谷歌Volley网络框架分析。(四)缓存机制
1.缓存使用前提:
服务器必须支持,缓存,配置Cache-Control等头信息,因为Volley需要从这些头信息判断缓存是否已经过期。如果已经过期Volley将会重新从网络获取数据。
Request.setShouldCache(true)将开启缓存。
2.缓存流程:
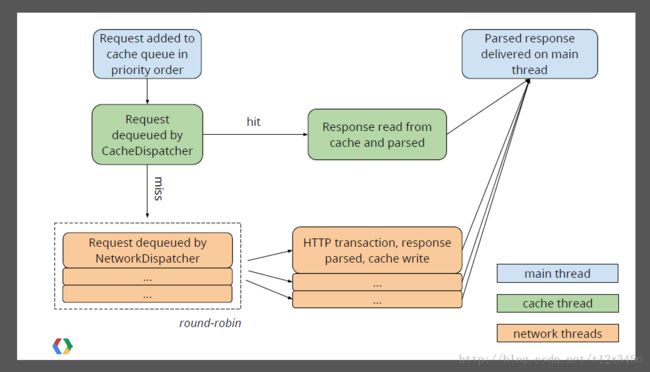
下面这张图很好的解释了使用缓存的相关流程:
1.如果Request设置Request.setShouldCache(true),RequestQueue则将会把Request添加到的缓存数据获取队列中(PriorityBlockingQueue<Request> mCacheQueue),将由CacheDispatcher(缓存调度)处理此Request。
相关代码:
public Request add(Request request) {
// Tag the request as belonging to this queue and add it to the set of current requests.
request.setRequestQueue(this);
synchronized (mCurrentRequests) {
mCurrentRequests.add(request);
}
// Process requests in the order they are added.
request.setSequence(getSequenceNumber());
request.addMarker("add-to-queue");
// If the request is uncacheable, skip the cache queue and go straight to the network.
if (!request.shouldCache()) {//不需要缓存的,则不需要判断是否已经在请求队列当中
mNetworkQueue.add(request);//添加到mNetworkQueue,将由,NetworkDiapatcher处理,直接请求网,获取数据
return request;
}
// Insert request into stage if there's already a request with the same cache key in flight.
synchronized (mWaitingRequests) {//需要缓存的,判断是否已经在请求队列当中
String cacheKey = request.getCacheKey();
if (mWaitingRequests.containsKey(cacheKey)) {//如果已经在获取缓存队列当中
// There is already a request in flight. Queue up.
Queue<Request> stagedRequests = mWaitingRequests.get(cacheKey);
if (stagedRequests == null) {
stagedRequests = new LinkedList<Request>();
}
stagedRequests.add(request);
mWaitingRequests.put(cacheKey, stagedRequests);
if (VolleyLog.DEBUG) {
VolleyLog.v("Request for cacheKey=%s is in flight, putting on hold.", cacheKey);
}
} else {
// Insert 'null' queue for this cacheKey, indicating there is now a request in
// flight.
mWaitingRequests.put(cacheKey, null);
mCacheQueue.add(request);//添加到mNetworkQueue,将由,CacheDiapatcher处理,将判断缓存是否可用。使用缓存数据,或者交给NetworkDiapatcher重新请求网络数据
}
return request;
}
}
2.缓存调度CacheDispatcher将会从本地判断缓存是否可用,如果本地缓存没有,或则已经过期,CacheDispatcher会将Request提交给NetworkDispatcher处理。
3.在本地有缓存,并且本地判断没有过期情况下。NetworkDispatcher会将本地缓存信息提交到服务器,CacheDispatcher将会再次校验本地缓存是否需要刷新。需要刷新 将会再次请求服务器。不需要刷新 直接返回数据到User.
@Override
public void run() {
if (DEBUG) VolleyLog.v("start new dispatcher");
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
// Make a blocking call to initialize the cache.
mCache.initialize();
while (true) {
try {
// Get a request from the cache triage queue, blocking until
// at least one is available.
final Request request = mCacheQueue.take();
request.addMarker("cache-queue-take");
// If the request has been canceled, don't bother dispatching it.
if (request.isCanceled()) {
request.finish("cache-discard-canceled");
continue;
}
// Attempt to retrieve this item from cache.
//获取本地缓存
Cache.Entry entry = mCache.get(request.getCacheKey());
if (entry == null) {//没有缓存,加入请求队列
request.addMarker("cache-miss");
// Cache miss; send off to the network dispatcher.
mNetworkQueue.put(request);
continue;
}
// If it is completely expired, just send it to the network.
if (entry.isExpired()) {//本地缓存已经过期,加入请求队列
request.addMarker("cache-hit-expired");
request.setCacheEntry(entry);
mNetworkQueue.put(request);
continue;
}
// We have a cache hit; parse its data for delivery back to the request.
request.addMarker("cache-hit");
Response<?> response = request.parseNetworkResponse(
new NetworkResponse(entry.data, entry.responseHeaders));
request.addMarker("cache-hit-parsed");
if (!entry.refreshNeeded()) {//根据服务器返回数据判断缓存是否需要刷新
// Completely unexpired cache hit. Just deliver the response.
mDelivery.postResponse(request, response);
} else {
// Soft-expired cache hit. We can deliver the cached response,
// but we need to also send the request to the network for
// refreshing.
request.addMarker("cache-hit-refresh-needed");
request.setCacheEntry(entry);
// Mark the response as intermediate.
response.intermediate = true;
// Post the intermediate response back to the user and have
// the delivery then forward the request along to the network.
mDelivery.postResponse(request, response, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
mNetworkQueue.put(request);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Not much we can do about this.
}
}
});
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// We may have been interrupted because it was time to quit.
if (mQuit) {
return;
}
continue;
}
}
}
4.NetworkDispatcher负责将请求到的缓存信息持久化(主要通过调用Cache.put()方法)。
但是这样好像每次都要重新写一下磁盘,DiskBasedCache并没有判断,数据是否一致,而是直接删除老缓存,重新写新的数据。
if (request.shouldCache() && response.cacheEntry != null) {//NetworkDispatcher.run()
mCache.put(request.getCacheKey(), response.cacheEntry);
request.addMarker("network-cache-written");
}