Tutorial: Using roslaunch to start Gazebo, world files and URDF models
Tutorial: Using roslaunch to start Gazebo, world files and URDF models
参考:http://gazebosim.org/tutorials?tut=ros_roslaunch&cat=connect_ros
1. 使用roslaunch 打开仿真模型
参数:
paused Start Gazebo in a paused state (default false)
usesimtime Tells ROS nodes asking for time to get the Gazebo-published simulation time, published over the ROS topic /clock (default true)
gui Launch the user interface window of Gazebo (default true)
headless Disable any function calls to simulator rendering (Ogre) components. Does not work with gui:=true (default false)
debug Start gzserver (Gazebo Server) in debug mode using gdb (default false)
1.1 empty_world.launch
roslaunch gazebo_ros empty_world.launch <arg name="paused" default="false"/> <arg name="use_sim_time" default="true"/> <arg name="extra_gazebo_args" default=""/> <arg name="gui" default="true"/> <arg name="headless" default="false"/> <arg name="debug" default="false"/> <arg name="physics" default="ode"/> <arg name="verbose" default="false"/> <arg name="world_name" default="worlds/empty.world"/>
roslaunch gazebo_ros empty_world.launch paused:=true use_sim_time:=false gui:=true throttled:=false headless:=false debug:=true
1.2 mud_world.launch
继承自emptyworld.launch文件,并将涉及需要的参数进行改变。 ===》word 文件
rosed gazebo_ros mud_world.launch
<launch>
<!-- We resume the logic in empty_world.launch, changing only the name of the world to be launched -->
<include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch">
<arg name="world_name" value="worlds/mud.world"/> <!-- Note: the world_name is with respect to GAZEBO_RESOURCE_PATH environmental variable -->
<arg name="paused" value="false"/>
<arg name="use_sim_time" value="true"/>
<arg name="gui" value="true"/>
<arg name="headless" value="false"/>
<arg name="debug" value="false"/>
</include>
</launch>
1.3 World Files
先找三个gazebo的模型,先从本地gazebo模型库中找,路径在.gazebo/models ,找不到再从网络在线库(需要链接到goole,这已经被墙了)
<sdf version="1.4">
<world name="default">
<include>
<uri>model://sun</uri>
</include>
<include>
<uri>model://ground_plane</uri>
</include>
<include>
<uri>model://double_pendulum_with_base</uri>
<name>pendulum_thick_mud</name>
<pose>-2.0 0 0 0 0 0</pose>
</include>
...
</world>
</sdf>
2. Creating your own Gazebo ROS Package
文件夹
/MYROBOT_description 机器人模型与描述文件
/MYROBOT_gazebo world文件与launch文件
../catkin_ws/src 文件夹结构
/MYROBOT_description
package.xml
CMakeLists.txt
/urdf
MYROBOT.urdf
/meshes
mesh1.dae
mesh2.dae
...
/materials
/cad
/MYROBOT_gazebo
/launch
MYROBOT.launch
/worlds
MYROBOT.world
/models
world_object1.dae
world_object2.stl
world_object3.urdf
/materials
/plugins
2.1 建world 文件
建launch文件夹 YOUROBOT.launch
<launch>
<!-- We resume the logic in empty_world.launch, changing only the name of the world to be launched -->
<include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch">
<arg name="world_name" value="$(find MYROBOT_gazebo)/worlds/MYROBOT.world"/>
<!-- more default parameters can be changed here -->
</include>
</launch> 建 world文件夹 MYROBOT.world
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<sdf version="1.4">
<world name="default">
<include>
<uri>model://ground_plane</uri>
</include>
<include>
<uri>model://sun</uri>
</include>
<include>
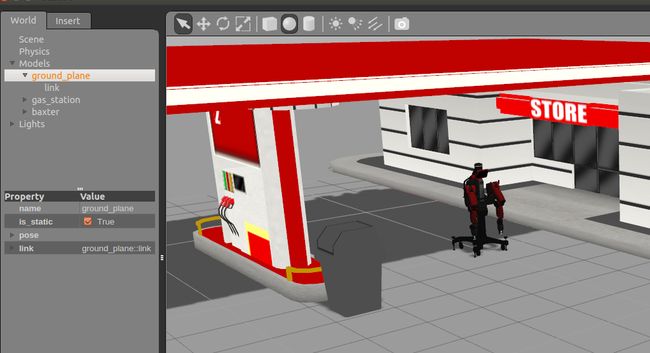
<uri>model://gas_station</uri>
<name>gas_station</name>
<pose>-2.0 7.0 0 0 0 0</pose>
</include>
</world>
</sdf>
用launch gazebo加载world文件
roslaunch MYROBOT_gazebo MYROBOT.launch
编辑world文件,可以依据gazebo 进行添加model,File->Save保存即可.
