lightoj1022&&1072&&1107&&1118&&1178&&1216【基础计算几何】
| PDF (English) | Statistics | Forum |
| Time Limit: 0.5 second(s) | Memory Limit: 32 MB |
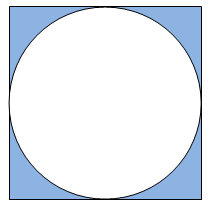
A circle is placed perfectly into a square. The term perfectly placed means that each side of the square is touched by the circle, but the circle doesn't have any overlapping part with the square. See the picture below.
Now you are given the radius of the circle. You have to find the area of the shaded region (blue part). Assume that pi = 2 * acos (0.0) (acos means cos inverse).
Input
Input starts with an integer T (≤ 1000), denoting the number of test cases.
Each case contains a floating point number r (0 < r ≤ 1000) denoting the radius of the circle. And you can assume that r contains at most four digits after the decimal point.
Output
For each case, print the case number and the shaded area rounded to two places after the decimal point.
Sample Input |
Output for Sample Input |
| 3 20 30.091 87.0921 |
Case 1: 343.36 Case 2: 777.26 Case 3: 6511.05 |
Note
This problem doesn't have special judge. So, be careful about precision problems. Better to add a small value to your result to avoid precision problems. For example, add 10-9 to your result.
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#define PI acos(-1.0)
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t,test=1;
double r;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
scanf("%lf",&r);
printf("Case %d: %.2lf\n",test++,4.0*r*r-PI*r*r);
}
return 0;
}
| PDF (English) | Statistics | Forum |
| Time Limit: 2 second(s) | Memory Limit: 32 MB |
George B. wants to be more than just a good American. He wants to make his daddy proud and become a hero. You know, like Shakib Khan.
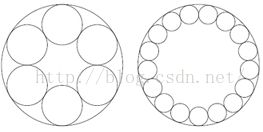
But sneaky as he is, he wants a special revolver that will allow him to shoot more often than just the usual six times. This way he can fool and kill the enemy easily (at least that's what he thinks, and that's the best he can think). George has kidnapped . . . uh, I mean . . . "invited" you and will only let you go if you help him with the math. The piece of the revolver that contains the bullets looks like this (examples for 6 and 17 bullets):
There is a large circle with radius R and n little circles each having radius r, are placed inside on the border of the large circle. George wants his bullets to be as large as possible, so there should be no space between the circles. George will decide how large the whole revolver will be and how many bullets it shall contain. Your job is, given R and n, to compute r. You have decided to help, because you know that an idiot can't make a revolver even if you help him with the math.
Input
Input starts with an integer T (≤ 125), denoting the number of test cases.
Each case contains a real number R (0 < R < 1000 and contains up to at most two places after the decimal point) and an integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100).
Output
For each test case, print the case number and r in a single line. Errors less than 10-6 will be ignored.
Sample Input |
Output for Sample Input |
| 4 4.0 6 4.0 17 3.14 100 42 2 |
Case 1: 1.3333333333 Case 2: 0.6209067545 Case 3: 0.0956260953 Case 4: 21 |
求出两圆心与大圆圆心的夹角列方程求解即可
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#define PI acos(-1.0)
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t,i,j,k,test=1;
double r,n;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
scanf("%lf%lf",&r,&n);
double angle=2.0*PI/n;
printf("Case %d: %.7lf\n",test++,(r*sin(angle/2.0)/(1+sin(angle/2.0))));
}
return 0;
}
| PDF (English) | Statistics | Forum |
| Time Limit: 2 second(s) | Memory Limit: 32 MB |
Mr Kopa Samsu is a farmer. He has a land of rectangular shape. But there are cows that disturb him a lot. The cows use to enter his land and ruin his crops. Now Mr Kopa Samsu has become smarter. He has a GPS system that will help him to know the position of the cows. So, you can think his land as a 2D grid, and cows can be treated as points. Now you are given the information of his land and cows. You have to tell him whether a cow is inside his land or not.
Input
Input starts with an integer T (≤ 50), denoting the number of test cases.
The first line of each case contains four integers x1 y1 x2 y2, where (x1, y1) is the lower left coordinate of his land and (x2, y2) is the upper right coordinate of his land. You can assume that the sides of the land are axis parallel. The next line contains an integer M (1 ≤ M ≤ 100) denoting the number of cows. Each of the next M lines contains two integers each denoting x y - the position of a cow. You can safely assume that no cow will lie on the boundary of the rectangle. All the coordinates will lie in the range [0, 10000].
Output
For each case you have to print the case number in a line first. Then for each cow, you have to print 'Yes' or 'No' depending whether the cow is inside the land or not.
Sample Input |
Output for Sample Input |
| 1 1 2 8 10 7 0 0 5 6 1 0 7 9 3 5 10 10 1 11 |
Case 1: No Yes No Yes Yes No No |
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=10010;
int main()
{
int x1,x2,y1,y2,t,x,y,test=1;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
int n,i;
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2);
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Case %d:\n",test++);
for(i=0;i<n;++i){
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
if(x>=x1&&x<=x2&&y>=y1&&y<=y2){
printf("Yes\n");
}else {
printf("No\n");
}
}
}
return 0;
}
| PDF (English) | Statistics | Forum |
| Time Limit: 0.5 second(s) | Memory Limit: 32 MB |
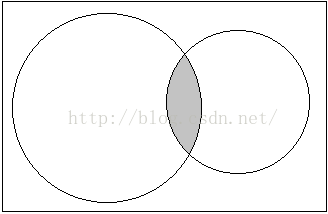
In the biological lab, you were examining some of the molecules. You got some interesting behavior about some of the molecules. There are some circular molecules, when two of them collide, they overlap with each other, and it's hard to find that which one is over the other one.
