Android进阶——使用Pull解析和生成轻量级数据XML
引言:
我们都知道XML被设计用来传输和存储数据。其设计宗旨是传输数据,而非显示数据,作为一种轻量级的数据格式,XML不仅可以应用于Web 开发的许多方面,常用于简化数据的存储和共享。而且在Android和Java中的数据交互方面也有大作为。
一 Pull解析器概述
作为一款开源的基于事件的解析器,Pull不仅可以在Android中直接使用,(事实上在Android内部很多XML的文件都是基于Pull的,Android官方也强烈推荐,所以不言而喻或许Pull 解析应该是你解析XML的第一选择吧)同样也适用于Java环境下的开发,唯一不同的是你需要自己去获取以下jar包文件:( kxml2-2.3.0.jar 和 xmlpull_1_x.jar下载)完成对应依赖库的配置。
二 Pull解析过程原理概述
Pull开始解析的时候,他会首先把xml文件读取到一个字符数组中,然后逐个字符读取当读取到结束标志”>”时,会去根据XML语法判断,若匹配了某种语法就会出发预定义的事件,比如说start document等,当解析到了start document之后就不会主动往后解析了,需要手动去调用parser.nextText()方法去往下遍历。需要注意的是与SAX不同它返回的是数字,需要我们自己去捕捉对应的事件并且完成相应的操作,如:开始元素和结束元素事件,使用parser.next()可以进入下一个元素并触发相应事件。事件将作为数值代码被发送,因此可以使用一个switch对感兴趣的事件进行处理。当元素开始解析时,调用parser.nextText()方法可以获取下一个Text类型元素的值。
简而言之,读取到XML的声明返回 START_DOCUMENT; 结束返回 END_DOCUMENT ; 开始标签返回 START_TAG;结束标签返回 END_TAG; 文本返回 TEXT。
三 利用Pull解析XML
1 根据面向对象的思想,把要解析的XML文件,封装构建成为对应的Java实体Bean
employeess.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<employees>
<employee id="26">
<name>cmo</name>
<position>android 开发工程师</position>
</employee>
<employee id="24">
<name>winds</name>
<position>Java开发工程师</position>
</employee>
</employees>Employees.java
package com.example.entity;
public class Employees {
private String id;
private String name;
private String position;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPosition() {
return position;
}
public void setPosition(String position) {
this.position = position;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee:"+ id +" 姓名:"+ name +"职位:"+ position;
}
}2 为了实现分层逻辑,提高代码的复用率和降低维护成本,定义一个接口,达到定义和实现逻辑分离的效果
package com.example.interfaces;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import com.example.entity.Employees;
public interface IEmployeeService {
//定义解析XML文件的方法
public List<Employees> parseXMLByPull(InputStream xml)throws Exception;
}3 在业务层实现具体的业务逻辑类
package com.example.model;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.xml.xpath.XPathFactory;
import org.xmlpull.v1.XmlPullParser;
import android.util.Xml;
import com.example.entity.Employees;
import com.example.interfaces.IEmployeeService;
public class EmployeeServiceIml implements IEmployeeService {
/* * (non-Javadoc) * @see com.example.interfaces.IEmployeeService#parseXMLByPull(java.io.InputStream) * 使用Pull解析XML */
@Override
public List<Employees> parseXMLByPull(InputStream xml) throws Exception {
List<Employees> empList=null;
Employees emp=null;
//首先得到Pull解析器
//XmlPullParser pull=(XmlPullParser) XPathFactory.newInstance();
XmlPullParser pull=Xml.newPullParser();
pull.setInput(xml, "UTF-8");//设置要解析XML数据源
//解析的过程中他会把xml读取到一个字符数组中,然后一个逐个字符读取当读取到结束标志">"时,会去根据XML语法判断,若匹配了某种语法就会出发预定义的事件比如说start document等,当解析到了start document之后就不会主动往后解析了
int event=pull.getEventType();//获取事件类型
while(event !=XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT){
switch (event) {
case XmlPullParser.START_DOCUMENT:
empList=new ArrayList<Employees>();
break;
//当解析到了Employee节点,触发Start_tag
case XmlPullParser.START_TAG:
if("employee".equals(pull.getName())){
