MonkeyRunner脚本的录制与回放分享
| 测试成功例子 |
| 你必须有android sdk, sdk的tools文件家里有一个monkeyrunner.bat.
2. 将如下录制内容拷贝到一个文件内,例如我起个名字为d:\monkey_recorder.py. |
|
device = mr.waitForConnection()
|
| Cmd命令输入命令:monkeyrunner d:\monkey_recorder.py |
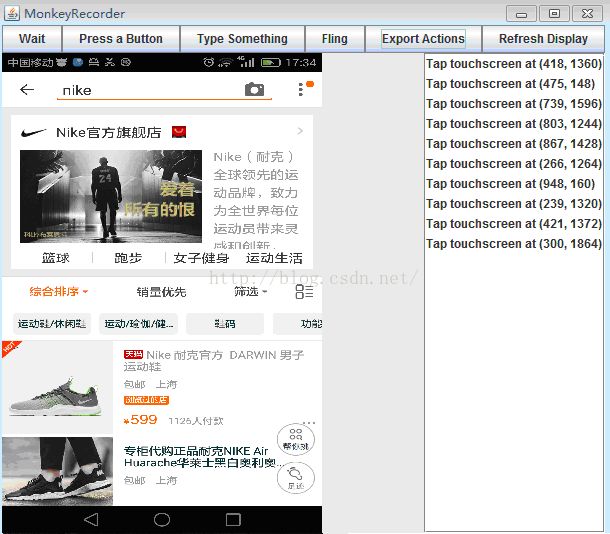
| 该窗口的功能: 1、可以自动显示手机当前的界面 2、自动刷新手机的最新状态 3、点击手机界面即可对手机进行操作,同时会反应到真机,而且会在右侧插入操作脚本 4:、wait: 用来插入下一次操作的时间间隔,点击后即可设置时间,单位是秒 Press a Button:用来确定需要点击的按钮,包括menu、home、search,以及对按钮的press、down、up属性 Type Something:用来输入内容到输入框 Fling:用来进行拖动操作,可以向上、下、左、右,以及操作的范围 Export Actions:用来导出脚本 Refresh Display:用来刷新手机界面,估计只有在断开手机后,重新连接时才会用到
|
| 当我们在这个工具上点击时,真机也会跟着执行,并且会显示每一步我们点击的位置的坐标,比如,我点击打开“我的淘宝”,并搜索nike会记录如下: (最好在每个操作直接插入wait等待)
|
| 我们看到了上面的画面, 电击或者选择按钮操作, 右边的一栏会把操作记录下来. 然后export 脚本文件.如d:\cc.mr录制的内容如下:
|
| PRESS|{'name':'MENU','type':'downAndUp',} WAIT|{'seconds':2.0,} TOUCH|{'x':432,'y':1376,'type':'downAndUp',} WAIT|{'seconds':4.0,} TOUCH|{'x':560,'y':140,'type':'downAndUp',} TOUCH|{'x':465,'y':148,'type':'downAndUp',} TYPE|{'message':'nike',} WAIT|{'seconds':4.0,} TOUCH|{'x':975,'y':148,'type':'downAndUp',} DRAG|{'start':(432,1449),'end':(432,289),'duration':1.0,'steps':10,} |
| 准备回放脚本play_back.py
|
| #!/usr/bin/env monkeyrunner # Copyright 2010, The Android Open Source Project # # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. # You may obtain a copy of the License at # # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 # # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and # limitations under the License.
import sys from com.android.monkeyrunner import MonkeyRunner
# The format of the file we are parsing is very carfeully constructed. # Each line corresponds to a single command. The line is split into 2 # parts with a | character. Text to the left of the pipe denotes # which command to run. The text to the right of the pipe is a python # dictionary (it can be evaled into existence) that specifies the # arguments for the command. In most cases, this directly maps to the # keyword argument dictionary that could be passed to the underlying # command.
# Lookup table to map command strings to functions that implement that # command. CMD_MAP = { 'TOUCH': lambda dev, arg: dev.touch(**arg), 'DRAG': lambda dev, arg: dev.drag(**arg), 'PRESS': lambda dev, arg: dev.press(**arg), 'TYPE': lambda dev, arg: dev.type(**arg), 'WAIT': lambda dev, arg: MonkeyRunner.sleep(**arg) }
# Process a single file for the specified device. def process_file(fp, device): for line in fp: (cmd, rest) = line.split('|') try: # Parse the pydict rest = eval(rest) except: print 'unable to parse options' continue
if cmd not in CMD_MAP: print 'unknown command: ' + cmd continue
CMD_MAP[cmd](device, rest)
def main(): file = sys.argv[1] fp = open(file, 'r') device = MonkeyRunner.waitForConnection()
process_file(fp, device) fp.close();
if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
|
|
| Cmd命令:(注:cc.mr文件是刚才录制生成的脚本) C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Android\sdk\tools>monkeyrunner d:\play_back.py d:\cc.mr |
|
运行结果就是刚才在手机上的录制操作重新再做一遍 |