3. Using roslaunch to Spawn URDF Robots
3.1 ROS Service Call Spawn Method 推荐
将机器人的描述文件可以分开,利用 spawn_model脚本在相应包里调用就可以。 简化了包的存储结构。
keep your robot's location relative to a ROS package path, but also requires you to make a ROS service call using a small (python) script.
使用脚本语句spawn_model调用节点gazebo_ros的服务回调加载URDF文件到gazebo中,相应参数。
URDF Example with Baxter
下载Baxter模型包,
git clone https://github.com/RethinkRobotics/baxter_common.git运行 gazebo_ros 与 脚本
spawn_model 加载机器人。
rosrun gazebo_ros spawn_model -file `rospack find MYROBOT_description`/urdf/MYROBOT.urdf -urdf -x 0 -y 0 -z 1 -model MYROBOT
This method uses a small python script called
spawn_model to makea service call request to the
gazebo_ros ROS node(named simply "gazebo" in the rostopic namespace) to add a custom URDF into Gazebo.The
spawn_model script is located within the
gazebo_ros package.You can use this script in the following way:
rosrun gazebo_ros spawn_model -file `rospack find MYROBOT_description`/urdf/MYROBOT.urdf -urdf -x 0 -y 0 -z 1 -model MYROBOT
To see all of the available arguments for spawn_model including namespaces, trimesh properties, joint positions and RPY orientation run:
rosrun gazebo_ros spawn_model -h
----------也可以放到launch文件里,与world一起加载。
XACRO Example with PR2URDF is not in XML format but rather in XACRO format, XACRO格式的urdf文件。<!-- Spawn a robot into Gazebo --> <node name="spawn_urdf" pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model" args="-file $(find baxter_description)/urdf/baxter.urdf -urdf -z 1 -model baxter" />
sudo apt-get install ros-indigo-pr2-common
在launch里面加载机器人描述
<!-- Convert an xacro and put on parameter server --> <param name="robot_description" command="$(find xacro)/xacro.py $(find pr2_description)/robots/pr2.urdf.xacro" /> <!-- Spawn a robot into Gazebo --> <node name="spawn_urdf" pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model" args="-param robot_description -urdf -model pr2" />

3.2 Model Database Method
自己 建gazebo 模型
../catkin_ws/src
/MYROBOT_description
package.xml
CMakeLists.txt
model.config
/urdf
MYROBOT.urdf
/meshes
mesh1.dae
mesh2.dae
...
/materials
/plugins
/cad
- /home/user/catkin_workspace/src - this is treated as the location of a Gazebo Model Database
- /MYROBOT_description - this directory is treated as a single Gazebo model folder 模型文件夹
- model.config - this is a required configuration file for Gazebo to find this model in its database 配置描述性信息
- MYROBOT.urdf - this is your robot description file, also used by Rviz, MoveIt!, etc
- /meshes - put your .stl or .dae files in here, just as you would with regular URDFs
Environment Variable -tells Gazebo where to look for model databases
export GAZEBO_MODEL_PATH=/home/user/catkin_ws/src/Next Steps
Now that you know how to create roslaunch files that open Gazebo, world files and URDF models, you are now ready to create your own Gazebo-ready URDF model in the tutorialUsing A URDF In Gazebo