glibc ctype
最近看了一下glibc,版本1.09.1。记录一下过程。
ctype.h
//实际上调用的都是__isctype
#define isalnum(c) __isctype((c), _ISalnum) #define isalpha(c) __isctype((c), _ISalpha) #define iscntrl(c) __isctype((c), _IScntrl) #define isdigit(c) __isctype((c), _ISdigit) #define islower(c) __isctype((c), _ISlower) #define isgraph(c) __isctype((c), _ISgraph) #define isprint(c) __isctype((c), _ISprint) #define ispunct(c) __isctype((c), _ISpunct) #define isspace(c) __isctype((c), _ISspace) #define isupper(c) __isctype((c), _ISupper) #define isxdigit(c) __isctype((c), _ISxdigit)
__isctype原型
#define __isctype(c, type) (__ctype_b[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) type)
_ISalnum,_ISalpha,_IScntrl的定义:
enum
{
_ISupper = 1 << 0, /* UPPERCASE. */
_ISlower = 1 << 1, /* lowercase. */
_IScntrl = 1 << 2, /* Control character. */
_ISdigit = 1 << 3, /* Numeric. */
_ISspace = 1 << 4, /* Whitespace. */
_IShex = 1 << 5, /* A - F, a - f. */
_ISpunct = 1 << 6, /* Punctuation. */
_NOgraph = 1 << 7, /* Printing but nongraphical. */
_ISblank = 1 << 8, /* Blank (usually SPC and TAB). */
_ISalpha = _ISupper | _ISlower, /* Alphabetic. */
_ISalnum = _ISalpha | _ISdigit, /* Alphanumeric. */
_ISxdigit = _ISdigit | _IShex, /* Hexadecimal numeric. */
_ISgraph = _ISalnum | _ISpunct, /* Graphical. */
_ISprint = _ISgraph | _NOgraph /* Printing. */
};
#define tolower(c) __tolower(c) #define toupper(c) __toupper(c) #define __tolower(c) ((int) __ctype_tolower[(int) (c)]) #define __toupper(c) ((int) __ctype_toupper[(int) (c)]) extern __const unsigned short int *__ctype_b; /* Characteristics. */ extern __const short int *__ctype_tolower; /* Case conversions. */ extern __const short int *__ctype_toupper; /* Case conversions. */
本来想查看__ctype_b所指向的内容。(http://refspecs.linuxfoundation.org/LSB_1.3.0/gLSB/gLSB/baselib---ctype-b.html)
__ctype_b is an array index for ctype functions.
__ctype_b is not in the source standard; it is only in the binary standard.
不能查看源代码,于是纠结了很长时间,到底里面是什么内容。
于是查看了the standard c library(http://download.csdn.net/detail/spch2008/4827435)
虽然具体实现未知,但根据书上的实现,大体明白了实现原理。
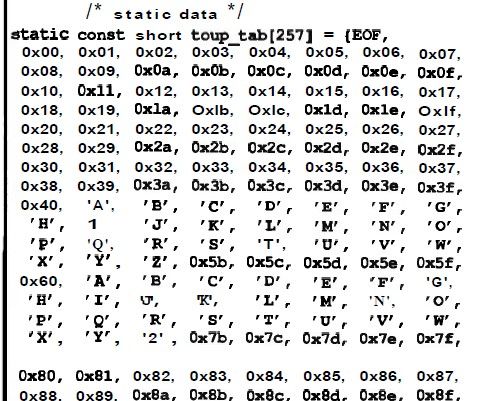
看一下toupper(c),__ctype_toupper[(int) (c)]。
相当于_ctype_toupper持有toup_tab地址,比如传入a(ASCLL值为97,0x61),
即__ctype_toupper[97]的值,查表得‘A’,于是返回‘A’的ASCLL码值65(0x41)。
同理, __tolower(c)的实现也是如此。
根据这个原理,可以推出 isalnum(c)类函数也是这样实现的。
上图,构建了特征表。上述enum枚举中定义的特征值应该与特征表对应。当然,这个图与特征表不对应,但是原理应该是一样的。
__ctype_b[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) type
用特征值与数组中的特征值&,如果为1,则匹配上,说明是所判断的类型,否则不是。
_ctype_b为unsigned short int*,_ctype_tolower,_ctype_toupper为short int*。
注释上是这样说的:
These point to the second element ([1]) of arrays of size (UCHAR_MAX + 1).
EOF is -1, so [EOF] is the first element of the original array.
ANSI requires that the ctype functions work for `unsigned char' values
and for EOF. The case conversion arrays are of `short int's rather than
`unsigned char's because tolower (EOF) must be EOF, which doesn't fit
into an `unsigned char'. */
即toupper, tolower遇到EOF的时候,返回-1,这样,就不能为unsigned。
而最大UCHAR_MAX为255,+1为256,显然char类型保存不下,所以只能扩大容量,
而第二小的即是short int。