step*batch_size) + ", Minibatch Loss= " + "{:.6f}".format(loss) + ", Training Accuracy= " + "{:.5f}".format(acc)
step += 1
print "Optimization Finished!"
# Calculate accuracy for 256 mnist test images
print "Testing Accuracy:", sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images[:256], y: mnist.test.labels[:256], keep_prob: 1.})
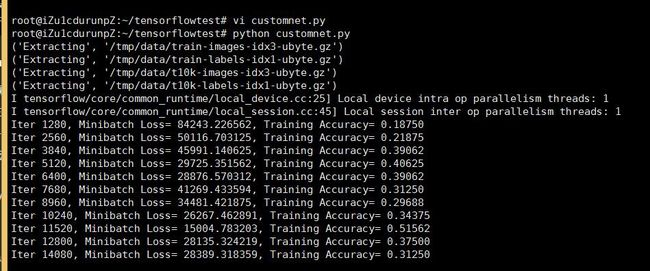
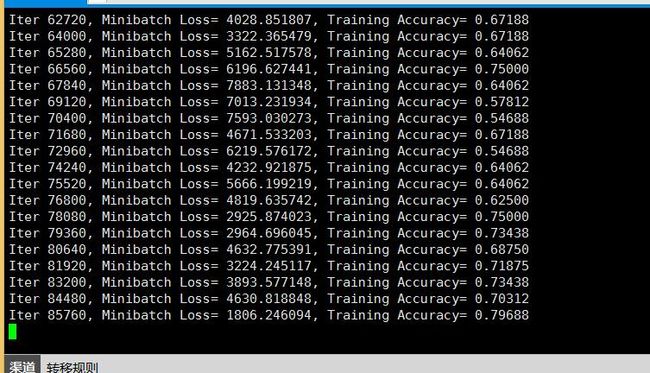
下面我们运行测试 我们的custom自定义net网络吧
下面是运行的截图
最后 精度为89 所以网络设计 是有很多值得考虑的事情 这个后面可能会讲到