Volley解析
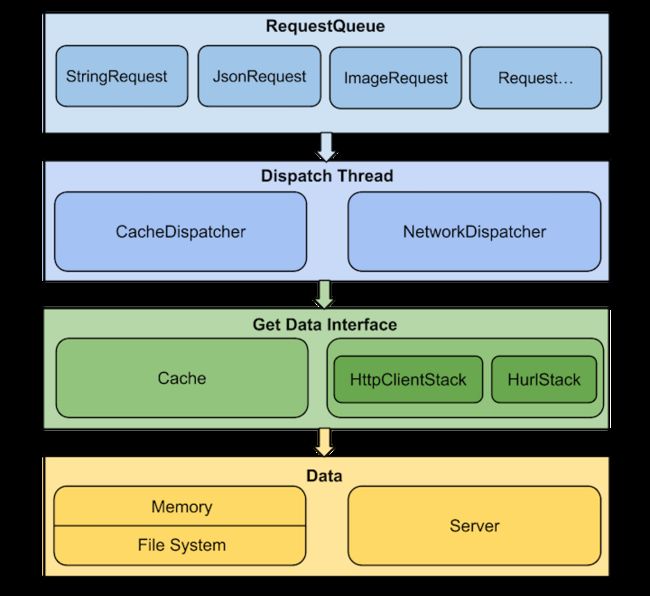
总体设计图
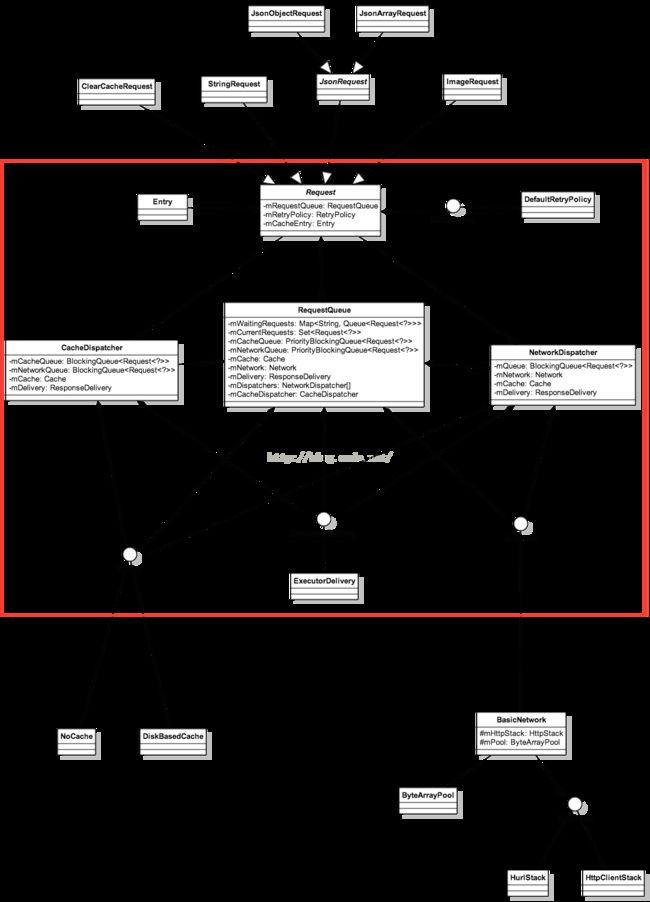
类图
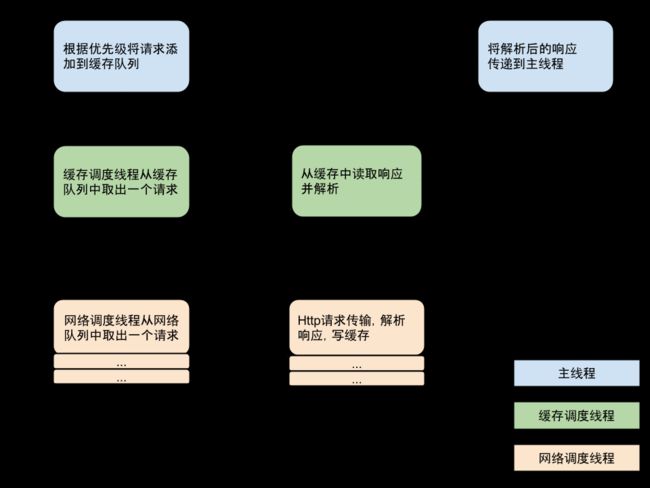
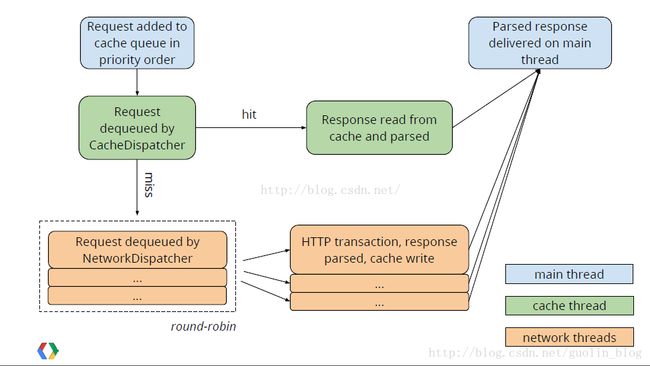
请求流程图
一.关于缓存的探讨
1.Volley.newRequestQueue创建一个请求队列
public static RequestQueue newRequestQueue(Context context, HttpStack stack, int maxDiskCacheBytes) {
File cacheDir = new File(context.getCacheDir(), DEFAULT_CACHE_DIR);
String userAgent = "volley/0";
try {
String packageName = context.getPackageName();
PackageInfo info = context.getPackageManager().getPackageInfo(packageName, 0);
userAgent = packageName + "/" + info.versionCode;
} catch (NameNotFoundException e) {
}
if (stack == null) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 9) {
stack = new HurlStack();
} else {
// Prior to Gingerbread, HttpUrlConnection was unreliable.
// See: http://android-developers.blogspot.com/2011/09/androids-http-clients.html
stack = new HttpClientStack(AndroidHttpClient.newInstance(userAgent));
}
}
Network network = new BasicNetwork(stack);
RequestQueue queue;
if (maxDiskCacheBytes <= -1)
{
// No maximum size specified
queue = new RequestQueue(new DiskBasedCache(cacheDir), network);
}
else
{
// Disk cache size specified
queue = new RequestQueue(new DiskBasedCache(cacheDir, maxDiskCacheBytes), network);
}
queue.start();
return queue;
}
第2行代码是在data/data//cache目录下创建一个名为volley(DEFAULT_CACHE_DIR)的文件夹,用于存放缓存文件
第n行这里才是真正去创建RequestQueue对象,我们进去看一下
public RequestQueue(Cache cache, Network network, int threadPoolSize,
ResponseDelivery delivery) {
mCache = cache;
