线程间通讯机制——深入浅出实现原理
前言:
这一篇博文主要是和大家讲解一下线程间通讯机制的内部实现原理,即Handler、Message、MessageQueue、Looper、HandlerThread、AsyncTask类的实现以及之间的关系。如果还没有接触过Handler+Message+Runnable、HandlerThread、AsyncTask的朋友可以先看看基础篇:
【Android开发】线程间通讯机制(基础篇)——Handler、Runnable、HandlerThread、AsyncTask的使用
有时候,如果你能带着问题或者目标去探索新知识的话,这样的学习效率就高很多。所以我们先从最基础的实现方式(Handler+Message+Runnable)说起。
一、Handler+Message+Runnable内部解析
问题:我们在使用Handler类的时候,都知道有sendMessage(Message)等发送消息的功能和post(Runnable)发送任务的功能,然后还有能够处理接受到的Message的功能。这时候我就会提出这样的问题:
1、有发送、接受Message的功能,是不是sendMessage方法是直接调用handleMessage的重写方法里呢?
2、不是有按时间计划发送Message和Runnable吗?如果问题1成立的话,handleMessage可能会同时接受多个Message,但是此方法不是线程安全的(没有synchronized修饰),这样会出现问题了。
解决问题:如果对API有任何疑惑,最根本的方法就是查看源代码。
在看源代码之前,需要了解几个类:
Handler:负责发送Message和Runnable到MessageQueue中,然后依次处理MessageQueue里面的队列。
MessageQueue:消息队列。负责存放一个线程的Message和Runnable的集合。
Message:消息实体类。
Looper:消息循环器。负责把MessageQueue中的Message或者Runnable循环取出来,然后分发到Handler中。
四者的关系:一个线程可以有多个Handler实例,一个线程对应一个Looper,一个Looper也只对应一个MessageQueue,一个MessageQueue对应多个Message和Runnable。所以就形成了一对多的对应关系,一方:线程、Looper、MessageQueue;多方:Handler、Message。同时可以看出另一个一对一关系:一个Message实例对应一个Handler实例。
一个Handler实例都会与一个线程和消息队列捆绑在一起,当实例化Handler的时候,就已经完成这样的工作。源码如下:
Handler类
/**
* Default constructor associates this handler with the {@link Looper} for the
* current thread.
*
* If this thread does not have a looper, this handler won't be able to receive messages
* so an exception is thrown.
*/
public Handler() {
this(null, false);
}
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {
if (FIND_POTENTIAL_LEAKS) {
final Class<? extends Handler> klass = getClass();
if ((klass.isAnonymousClass() || klass.isMemberClass() || klass.isLocalClass()) &&
(klass.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) == 0) {
Log.w(TAG, "The following Handler class should be static or leaks might occur: " +
klass.getCanonicalName());
}
}
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
if (mLooper == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()");
}
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
mCallback = callback;
mAsynchronous = async;
}
可以从mLooper = Looper.myLooper()
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;看出,实例化Handler就会绑定一个Looper实例,并且一个Looper实例包涵一个MessageQueue实例。
问题来了,为什么说一个线程对应一个Looper实例?我们通过Looper.myLooper()找原因:
Looper类
// sThreadLocal.get() will return null unless you've called prepare().
static final ThreadLocal<Looper> sThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Looper>();
/**
* Return the Looper object associated with the current thread. Returns
* null if the calling thread is not associated with a Looper.
*/
public static Looper myLooper() {
return sThreadLocal.get();
}
ThreadLocal类
Implements a thread-local storage, that is, a variable for which each thread has its own value. All threads sharethe sameThreadLocal object, but each sees a different value when accessing it, and changes made by onethread do not affect the other threads. The implementation supportsnull values.
——实现一个线程本地的存储,就是说每个线程都会有自己的内存空间来存放线程自己的值。所有线程都共享一个ThreadLocal对象,但是不同的线程都会对应不同的value,而且单独修改不影响其他线程的value,并且支持null值。
所以说,每个线程都会存放一个独立的Looper实例,通过ThreadLocal.get()方法,就会获得当前线程的Looper的实例。
好了,接下来就要研究一下Handler发送Runnable,究竟怎么发送?