Given two molecules as circles, you have to find the common area of the given molecules that is shaded in the picture.
Overlapping Molecules
Input
Input starts with an integer T (≤ 12), denoting the number of test cases.
Each case contains six integers x1, y1, r1 and x2, y2, r2. Where (x1, y1) is the center of the first molecule and r1 is the radius and (x2, y2) is the center of the second molecule and r2 is the radius. Both the radiuses are positive. No integer will contain more than 3 digits.
Output
For each test case, print the case number and the common area of the given molecules. Errors less than 10-6 will be ignored.
Sample Input |
Output for Sample Input |
| 3 0 0 10 15 0 10 -10 -10 5 0 -10 10 100 100 20 100 110 20 |
Case 1: 45.3311753978 Case 2: 35.07666099 Case 3: 860.84369 |
两圆相交面积
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#define eps 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
using namespace std;
double area(double x1,double y1,double r1,double x2,double y2,double r2){
double d=sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2));
double angle1,angle2,h1,h2,s1,s2;
if(d>=r1+r2){
return 0;
}
if(d<=fabs(r1-r2)){
return min(PI*r1*r1,PI*r2*r2);
}
angle1=acos((d*d+r1*r1-r2*r2)/(2*d*r1));
angle2=acos((d*d+r2*r2-r1*r1)/(2*d*r2));
h1=angle1*r1*r1;h2=angle2*r2*r2;
s1=r1*r1*cos(angle1)*sin(angle1);
s2=r2*r2*cos(angle2)*sin(angle2);
return h1+h2-(s1+s2);
}
int main()
{
int t,test=1;
double x1,y1,x2,y2,r1,r2;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf",&x1,&y1,&r1,&x2,&y2,&r2);
printf("Case %d: %.7lf\n",test++,area(x1,y1,r1,x2,y2,r2));
}
return 0;
}
| PDF (English) | Statistics | Forum |
| Time Limit: 0.5 second(s) | Memory Limit: 32 MB |
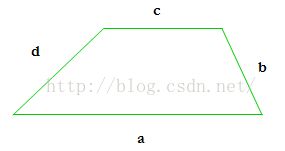
You are given the length of the four sides of a trapezium; you have to calculate the area. In geometry a 4-sided figure with exactly one pair of parallel sides is called a trapezium.
Input
Input starts with an integer T (≤ 20), denoting the number of test cases.
Each case contains four real numbers a b c d denoting the sides of the trapezium. Here a and c denote the parallel sides. You can safely assume that the given trapezium is valid. Each of the numbers will be positive and not more than 200. And no number contains more than 4 digits after the decimal point.
Output
For each case, print the case number and the area. Errors less than 10-6 will be ignored.
Sample Input |
Output for Sample Input |
| 2 6 5 12 5.0 9 5 6 4 |
Case 1: 36 Case 2: 30.0000000 |
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<list>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=10010;
int main()
{
int t,test=1;
double a,b,c,d;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&a,&b,&c,&d);
double x=fabs(a-c);
double p=(b+d+x)/2;
double tarea=sqrt(p*(p-d)*(p-b)*(p-x));
double h=tarea*2/x;
printf("Case %d: %.7lf\n",test++,min(a,c)*h+tarea);
}
return 0;
}
| PDF (English) | Statistics | Forum |
| Time Limit: 2 second(s) | Memory Limit: 32 MB |
Once upon a time, there lived a mad programmer. He loved to solve creative problems other than anything. His wife loved him quite a lot but disliked his curiosity for the problems. One day he came from office, his wife gave him a glass of cold lime juice. She was in a romantic mood and waiting for some romantic stuff. But the programmer asked her curiously, "If I give u radius of the top and bottom part of the glass and the height, can you come up with the volume of the glass?" His wife became a bit disappointed but as she is smart she replied with a smile, "You already have drunk some juice, and the glass is not full. If I give you the height of the juice, can you find the volume of the remaining juice in the glass?" Then the programmer kissed his wife and said, "You are the best problem setter in the world!"
Now he set the same problem for you. The radius of the upper part r1 and lower part r2 is given. If height of the glass is h and height of the juice is p what is the volume of the juice in the glass?
Input
Input starts with an integer T (≤ 100), denoting the number of test cases.
Each case starts with a line containing four integers r1 r2 h p (1 ≤ r2 < r1 ≤ 100, 1 ≤ p ≤ h ≤ 100).
Output
For each case, print the case number and the volume of the juice in the glass. Errors less than 10-6 will be ignored.
Sample Input |
Output for Sample Input |
| 2 5 2 3 2 5 2 3 3 |
Case 1: 58.643062867 Case 2: 122.52211349 |
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
#define PI acos(-1.0)
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t,test=1;
double h,p,r1,r2;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&r1,&r2,&h,&p);
double H=(h/(r1-r2))*r1;
double r3=r2+((r1-r2)/h)*p;
double v1=PI*r3*r3*(H-h+p)/3.0;
double v2=PI*r2*r2*(H-h)/3.0;
printf("Case %d: %.7lf\n",test++,v1-v2);
}
return 0;
}