mNetwork = network;
mDispatchers = new NetworkDispatcher[threadPoolSize];
mDelivery = delivery;
}直接进入第5行看个究竟
public class NetworkDispatcher extends ThreadNetworkDispatcher是一个线程类,它是在ReuqestQueue的start()方法中被调用的,我们去看看它的run方法中到底做了什么
public void run() {
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
Request<?> request;
while (true) {
long startTimeMs = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
// release previous request object to avoid leaking request object when mQueue is drained.
request = null;
try {
// Take a request from the queue.
request = mQueue.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// We may have been interrupted because it was time to quit.
if (mQuit) {
return;
}
continue;
}
try {
request.addMarker("network-queue-take");
// If the request was cancelled already, do not perform the
// network request.
if (request.isCanceled()) {
request.finish("network-discard-cancelled");
continue;
}
addTrafficStatsTag(request);
// Perform the network request.
NetworkResponse networkResponse = mNetwork.performRequest(request);
request.addMarker("network-http-complete");
// If the server returned 304 AND we delivered a response already,
// we're done -- don't deliver a second identical response.
if (networkResponse.notModified && request.hasHadResponseDelivered()) {
request.finish("not-modified");
continue;
}
// Parse the response here on the worker thread.
Response<?> response = request.parseNetworkResponse(networkResponse);
request.addMarker("network-parse-complete");
// Write to cache if applicable.