Handler类:
public final boolean post(Runnable r)
{
return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r), 0);
}
private static Message getPostMessage(Runnable r) {
Message m = Message.obtain();
m.callback = r;
return m;
}
可以看出,其实传入的Runnable对象都是封装到Message类中,看下Message是存放什么信息:
Message类:
public final class Message implements Parcelable {
public int what;
public int arg1;
public int arg2;
public Object obj;
public Messenger replyTo;
long when;
Bundle data;
Handler target;
Runnable callback;
Message next;
private static Object mPoolSync = new Object();
private static Message mPool;
private static int mPoolSize = 0;
private static final int MAX_POOL_SIZE = 10;
When: 向Handler发送Message生成的时间
Data: 在Bundler 对象上绑定要线程中传递的数据
Next: 当前Message 对一下个Message 的引用
Handler: 处理当前Message 的Handler对象.
mPool: 通过字面理解可能叫他Message池,但是通过分析应该叫有下一个Message引用的Message链更加适合.
其中Message.obtain(),通过源码分析就是获取断掉Message链关系的第一个Message.
对于源码的解读,可以明确两点:
1)Message.obtain()是通过从全局Message pool中读取一个Message,回收的时候也是将该Message 放入到pool中。
2)Message中实现了Parcelable接口
所以接下来看下Handler如何发送Message:
Handler类
/**
* Enqueue a message into the message queue after all pending messages
* before the absolute time (in milliseconds) <var>uptimeMillis</var>.
* <b>The time-base is {@link android.os.SystemClock#uptimeMillis}.</b>
* You will receive it in {@link #handleMessage}, in the thread attached
* to this handler.
*
* @param uptimeMillis The absolute time at which the message should be
* delivered, using the
* {@link android.os.SystemClock#uptimeMillis} time-base.
*
* @return Returns true if the message was successfully placed in to the
* message queue. Returns false on failure, usually because the
* looper processing the message queue is exiting. Note that a
* result of true does not mean the message will be processed -- if
* the looper is quit before the delivery time of the message
* occurs then the message will be dropped.
*/
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
if (queue == null) {
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");
Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
}
return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);
}
private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
msg.target = this;
if (mAsynchronous) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
}
其实无论是按时间计划发送Message或者Runnable,最终是调用了sendMessageAtTime方法,里面核心执行的是enqueueMessage方法,就是调用了MessageQueue中的enqueueMessage方法,就是把消息Message加入到消息队列中。
这时候问题又来了,如果发送消息只是把消息加入到消息队列中,那谁来把消息分发到Handler中呢?
不妨我们看看Looper类:
/**
* Run the message queue in this thread. Be sure to call
* {@link #quit()} to end the loop.
*/
public static void loop() {
final Looper me = myLooper();
if (me == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
}
final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;
// Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,
// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.
Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
for (;;) {
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
}
// This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger
Printer logging = me.mLogging;
if (logging != null) {
logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +
msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);
}
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
if (logging != null) {
logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback);
}
// Make sure that during the course of dispatching the
// identity of the thread wasn't corrupted.
final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
if (ident != newIdent) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to "
+ msg.target.getClass().getName() + " "
+ msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what);
}
msg.recycle();
}
}
里面loop方法找到调用Handler的dispatchMessage的方法,我们再看看Handler的dispatchMessage:
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.callback != null) {
handleCallback(msg);
} else {
if (mCallback != null) {
if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
return;
}
}
handleMessage(msg);
}
}
dispatchMessage最终是回调了handleMessage。换句话说,Loop的loop()方法就是取得当前线程中的MessageQueue实例,然后不断循环消息分发到对应的Handler实例上。就是只要调用Looper.loop()方法,就可以执行消息分发。
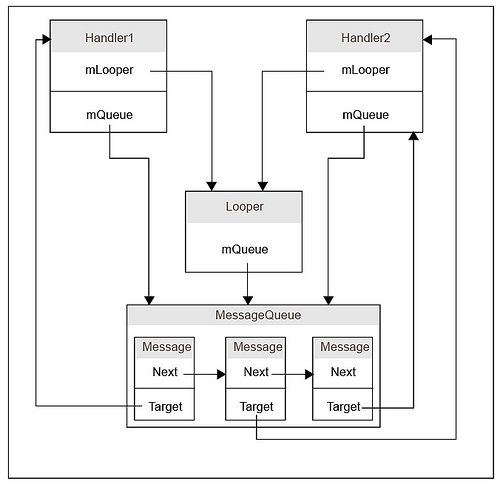
小结:Handler、Message、MessageQueue、Looper的关系原理图:
整个机制实现原理流程:当应用程序运行的时候,会创建一个主线程(UI线程)ActivityThread,这个类里面有个main方法,就是java程序运行的最开始的入口
public static void main(String[] args) {
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
// CloseGuard defaults to true and can be quite spammy. We
// disable it here, but selectively enable it later (via
// StrictMode) on debug builds, but using DropBox, not logs.
CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);
Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>");
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = new Handler();
}
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
UI线程就开始就已经调用了loop消息分发,所以当在UI线程实例的Handler对象发送消息或者任务时,会把Message加入到MessageQueue消息队列中,然后分发到Handler的handleMessage方法里。
二、HandlerThread
其实上述就是线程间通讯机制的实现,而HandlerThread和AsyncTask只是对通讯机制进行进一步的封装,要理解也很简单:
HandlerThread类:
public class HandlerThread extends Thread {
int mPriority;
int mTid = -1;
Looper mLooper;
public HandlerThread(String name) {
super(name);
mPriority = Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_DEFAULT;
}
/**
* Constructs a HandlerThread.
* @param name
* @param priority The priority to run the thread at. The value supplied must be from
* {@link android.os.Process} and not from java.lang.Thread.
*/
public HandlerThread(String name, int priority) {
super(name);
mPriority = priority;
}
/**
* Call back method that can be explicitly overridden if needed to execute some
* setup before Looper loops.
*/
protected void onLooperPrepared() {
}
public void run() {
mTid = Process.myTid();
Looper.prepare();
synchronized (this) {
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
notifyAll();
}
Process.setThreadPriority(mPriority);
onLooperPrepared();
Looper.loop();
mTid = -1;
}
/**
* This method returns the Looper associated with this thread. If this thread not been started
* or for any reason is isAlive() returns false, this method will return null. If this thread
* has been started, this method will block until the looper has been initialized.
* @return The looper.
*/
public Looper getLooper() {
if (!isAlive()) {
return null;
}
// If the thread has been started, wait until the looper has been created.
synchronized (this) {
while (isAlive() && mLooper == null) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
return mLooper;
}
/**
* Ask the currently running looper to quit. If the thread has not
* been started or has finished (that is if {@link #getLooper} returns
* null), then false is returned. Otherwise the looper is asked to
* quit and true is returned.
*/
public boolean quit() {
Looper looper = getLooper();
if (looper != null) {
looper.quit();
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* Returns the identifier of this thread. See Process.myTid().
*/
public int getThreadId() {
return mTid;
}
}
可以看得出,HandlerThread继承了Thread,从run()方法可以看出,HandlerThread要嗲用start()方法,才能实例化HandlerThread的Looper对象,和消息分发功能。
所以使用HandlerThread,必须先运行HandlerThread,才能取出对应的Looper对象,然后使用Handler(Looper)构造方法实例Handler,这样Handler的handleMessage方法就是子线程执行了。
三、AsyncTask
AsyncTask现在是android应用开发最常用的工具类,这个类面向调用者是轻量型的,但是对于系统性能来说是重量型的。这个类很强大,使用者很方便就能使用,只需要在对应的方法实现特定的功能即可。就是因为AsyncTask的强大封装,所以说不是轻量型的,先看下源代码吧:
public abstract class AsyncTask<Params, Progress, Result> {
private static final String LOG_TAG = "AsyncTask";
private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE = 5;
private static final int MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE = 128;
private static final int KEEP_ALIVE = 1;
private static final ThreadFactory sThreadFactory = new ThreadFactory() {
private final AtomicInteger mCount = new AtomicInteger(1);
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "AsyncTask #" + mCount.getAndIncrement());
}
};
private static final BlockingQueue<Runnable> sPoolWorkQueue =
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(10);
/**
* An {@link Executor} that can be used to execute tasks in parallel.
