AppWidget手把手教你(一步步很明白)
什么是AppWidget?AppWidget就是我们平常在桌面上见到的那种一个个的小窗口,利用这个小窗口可以给用户提供一些方便快捷的操作。本篇打算从以下几个点来介绍AppWidget:
1.如何创建一个简单的AppWidget
2.如何使得AppWidget与客户端程序交互
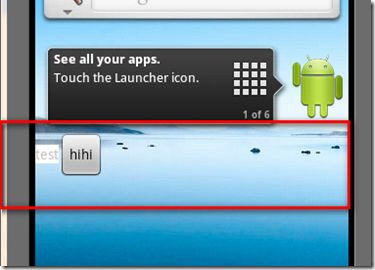
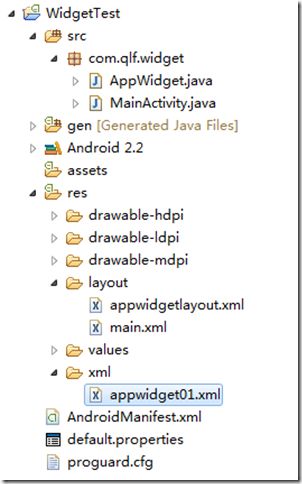
在介绍之前给大家看一下程序运行的最后结果和项目结构图,以便大家有个整体的印象。
运行结果图:
项目结构图:
第一步:
首先在res文件夹下新建一个名字为xml的文件夹,然后在xml目录下创建一个名为appwidget01的xml文件(如上图所示)。这个appwidget01中的内容如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<?
xml
version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<
appwidget-provider
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:minWidth = "294dp"
android:minHeight = "72dp"
android:updatePeriodMillis = "86400000"
android:initialLayout = "@layout/appwidgetlayout"
>
</
appwidget-provider
>
|
这个xml是用来描述你所要创建的appWidget的一些描述信息的,比如高度、宽度、刷新间隔、布局文件等等。仅仅这个描述文件还不够,我们看到的appWidget可都是有界面元素的呀,比如说文本,图片,按钮等等,这些东西的定义都需要放到layout文件夹下面。这个文件就是上面代码中写到的那个appwidgetlayout。
第二步:
在layout文件夹下面新建一个appwidgetlayout.xml文件,在这个文件中描述了appWidget的控件和布局等等信息,就和我们平常创建的一个activity的布局文件没什么两样,因为只是简单的演示,所以仅用一个文本和一个按钮。xml的内容如下:
<?
xml
version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<
LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<
TextView
android:id="@+id/txtapp" android:text="test" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#ffffff"></
TextView
>
<
Button
android:id="@+id/btnSend" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Send"></
Button
>
</
LinearLayout
>
|
第三步:
既然appWidget中存在按钮等等控件,那么就肯定少不了处理这些控件事件的处理代码啦。这些代码被放在一个继承于AppWidgetProvider的类中,在本例子中我新建了一个AppWidget的类,该类继承于AppWidgetProvider,以后所有的AppWidget上面的控件事件都会在这个类中处理。看一下类的内容:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
public
class
AppWidget
extends
AppWidgetProvider
{
private
final
String broadCastString =
"com.qlf.appWidgetUpdate"
;
/**
* 删除一个AppWidget时调用
* */
@Override
public
void
onDeleted(Context context,
int
[] appWidgetIds)
{
super
.onDeleted(context, appWidgetIds);
}
/**
* 最后一个appWidget被删除时调用
* */
@Override
public
void
onDisabled(Context context)
{
super
.onDisabled(context);
}
/**
* AppWidget的实例第一次被创建时调用
* */
@Override
public
void
onEnabled(Context context)
{
super
.onEnabled(context);
}
/**
* 接受广播事件
* */
@Override
public
void
onReceive(Context context, Intent intent)
{
super
.onReceive(context, intent);
}
/**
* 到达指定的更新时间或者当用户向桌面添加AppWidget时被调用
* */
@Override
public
void
onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager,
int
[] appWidgetIds)
{
}
}
|
各个方法的作用大家一看上面的注释就明白了。我们暂时不需要实现里面的方法。
第四步:
在AndroidManifest.xml中定义一些创建AppWidget必要的东西,先看代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<?