// TODO: Only update cache metadata instead of entire record for 304s.
if (request.shouldCache() && response.cacheEntry != null) {
mCache.put(request.getCacheKey(), response.cacheEntry);
request.addMarker("network-cache-written");
}
// Post the response back.
request.markDelivered();
mDelivery.postResponse(request, response);
} catch (VolleyError volleyError) {
volleyError.setNetworkTimeMs(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - startTimeMs);
parseAndDeliverNetworkError(request, volleyError);
} catch (Exception e) {
VolleyLog.e(e, "Unhandled exception %s", e.toString());
VolleyError volleyError = new VolleyError(e);
volleyError.setNetworkTimeMs(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - startTimeMs);
mDelivery.postError(request, volleyError);
}
}
}
代码比较长,我们挑重点看
第10行,从请求队列中拿出一个请求
第24行,判断请求是否被取消
重点来了,第32行,NetworkResponse networkResponse = mNetwork.performRequest(request);获得一个网络返回,我们进入performRequest中一看究竟
进入BasicNetWork中
public NetworkResponse performRequest(Request<?> request) throws VolleyError {
long requestStart = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
while (true) {
HttpResponse httpResponse = null;
byte[] responseContents = null;
Map<String, String> responseHeaders = Collections.emptyMap();
try {
// Gather headers.
Map<String, String> headers = new HashMap<String, String>();
addCacheHeaders(headers, request.getCacheEntry());
httpResponse = mHttpStack.performRequest(request, headers);
StatusLine statusLine = httpResponse.getStatusLine();
int statusCode = statusLine.getStatusCode();
responseHeaders = convertHeaders(httpResponse.getAllHeaders());
// Handle cache validation.
if (<span style="color:#ff0000;">statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_NOT_MODIFIED</span>) {
Entry entry = request.getCacheEntry();
if (entry == null) {
return new NetworkResponse(HttpStatus.SC_NOT_MODIFIED, null,
responseHeaders, true,
SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart);
}
// A HTTP 304 response does not have all header fields. We
// have to use the header fields from the cache entry plus
// the new ones from the response.
// http://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec10.html#sec10.3.5
entry.responseHeaders.putAll(responseHeaders);
return new NetworkResponse(HttpStatus.SC_NOT_MODIFIED, entry.data,
entry.responseHeaders, true,
SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart);
}
// Handle moved resources
if (statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_MOVED_PERMANENTLY || statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_MOVED_TEMPORARILY) {
String newUrl = responseHeaders.get("Location");
request.setRedirectUrl(newUrl);
}
// Some responses such as 204s do not have content. We must check.
if (httpResponse.getEntity() != null) {
responseContents = entityToBytes(httpResponse.getEntity());
} else {
// Add 0 byte response as a way of honestly representing a
// no-content request.
responseContents = new byte[0];
}
// if the request is slow, log it.
long requestLifetime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart;
logSlowRequests(requestLifetime, request, responseContents, statusLine);
if (statusCode < 200 || statusCode > 299) {
throw new IOException();
}
return new NetworkResponse(statusCode, responseContents, responseHeaders, false,
SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart);
} catch (SocketTimeoutException e) {
attemptRetryOnException("socket", request, new TimeoutError());
} catch (ConnectTimeoutException e) {
attemptRetryOnException("connection", request, new TimeoutError());
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Bad URL " + request.getUrl(), e);
} catch (IOException e) {
int statusCode = 0;
NetworkResponse networkResponse = null;
if (httpResponse != null) {
statusCode = httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
} else {
throw new NoConnectionError(e);
}
if (statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_MOVED_PERMANENTLY ||
statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_MOVED_TEMPORARILY) {
VolleyLog.e("Request at %s has been redirected to %s", request.getOriginUrl(), request.getUrl());
} else {
VolleyLog.e("Unexpected response code %d for %s", statusCode, request.getUrl());
}
if (responseContents != null) {
networkResponse = new NetworkResponse(statusCode, responseContents,
responseHeaders, false, SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart);
if (statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_UNAUTHORIZED ||
statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_FORBIDDEN) {
attemptRetryOnException("auth",
request, new AuthFailureError(networkResponse));
} else if (statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_MOVED_PERMANENTLY ||
statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_MOVED_TEMPORARILY) {
attemptRetryOnException("redirect",
request, new RedirectError(networkResponse));
} else {
// TODO: Only throw ServerError for 5xx status codes.
throw new ServerError(networkResponse);
}
} else {
throw new NetworkError(e);
}
}
}
}
第1行,如果返回状态为304则去读取缓存信息
所以会先去访问网络信息,根据返回状态判断去从网络上获取数据还是从缓存中