*/
public static final Executor THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR
= new ThreadPoolExecutor(CORE_POOL_SIZE, MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE, KEEP_ALIVE,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, sPoolWorkQueue, sThreadFactory);
/**
* An {@link Executor} that executes tasks one at a time in serial
* order. This serialization is global to a particular process.
*/
public static final Executor SERIAL_EXECUTOR = new SerialExecutor();
private static final int MESSAGE_POST_RESULT = 0x1;
private static final int MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS = 0x2;
private static final InternalHandler sHandler = new InternalHandler();
private static volatile Executor sDefaultExecutor = SERIAL_EXECUTOR;
private final WorkerRunnable<Params, Result> mWorker;
private final FutureTask<Result> mFuture;
private volatile Status mStatus = Status.PENDING;
private final AtomicBoolean mCancelled = new AtomicBoolean();
private final AtomicBoolean mTaskInvoked = new AtomicBoolean();
private static class SerialExecutor implements Executor {
final ArrayDeque<Runnable> mTasks = new ArrayDeque<Runnable>();
Runnable mActive;
public synchronized void execute(final Runnable r) {
mTasks.offer(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
r.run();
} finally {
scheduleNext();
}
}
});
if (mActive == null) {
scheduleNext();
}
}
protected synchronized void scheduleNext() {
if ((mActive = mTasks.poll()) != null) {
THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR.execute(mActive);
}
}
}
/**
* Indicates the current status of the task. Each status will be set only once
* during the lifetime of a task.
*/
public enum Status {
/**
* Indicates that the task has not been executed yet.
*/
PENDING,
/**
* Indicates that the task is running.
*/
RUNNING,
/**
* Indicates that {@link AsyncTask#onPostExecute} has finished.
*/
FINISHED,
}
/** @hide Used to force static handler to be created. */
public static void init() {
sHandler.getLooper();
}
/** @hide */
public static void setDefaultExecutor(Executor exec) {
sDefaultExecutor = exec;
}
/**
* Creates a new asynchronous task. This constructor must be invoked on the UI thread.
*/
public AsyncTask() {
mWorker = new WorkerRunnable<Params, Result>() {
public Result call() throws Exception {
mTaskInvoked.set(true);
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
//noinspection unchecked
return postResult(doInBackground(mParams));
}
};
mFuture = new FutureTask<Result>(mWorker) {
@Override
protected void done() {
try {
postResultIfNotInvoked(get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
android.util.Log.w(LOG_TAG, e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("An error occured while executing doInBackground()",
e.getCause());
} catch (CancellationException e) {
postResultIfNotInvoked(null);
}
}
};
}
private void postResultIfNotInvoked(Result result) {
final boolean wasTaskInvoked = mTaskInvoked.get();
if (!wasTaskInvoked) {
postResult(result);
}
}
private Result postResult(Result result) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Message message = sHandler.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_POST_RESULT,
new AsyncTaskResult<Result>(this, result));
message.sendToTarget();
return result;
}
public final Status getStatus() {
return mStatus;
}
protected abstract Result doInBackground(Params... params);
protected void onPreExecute() {
}
@SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"})
protected void onPostExecute(Result result) {
}
@SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"})
protected void onProgressUpdate(Progress... values) {
}
@SuppressWarnings({"UnusedParameters"})
protected void onCancelled(Result result) {
onCancelled();
}
protected void onCancelled() {
}
public final boolean isCancelled() {
return mCancelled.get();
}
public final boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
mCancelled.set(true);
return mFuture.cancel(mayInterruptIfRunning);
}