xml
version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<
manifest
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.qlf.widget" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0">
<
application
android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<
activity
android:name=".MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name">
<
intent-filter
>
<
action
android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<
category
android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</
intent-filter
>
</
activity
>
<
receiver
android:name="AppWidget">
<
intent-filter
>
<
action
android:name="android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_UPDATE"></
action
>
</
intent-filter
>
<
meta-data
android:name="android.appwidget.provider"
android:resource="@xml/appwidget01" />
</
receiver
>
</
application
>
<
uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8" />
</
manifest
>
|
可以看到我们在配置文件里面定义了一个receiver,他的名字是上面创建处理控件代码的那个类,下面那个intent-filter中的action是系统自带的用于更新所有appwidget的广播动作。然后meta-data标签是一个描述我们创建appwidget的元数据,那个android:name="android.appwidget.provider"是固定的,android:resource="@xml/appwidget01"指定创建的appWidget的描述信息的位置。这样程序就知道到哪里去初始化这些appWidget啦。
经过上面四个步骤,我想您已经能够成功在桌面上添加小工具了,效果就是我们最前面发出的样子。
前面我们只是简单的介绍了如何创建一个appWidget,但是目前这个appWidget还没有任何的交互功能。下面我们介绍一下appWidget如何与程序进行交互。首先要介绍一个对象,这个对象在appwidget和程序的交互中很重要,他就是RemoteViews。因为appwidget运行的进程和我们创建的应用不在一个进程中,所以我们也就不能像平常引用控件那样来获得控件的实例。这个时候RemoteViews出场了,从字面上看他的意思是远程的视图,也就是说通过这个东西我们能够获得不在同一进程中的对象,这也就为我们编写appwidget的处理事件提供了帮助。我们使用一下代码来创建一个RemoteViews :
|
1
2
3
|
RemoteViews remoteViews =
new
RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(),R.layout.appwidgetlayout);
remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.btnSend, pendingIntent);
//为小工具上的按钮绑定事件
|
可以看到上面又出现了一个陌生的对象pendingIntent,这个又是用来干嘛的呢?我们知道在一般的程序中绑定按钮的点击事件是直接在实现了OnClickListener接口的类中中完成的。不过因为appwidget并不在我们应用的进程中,所以当然他也访问不到我们在应用中设置的onclick代码啦。而PendingIntent就是被用来解决这个问题的。PendingIntent可以看成是一个特殊的Intent,如果我们把Intent看成一封信,那么PendingIntent就是一封被信封包裹起来的信。这封信在remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent()中被“邮寄”到了appwidget, 当appwidget中的按钮单击时他知道将这封信打开,并执行里面的内容。这样就避免了直接从appwidget中执行本地代码。我们来看看PendingIntent是如何定义的:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
//创建一个Intent对象
Intent intent =
new
Intent();
intent.setAction(broadCastString);
//这一步相当于写信,说明这个信的作用到底是什么,在这里表示将发送一个广播
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context,
0
, intent,
0
);
|
有了上面的介绍,我们在创建appwidget的交互应用时就简单不少了。我们剩下要做的工作就是在appwidget在创建的时候调用上面说到的方法为appwidget中的控件绑定事件,也就是在AppWidget类下的onUpdate方法中完成这个过程。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
/**
* 到达指定的更新时间或者当用户向桌面添加AppWidget时被调用
* */
@Override
public
void
onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager,
int
[] appWidgetIds)
{
//创建一个Intent对象
Intent intent =
new
Intent();
intent.setAction(broadCastString);
//设置pendingIntent的作用
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context,
0
, intent,
0
);
RemoteViews remoteViews =
new
RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(),R.layout.appwidgetlayout);
//绑定事件
remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.btnSend, pendingIntent);
//更新Appwidget
appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetIds, remoteViews);
}
|
通过上面的代码我们就为button按钮绑定了一个事件,这个事件的作用是发送一个广播便于其他应用接收、更新信息。这是appwidget发送广播,那么appwidget如何接受来自其他程序发送的广播呢?这就是public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent)的功能啦。这个方法会接收来自其他应用发出的广播,我们只要在这个程序中过滤我们需要的广播就能响应其他应用的操作来更新appwidget的信息了。要注意的是,因为appwidget运行的进程和我们创建的应用不在一个进程中的限制,所以更新的appwidget的时候也要通过远程对象来操作,具体代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
/**
* 接受广播事件
* */
@Override
public
void
onReceive(Context context, Intent intent)
{
if
(intent.getAction().equals(broadCastString))
{
//只能通过远程对象来设置appwidget中的控件状态
RemoteViews remoteViews =
new
RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(),R.layout.appwidgetlayout);
//通过远程对象将按钮的文字设置为”hihi”
remoteViews.setTextViewText(R.id.btnSend,
"hihi"
);
//获得appwidget管理实例,用于管理appwidget以便进行更新操作
AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager = AppWidgetManager.getInstance(context);
//相当于获得所有本程序创建的appwidget
ComponentName componentName =
new
ComponentName(context,AppWidget.
