java web从零单排第三期 《servlet》(1)
前两期不知道大家有没有一点感触。肯定会感觉有点迷茫,第一点,什么是jsp?
jsp是java server page的缩写,其中可以镶嵌一些html代码,<% %>中可以添加任何java代码,javascript脚本。
但跟servlet有什么关系呢,有关servlet在《servlet的那些事儿》中有一些简单地介绍。
jsp文件在编译时转换成了servlet,servlet其实就是java代码,因为java虚拟机本身比不识别jsp中的代码,就拿上一期中jsp中的代码为为例,他转换的servlet如下:
package org.apache.jsp;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.jsp.*;
import java.util.*;
public final class index_jsp extends org.apache.jasper.runtime.HttpJspBase
implements org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceDependent {
private static final JspFactory _jspxFactory = JspFactory.getDefaultFactory();
private static java.util.List _jspx_dependants;
private javax.el.ExpressionFactory _el_expressionfactory;
private org.apache.AnnotationProcessor _jsp_annotationprocessor;
public Object getDependants() {
return _jspx_dependants;
}
public void _jspInit() {
_el_expressionfactory = _jspxFactory.getJspApplicationContext(getServletConfig().getServletContext()).getExpressionFactory();
_jsp_annotationprocessor = (org.apache.AnnotationProcessor) getServletConfig().getServletContext().getAttribute(org.apache.AnnotationProcessor.class.getName());
}
public void _jspDestroy() {
}
public void _jspService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException, ServletException {
PageContext pageContext = null;
HttpSession session = null;
ServletContext application = null;
ServletConfig config = null;
JspWriter out = null;
Object page = this;
JspWriter _jspx_out = null;
PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;
try {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=ISO-8859-1");
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,
null, true, 8192, true);
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;
application = pageContext.getServletContext();
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();
session = pageContext.getSession();
out = pageContext.getOut();
_jspx_out = out;
out.write('\r');
out.write('\n');
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
out.write("\r\n");
out.write("\r\n");
out.write("<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC \"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN\">\r\n");
out.write("<html>\r\n");
out.write(" <head>\r\n");
out.write(" <base href=\"");
out.print(basePath);
out.write("\">\r\n");
out.write(" \r\n");
out.write(" <title>My JSP 'index.jsp' starting page</title>\r\n");
out.write("\t<meta http-equiv=\"pragma\" content=\"no-cache\">\r\n");
out.write("\t<meta http-equiv=\"cache-control\" content=\"no-cache\">\r\n");
out.write("\t<meta http-equiv=\"expires\" content=\"0\"> \r\n");
out.write("\t<meta http-equiv=\"keywords\" content=\"keyword1,keyword2,keyword3\">\r\n");
out.write("\t<meta http-equiv=\"description\" content=\"This is my page\">\r\n");
out.write("\t<!--\r\n");
out.write("\t<link rel=\"stylesheet\" type=\"text/css\" href=\"styles.css\">\r\n");
out.write("\t-->\r\n");
out.write(" </head>\r\n");
out.write(" \r\n");
out.write(" <body>\r\n");
out.write(" This is my JSP page. <br>\r\n");
out.write(" </body>\r\n");
out.write("</html>\r\n");
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (!(t instanceof SkipPageException)){
out = _jspx_out;
if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0)
try { out.clearBuffer(); } catch (java.io.IOException e) {}
if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t);
}
} finally {
_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);
}
}
}
一看,感觉乱乱的,的确servlet的代码量确实非常多,我们把注意力集中在public void _jspService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException, ServletException {}中,这里有两个参数,HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response。
公共接口类HttpServletRequest继承自ServletRequest.客户端浏览器发出的请求被封装成为一个HttpServletRequest对象。所有的信息包括请求的地址,请求的参数,提交的数据,上传的文件客户端的ip甚至客户端操作系统都包含在其内。HttpServletResponse继承了ServletResponse接口,并提供了与Http协议有关的方法,这些方法的主要功能是设置HTTP状态码和管理Cookie。
Web服务器收到一个http请求,会针对每个请求创建一个HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse对象,向客户端发送数据找HttpServletResponse,从客户端取数据找HttpServletRequest;
HttpServletResponse对象可以向客户端发送三种类型的数据:a.响应头b.状态码c.数据
好了,下面看try里面的代码。
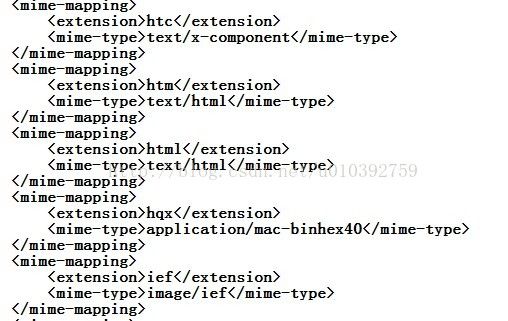
response.setContentType(MIME)的作用是使客户端浏览器,区分不同种类的数据,并根据不同的MIME调用浏览器内不同的程序嵌入模块来处理相应的数据,具体的mime类型在Tomcat 目录下的conf中的web.xml。部分如下:
ContentType 属性指定服务器响应的 HTTP 内容类型。如果未指定 ContentType,默认为 text/html。
out.println()主要是打印一些文本,这些文本会发送到浏览器上,展现给客户端。很显然jsp和servlet本质是一样的,在以前,sun公司首推出的是servlet,可这种代码非常拖沓,不易程序员编写,后来jsp的产生,简化了servlet的代码量 。
servlet代码在tomcat /work文件夹下,感兴趣同学可亲自研究研究。