String id=pull.getAttributeValue(null,"id");//因为元素节点Employee只有一个属性,所以索引为0
emp=new Employees();
emp.setId(id);
}
if("name".equals(pull.getName())){
String name=pull.nextText();
emp.setName(name);
}
if("position".equals(pull.getName())){
String position=pull.nextText();
emp.setPosition(position);
}
break;
//解析到结束标志时触发
case XmlPullParser.END_TAG:
if("employee".equals(pull.getName())){
empList.add(emp);
emp=null;
}
break;
}
event=pull.next();//主动去遍历下一个节点
}
xml.close();
return empList;
}
}4 在单元测试框架下,测试解析方法
package com.example.test;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import com.example.entity.Employees;
import com.example.interfaces.IEmployeeService;
import com.example.model.EmployeeServiceIml;
import android.test.AndroidTestCase;
import android.util.Log;
public class TestParseXML extends AndroidTestCase {
public void testParseXML() throws Exception{
IEmployeeService mEmpservice=new EmployeeServiceIml();
List<Employees> empList;
InputStream ins=getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("employeess.xml");
if(ins==null){
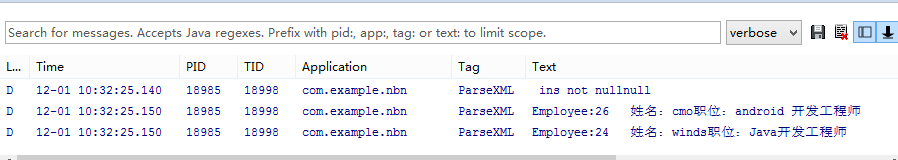
Log.d("ParseXML", " ins nullnull");
}else{
Log.d("ParseXML", " ins not nullnull");
}
empList=mEmpservice.parseXMLByPull(ins);
if(empList==null){
Log.d("ParseXML", " emp nullnull");
}
for (Employees employees : empList) {
Log.d("ParseXML",employees .toString());
}
}
}四 利用Pull生成XML
虽然我们需要生成一个XML文件的方法有很多,如:可以只使用一个StringBuilder组拼XML内容,然后把内容写入到文件中;或者使用DOM API生成XML文件,或者也可以使用Pull解析器生成XML文件,官方推荐我们使用Pull解析器,业务逻辑和代码结构还是采用我们解析XML时的,
/* * (non-Javadoc) * * @see * com.example.interfaces.IEmployeeService#saveXMLByPull(java.util.List, * java.io.Writer) Writer 数据的输出指向 */
@Override
public void saveXMLByPull(List<Employees> empList, OutputStream out)
throws Exception {
XmlSerializer serializer = Xml.newSerializer();
serializer.setOutput(out, "UTF-8");
serializer.startDocument("UTF-8", true);
// 第一个参数为命名空间,如果不使用命名空间,可以设置为null
serializer.startTag(null, "employees");
for (Employees emp : empList) {
serializer.startTag(null, "employee");// 生成这个<employees>
serializer.attribute(null, "id", emp.getId());// 设置属性id的值
serializer.startTag(null, "name");
serializer.text(emp.getName());
serializer.endTag(null, "name");
serializer.startTag(null, "position");
serializer.text(emp.getPosition());
serializer.endTag(null, "position");
serializer.endTag(null, "employee");// </employees>
}
serializer.endTag(null, "employees");
serializer.endDocument();
out.flush();
out.close();
}测试保存XML方法,保存到data/data/<应用包名>路径下
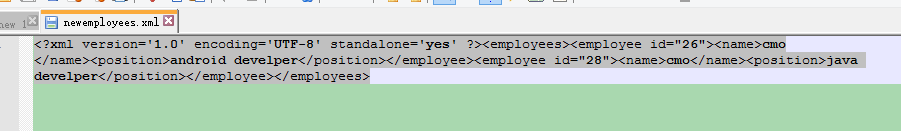
public void testSaveXMLByPull() throws Exception{
List<Employees> empList=new ArrayList<Employees>();
IEmployeeService mEmpservice=new EmployeeServiceIml();
empList.add(new Employees("26","cmo","android develper"));
empList.add(new Employees("28","cmo","java develper"));
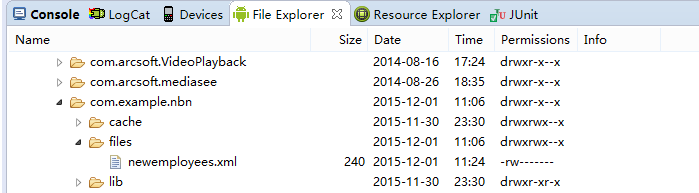
File xml=new File(getContext().getFilesDir(),"newemployees.xml");//保存文件到/<package>/files下
FileOutputStream fout=new FileOutputStream(xml);
mEmpservice.saveXMLByPull(empList, fout);
}