class
);
//更新appwidget
appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(componentName, remoteViews);
}
super
.onReceive(context, intent);
}
|
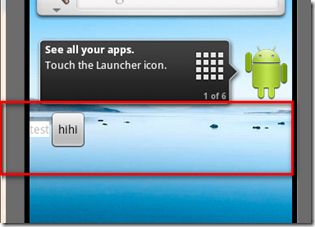
总结下就是appwidget上的操作都必须借助远程对象来操作。最后看一下运行的图片吧:
按之前:
按之后:
什么是AppWidget?AppWidget就是我们平常在桌面上见到的那种一个个的小窗口,利用这个小窗口可以给用户提供一些方便快捷的操作。本篇打算从以下几个点来介绍AppWidget:
1.如何创建一个简单的AppWidget
2.如何使得AppWidget与客户端程序交互
在介绍之前给大家看一下程序运行的最后结果和项目结构图,以便大家有个整体的印象。
运行结果图:
项目结构图:
第一步:
首先在res文件夹下新建一个名字为xml的文件夹,然后在xml目录下创建一个名为appwidget01的xml文件(如上图所示)。这个appwidget01中的内容如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<?
xml
version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<
appwidget-provider
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:minWidth = "294dp"
android:minHeight = "72dp"
android:updatePeriodMillis = "86400000"
android:initialLayout = "@layout/appwidgetlayout"
>
</
appwidget-provider
>
|
这个xml是用来描述你所要创建的appWidget的一些描述信息的,比如高度、宽度、刷新间隔、布局文件等等。仅仅这个描述文件还不够,我们看到的appWidget可都是有界面元素的呀,比如说文本,图片,按钮等等,这些东西的定义都需要放到layout文件夹下面。这个文件就是上面代码中写到的那个appwidgetlayout。
第二步:
在layout文件夹下面新建一个appwidgetlayout.xml文件,在这个文件中描述了appWidget的控件和布局等等信息,就和我们平常创建的一个activity的布局文件没什么两样,因为只是简单的演示,所以仅用一个文本和一个按钮。xml的内容如下:
<?
xml
version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<
LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<
TextView
android:id="@+id/txtapp" android:text="test" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#ffffff"></
TextView
>
<
Button
android:id="@+id/btnSend" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Send"></
Button
>
</
LinearLayout
>
|
第三步:
既然appWidget中存在按钮等等控件,那么就肯定少不了处理这些控件事件的处理代码啦。这些代码被放在一个继承于AppWidgetProvider的类中,在本例子中我新建了一个AppWidget的类,该类继承于AppWidgetProvider,以后所有的AppWidget上面的控件事件都会在这个类中处理。看一下类的内容:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
public
class
AppWidget
extends
AppWidgetProvider
{
private
final
String broadCastString =
"com.qlf.appWidgetUpdate"
;
/**
* 删除一个AppWidget时调用
* */
@Override
public
void
onDeleted(Context context,
int
[] appWidgetIds)
{
super
.onDeleted(context, appWidgetIds);
}
/**
* 最后一个appWidget被删除时调用
* */
@Override
public
void
onDisabled(Context context)
{
super
.onDisabled(context);
}
/**
* AppWidget的实例第一次被创建时调用
* */
@Override
public
void
onEnabled(Context context)
{
super
.onEnabled(context);
}
/**
* 接受广播事件
* */
@Override
public
void
onReceive(Context context, Intent intent)
{
super
.onReceive(context, intent);
}
/**
* 到达指定的更新时间或者当用户向桌面添加AppWidget时被调用
* */
@Override
public
void
onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager,
int
[] appWidgetIds)
{
}
}
|
各个方法的作用大家一看上面的注释就明白了。我们暂时不需要实现里面的方法。
第四步:
在AndroidManifest.xml中定义一些创建AppWidget必要的东西,先看代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<?