public final Result get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
return mFuture.get();
}
public final Result get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException,
ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
return mFuture.get(timeout, unit);
}
public final AsyncTask<Params, Progress, Result> execute(Params... params) {
return executeOnExecutor(sDefaultExecutor, params);
}
public final AsyncTask<Params, Progress, Result> executeOnExecutor(Executor exec,
Params... params) {
if (mStatus != Status.PENDING) {
switch (mStatus) {
case RUNNING:
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:"
+ " the task is already running.");
case FINISHED:
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:"
+ " the task has already been executed "
+ "(a task can be executed only once)");
}
}
mStatus = Status.RUNNING;
onPreExecute();
mWorker.mParams = params;
exec.execute(mFuture);
return this;
}
public static void execute(Runnable runnable) {
sDefaultExecutor.execute(runnable);
}
protected final void publishProgress(Progress... values) {
if (!isCancelled()) {
sHandler.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS,
new AsyncTaskResult<Progress>(this, values)).sendToTarget();
}
}
private void finish(Result result) {
if (isCancelled()) {
onCancelled(result);
} else {
onPostExecute(result);
}
mStatus = Status.FINISHED;
}
private static class InternalHandler extends Handler {
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "RawUseOfParameterizedType"})
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
AsyncTaskResult result = (AsyncTaskResult) msg.obj;
switch (msg.what) {
case MESSAGE_POST_RESULT:
// There is only one result
result.mTask.finish(result.mData[0]);
break;
case MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS:
result.mTask.onProgressUpdate(result.mData);
break;
}
}
}
private static abstract class WorkerRunnable<Params, Result> implements Callable<Result> {
Params[] mParams;
}
@SuppressWarnings({"RawUseOfParameterizedType"})
private static class AsyncTaskResult<Data> {
final AsyncTask mTask;
final Data[] mData;
AsyncTaskResult(AsyncTask task, Data... data) {
mTask = task;
mData = data;
}
}
}
要理解这个工具类,主要是理解这几个成员对象:
private static final InternalHandler sHandler = new InternalHandler();
private static volatile Executor sDefaultExecutor = SERIAL_EXECUTOR;
private final WorkerRunnable<Params, Result> mWorker;
private final FutureTask<Result> mFuture;
分析:sHandler
消息的发送者和处理者
sDefualtExecutor
线程执行者。实际上就是一个线程池。
mWorker
WorkerRunnable实现了Callable接口,就是有返回值的线程任务。
mFuture
FutureTask是对Callable执行的一个管理类,能够获得线程执行返回的结果,和取消执行等操作。我们再深入一下FutureTask,其中的done()方法是回调方法:
/**
* Removes and signals all waiting threads, invokes done(), and
* nulls out callable.
*/
private void finishCompletion() {
// assert state > COMPLETING;
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) {
for (;;) {
Thread t = q.thread;
if (t != null) {
q.thread = null;
LockSupport.unpark(t);
}
WaitNode next = q.next;
if (next == null)
break;
q.next = null; // unlink to help gc
q = next;
}
break;
}
}
done();
callable = null; // to reduce footprint
}
只要线程移除或者挂起(取消)的时候,就会调用done()方法,然后在AsyncTask类中的mTask实现了done()方法,最后回调onCancelled()方法。
具体的流程原理是这样的:
1、当第一次AsyncTask在UI线程实例化,其实是实例化Handler,同时UI线程的Looper和MessageQueue绑定在sHandler对象中,之后再去实例话AsyncTask不会在初始化Handler,因为sHandler是类变量。
2、当执行execute方法的时候,实际上是调用线程池的execute方法运行线程
3、callable线程执行体就是调用了doInBackground(mParams)方法,然后以返回结果result当参数,又调用postResult(Result result),实际上就是利用sHandler来发送result到UI线程的MessageQueue中,最后sHandler接受到result后,回调onPostExecute方法。
4、如果主动调用publishProgress(Progress... values)方法,就会利用sHandler把value发送到UI线程的MessageQueue中,然后sHandler接收到value后,回调onProgressUpdate(Progress... values)方法。
注意:sHandler和mDefaultExecutor是类变量
mWorker和mFuture是实例变量
所以,无论进程中生成多少个AysncTask对象,sHandler和mDefaultExecutor都是同一个,只是任务不同而已。
四、总结
由于我放上去的源代码删除了一些注释,如果还不能了解清楚的话,可以自行去源代码上观看。线程间通讯机制的核心就是Handler+Message+Looper+MessageQueue,只要理解这个四者的实现原理,再多的封装好的工具类也难理解。所以,必须记住一点:android应用开发多线程是必不可少的,所以我们必须遵循UI线程模式开发,就是所有耗时不能在UI线程执行,操作UI必须在UI线程中执行。