Android事件总线框架之AndroidEventBus
实际项目开发过程中,经常遇到如下场景:不同的应用程序组件的控件间具有一定的相互关联性,其中用户对后者进行的某种操作会引起前者的相应改变。举一个具体的场景:以新浪微博为例,在新浪微博首页好友动态列表页和好友动态详情页(微博正文),对于每个详情页而言,布局基本一致,在详情页点击了个赞,赞的数量增加,同时赞的图标发生了变化,此时返回到列表页,此新浪微博首页上的赞图标以及数量与刚刚详情页的需要保持一致。再举一个例子,对于多个底部导航tab下的资讯类阅读app,在咨询详情页点击了收藏,然后收藏成功,此时回到底部tab中的个人中心,假如个人中心中有我的收藏,同时后面显示的是收藏数量,此时此收藏数量需要同于于刚刚用户所进行的收藏/取消收藏而即时更改数字。显而易见,类似场景需求非常常见。
有时候,当此类需求相对简单时,通过接口以实现回调等方式可以完成,但是当不同组件/控件之间的关系纷繁复杂时,基于接口的方案不仅使得代码非常繁琐,同时是的程序逻辑很混乱,基于此,Android事件总线框架(AndroidEventBus 、EventBus、Otto) ,为此类需求的实现提供了非常方便的方案。
这里我以AndroidEventBus框架为例,为大家实现该功能。
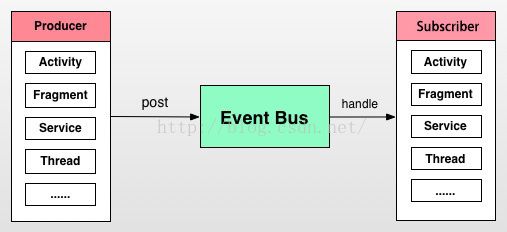
AndroidEventBus框架 基本结构
你可以按照下面几个步骤来使用AndroidEventBus.
1. 注册事件接收对象
public class YourActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main_activity);
// 注册对象
EventBus.getDefault().register(this);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
// 注销
EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);
super.onDestroy();
}
}
2. 通过Subscriber注解来标识事件接收对象中的接收方法
public class YourActivity extends Activity {
// code ......
// 接收方法,默认的tag,执行在UI线程
@Subscriber
private void updateUser(User user) {
Log.e("", "### update user name = " + user.name);
}
// 含有my_tag,当用户post事件时,只有指定了"my_tag"的事件才会触发该函数,执行在UI线程
@Subscriber(tag = "my_tag")
private void updateUserWithTag(User user) {
Log.e("", "### update user with my_tag, name = " + user.name);
}
// 含有my_tag,当用户post事件时,只有指定了"my_tag"的事件才会触发该函数,
// post函数在哪个线程执行,该函数就执行在哪个线程
@Subscriber(tag = "my_tag", mode=ThreadMode.POST)
private void updateUserWithMode(User user) {
Log.e("", "### update user with my_tag, name = " + user.name);
}
// 含有my_tag,当用户post事件时,只有指定了"my_tag"的事件才会触发该函数,执行在一个独立的线程
@Subscriber(tag = "my_tag", mode = ThreadMode.ASYNC)
private void updateUserAsync(User user) {
Log.e("", "### update user async , name = " + user.name + ", thread name = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
User类大致如下 :
public class User {
String name ;
public User(String aName) {
name = aName ;
}
}
接收函数使用tag来标识可接收的事件类型,与BroadcastReceiver中指定action是一样的,这样可以精准的投递消息。mode可以指定目标函数执行在哪个线程,默认会执行在UI线程,方便用户更新UI。目标方法执行耗时操作时,可以设置mode为ASYNC,使之执行在子线程中。
3. 在其他组件,例如Activity, Fragment,Service中发布事件
EventBus.getDefault().post(new User("android"));
// post a event with tag, the tag is like broadcast's action
EventBus.getDefault().post(new User("mr.simple"), "my_tag");
发布事件之后,注册了该事件类型的对象就会接收到响应的事件.
Android Studio集成<span style="font-weight: normal;"><span style="font-size:18px;">dependencies {
compile fileTree(include: ['*.jar'], dir: 'libs')
compile files('libs/androideventbus-1.0.5.jar')
}
</span></span>
我的simple例子
MainActivity
package com.cloudhome.androideventbus;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.design.widget.FloatingActionButton;
import android.support.design.widget.Snackbar;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.widget.TextView;
import org.simple.eventbus.EventBus;
import org.simple.eventbus.Subscriber;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Toolbar toolbar = (Toolbar) findViewById(R.id.toolbar);
setSupportActionBar(toolbar);
FloatingActionButton fab = (FloatingActionButton) findViewById(R.id.fab);
fab.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Snackbar.make(view, "Replace with your own action", Snackbar.LENGTH_LONG)
.setAction("Action", null).show();
}
});
//eventBus 注册
EventBus.getDefault().register(this);
}
//当在OtherActivity点击了更新按钮时,该方法会被执行,
//接受从OtherActivity传过来的参数,并显示在界面上
@Subscriber(tag = "update")
public void update(String msg){
TextView tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv);
tv.setText(msg);
}
//点击按钮跳转到OtherActivity
public void toOtherActivity(View view){
startActivity(new Intent(this, OtherActivity.class));
}
//点击按钮跳转到TestProgressBarActivity
public void updateProgressbar(View view){
startActivity(new Intent(this, TestProgressBarActivity.class));
}
// EventBus不要忘记注销!!!!
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
// Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will
// automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long
// as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml.
int id = item.getItemId();
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
if (id == R.id.action_settings) {
return true;
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
}
OtherActivity.java
package com.cloudhome.androideventbus;
import org.simple.eventbus.EventBus;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
public class OtherActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_other);
EventBus.getDefault().register(this);
}
//更新MainActivity
public void updateClick(View view){
String msg = "this msg was send by OtherActivity";
//这里post了一个带tag的消息,将msg传给MainActivity,MainActivity中带有名为update的tag的方法会被执行
EventBus.getDefault().post(msg, "update");
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);
}
}
TestProgressBarActivity.java
package com.cloudhome.androideventbus;
import org.simple.eventbus.EventBus;
import org.simple.eventbus.Subscriber;
import org.simple.eventbus.ThreadMode;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ProgressBar;
public class TestProgressBarActivity extends Activity {
private ProgressBar pb;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_testprogressbar);
pb = (ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.pb);
EventBus.getDefault().register(this);
}
//模拟下载
public void btnClick(View view){
//这里post了一个带tag的消息,则下面对应该tag的方法会被执行
EventBus.getDefault().post(view, "start download");
}
/**
* 这里的mode属性指定了该方法执行在哪个线程,有三个取值:MAIN, POST, ASYNC
* MAIN即该方法执行在UI线程,ASYNC即该方法执行在异步线程,POST则代表该方法
* 执行在与被调用的post方法相同的线程中,这里因为是模拟耗时的网络操作,所以
* 该方法一定要异步执行,若将mode改为MAIN,则界面会阻塞
* @param view
*/
@Subscriber(tag = "start download", mode = ThreadMode.ASYNC)
public void startDownload(View view){
int progress = 0;
while(progress <= 100){
progress += 10;
//这里post当前的下载进度,下面与这里指定的tag相同的方法会被执行
EventBus.getDefault().post(progress, "update progress");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//该方法的参数就是上面post的数据,在这里更新UI,且在主线程执行该方法
@Subscriber(tag = "update progress", mode = ThreadMode.MAIN)
public void updateProgress(int progress){
pb.setProgress(progress);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);
}
}
资源下载