xml
version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<
manifest
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.qlf.widget" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0">
<
application
android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<
activity
android:name=".MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name">
<
intent-filter
>
<
action
android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<
category
android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</
intent-filter
>
</
activity
>
<
receiver
android:name="AppWidget">
<
intent-filter
>
<
action
android:name="android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_UPDATE"></
action
>
</
intent-filter
>
<
meta-data
android:name="android.appwidget.provider"
android:resource="@xml/appwidget01" />
</
receiver
>
</
application
>
<
uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8" />
</
manifest
>
|
可以看到我们在配置文件里面定义了一个receiver,他的名字是上面创建处理控件代码的那个类,下面那个intent-filter中的action是系统自带的用于更新所有appwidget的广播动作。然后meta-data标签是一个描述我们创建appwidget的元数据,那个android:name="android.appwidget.provider"是固定的,android:resource="@xml/appwidget01"指定创建的appWidget的描述信息的位置。这样程序就知道到哪里去初始化这些appWidget啦。
经过上面四个步骤,我想您已经能够成功在桌面上添加小工具了,效果就是我们最前面发出的样子。
前面我们只是简单的介绍了如何创建一个appWidget,但是目前这个appWidget还没有任何的交互功能。下面我们介绍一下appWidget如何与程序进行交互。首先要介绍一个对象,这个对象在appwidget和程序的交互中很重要,他就是RemoteViews。因为appwidget运行的进程和我们创建的应用不在一个进程中,所以我们也就不能像平常引用控件那样来获得控件的实例。这个时候RemoteViews出场了,从字面上看他的意思是远程的视图,也就是说通过这个东西我们能够获得不在同一进程中的对象,这也就为我们编写appwidget的处理事件提供了帮助。我们使用一下代码来创建一个RemoteViews :
|
1
2
3
|
RemoteViews remoteViews =
new
RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(),R.layout.appwidgetlayout);
remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.btnSend, pendingIntent);
//为小工具上的按钮绑定事件
|
可以看到上面又出现了一个陌生的对象pendingIntent,这个又是用来干嘛的呢?我们知道在一般的程序中绑定按钮的点击事件是直接在实现了OnClickListener接口的类中中完成的。不过因为appwidget并不在我们应用的进程中,所以当然他也访问不到我们在应用中设置的onclick代码啦。而PendingIntent就是被用来解决这个问题的。PendingIntent可以看成是一个特殊的Intent,如果我们把Intent看成一封信,那么PendingIntent就是一封被信封包裹起来的信。这封信在remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent()中被“邮寄”到了appwidget, 当appwidget中的按钮单击时他知道将这封信打开,并执行里面的内容。这样就避免了直接从appwidget中执行本地代码。我们来看看PendingIntent是如何定义的:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
//创建一个Intent对象
Intent intent =
new
Intent();
intent.setAction(broadCastString);
//这一步相当于写信,说明这个信的作用到底是什么,在这里表示将发送一个广播
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context,
0
, intent,
0
);
|
有了上面的介绍,我们在创建appwidget的交互应用时就简单不少了。我们剩下要做的工作就是在appwidget在创建的时候调用上面说到的方法为appwidget中的控件绑定事件,也就是在AppWidget类下的onUpdate方法中完成这个过程。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
/**
* 到达指定的更新时间或者当用户向桌面添加AppWidget时被调用
* */
@Override
public
void
onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager,
int
[] appWidgetIds)
{
//创建一个Intent对象
Intent intent =
new
Intent();
intent.setAction(broadCastString);
//设置pendingIntent的作用
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context,
0
, intent,
0
);
RemoteViews remoteViews =
new
RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(),R.layout.appwidgetlayout);
//绑定事件
remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.btnSend, pendingIntent);
//更新Appwidget
appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetIds, remoteViews);
}
|
通过上面的代码我们就为button按钮绑定了一个事件,这个事件的作用是发送一个广播便于其他应用接收、更新信息。这是appwidget发送广播,那么appwidget如何接受来自其他程序发送的广播呢?这就是public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent)的功能啦。这个方法会接收来自其他应用发出的广播,我们只要在这个程序中过滤我们需要的广播就能响应其他应用的操作来更新appwidget的信息了。要注意的是,因为appwidget运行的进程和我们创建的应用不在一个进程中的限制,所以更新的appwidget的时候也要通过远程对象来操作,具体代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
/**
* 接受广播事件
* */
@Override
public
void
onReceive(Context context, Intent intent)
{
if
(intent.getAction().equals(broadCastString))
{
//只能通过远程对象来设置appwidget中的控件状态
RemoteViews remoteViews =
new
RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(),R.layout.appwidgetlayout);
//通过远程对象将按钮的文字设置为”hihi”
remoteViews.setTextViewText(R.id.btnSend,
"hihi"
);
//获得appwidget管理实例,用于管理appwidget以便进行更新操作
AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager = AppWidgetManager.getInstance(context);
//相当于获得所有本程序创建的appwidget
ComponentName componentName =
new
ComponentName(context,AppWidget.
class
);
//更新appwidget
appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(componentName, remoteViews);
}
super
.onReceive(context, intent);
}
|
总结下就是appwidget上的操作都必须借助远程对象来操作。最后看一下运行的图片吧:
按之前:
按之后: