Centos 7.2 KVM 配置
z
[root@dlp ~]# nmcli c add type bridge autoconnect yes con-name br0 ifname br0
Connection 'br0' (0f4b7bc8-8c7a-461a-bff1-d516b941a6ec) successfully added.
[root@dlp ~]#nmcli c modify br0 ipv4.addresses 10.0.0.30/24 ipv4.method manual
[root@dlp ~]#nmcli c modify br0 ipv4.gateway 10.0.0.1
[root@dlp ~]#nmcli c modify br0 ipv4.dns 10.0.0.1
[root@dlp ~]#nmcli c delete eno16777736
[root@dlp ~]#nmcli c add type bridge-slave autoconnect yes con-name eno16777736 ifname eno16777736 master br0
[root@dlp ~]# reboot [root@dlp ~]#ip addr
[root@dlp ~]# mkdir /etc/libvirt/storage
[root@dlp ~]# virsh pool-define /etc/libvirt/storage/disk01.xml
[root@dlp ~]# virsh pool-start disk01
[root@dlp ~]# virsh pool-autostart disk01
[root@dlp ~]# virsh pool-list
[root@dlp ~]# virsh pool-info disk01
[root@dlp ~]# virt-top
[root@kvm01 ~]# virsh list
[root@kvm02 ~]# virsh list
[root@kvm02 ~]# virsh migrate --live centos7 qemu+ssh://10.0.0.21/system
[email protected]'s password: [root@kvm02 ~]# virsh list
|
It's Virtualization with KVM ( Kernel-based Virtual Machine ) + QEMU.
This requires that the CPU on your computer which has a function Intel VT or AMD-V. |
|
| [1] | Install KVM. |
|
[root@dlp ~]# yum -y install qemu-kvm libvirt virt-install bridge-utils
# make sure modules are loaded
[root@dlp ~]# lsmod | grep kvm kvm_intel 138567 0 kvm 441119 1 kvm_intel [root@dlp ~]# lsmod | grep kvm
|
| [2] | Configure Bridge networking for KVM virtual machine. Replace the interface name "eno16777736" for your own environment's one. |
# add bridge "br0"
[root@dlp ~]# nmcli c add type bridge autoconnect yes con-name br0 ifname br0
Connection 'br0' (0f4b7bc8-8c7a-461a-bff1-d516b941a6ec) successfully added.
# set IP for br0
[root@dlp ~]#nmcli c modify br0 ipv4.addresses 10.0.0.30/24 ipv4.method manual
# set Gateway for br0
[root@dlp ~]#nmcli c modify br0 ipv4.gateway 10.0.0.1
# set DNS for "br0"
[root@dlp ~]#nmcli c modify br0 ipv4.dns 10.0.0.1
# remove the current setting
[root@dlp ~]#nmcli c delete eno16777736
# add an interface again as a member of br0
[root@dlp ~]#nmcli c add type bridge-slave autoconnect yes con-name eno16777736 ifname eno16777736 master br0
# restart
[root@dlp ~]# reboot
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eno16777736: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP>
mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master br0 state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:9f:9b:d3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: virbr0: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state DOWN group default
link/ether 22:f8:64:25:97:44 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.122.1/24 brd 192.168.122.255 scope global virbr0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
4: br0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 00:0c:29:9f:9b:d3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.0.0.30/24 brd 10.0.0.255 scope global br0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fe9f:9bd3/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
|
Install GuestOS and create a Virtual Machine. This example shows to install CentOS 7.
|
|
| [1] | Install GuestOS on text mode via network, it's OK on Console or remote connection with Putty and so on.Furthermore, Virtual Machine's images are placed at /var/lib/libvirt/images by default as a Storage Pool,but this example shows to create and use a new Storage Pool. |
| [root@dlp ~]# mkdir -p /var/kvm/images # create a new Storage Pool
--name centos7 \
Starting install...
--ram 4096 \
--disk path=/var/kvm/images/centos7.img,size=30 \ --vcpus 2 \ --os-type linux \ --os-variant rhel7 \ --network bridge=br0 \ --graphics none \ --console pty,target_type=serial \ --location 'http://ftp.iij.ad.jp/pub/linux/centos/7/os/x86_64/' \ --extra-args 'console=ttyS0,115200n8 serial'
# start installation
|
|
The example of options above means like follows. There are many options for others, make sure with "man virt-install".
--name
specify the name of Virtual Machine
--ram
specify the amount of memories of Virtual Machine
--disk path=xxx ,size=xxx
'path=' ⇒ specify the location of disks of Virtual Machine
--vcpus'size=' ⇒ specify the amount of disks of Virtual Machine
specify the virtual CPUs
--os-type
specify the type of GuestOS
--os-variant
specify the kind of GuestOS - possible to confirm the list with the command below
--network# osinfo-query os
specify network types of Virtual Machine
--graphics
specify the kind of graphics. if set 'none', it means nographics.
--console
specify the console type
--location
specify the location of installation where from
--extra-args
specify parameters that is set in kernel
|
| [2] | Install on text mode, it's the same with common procedure of installation.After finishing installation, reboot first and then login prompt is shown like follwos. |
CentOS Linux 7 (Core) Kernel 3.10.0-123.el7.x86_64 on an x86_64 localhost login: |
| [3] | Move to GuestOS to HostOS with Ctrl + ] key. Move to HostOS to GuestOS with a command 'virsh console (name of virtual machine)'. |
|
[root@localhost ~]# # push Ctrl + ]
[root@dlp ~]# virsh console centos7
[root@dlp ~]# # Host's console
# move to Guest
Connected to domain www
Escape character is ^] # Enter key
[root@localhost ~]# # Guest's console
|
| [4] | Because after installing GuestOS from network, it is minimum settings,so it's useful to save it as a template in order to create new virtual machines later. |
| [root@dlp ~]# virt-clone --original centos7 --name template --file /var/kvm/images/template.img
Allocating 'template.img'
| 20 GB 01:44
Clone 'template' created successfully.
[root@dlp ~]# ll /var/kvm/images/template.img
# disk image
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 32212254720 Jul 11 23:34 /var/kvm/images/template.img [root@dlp ~]# ll /etc/libvirt/qemu/template.xml
# xml file
-rw------- 1 root root 1843 Jul 11 23:32 /etc/libvirt/qemu/template.xml |
| [5] |
Set basic initial configuration to GuestOS first before using it.
|
| [6] | Define a new Storage Pool. |
[root@dlp ~]# vi /etc/libvirt/storage/disk01.xml
# create new
<pool type='dir'>
<name>disk01</name>
<capacity>0</capacity>
<allocation>0</allocation>
<available>0</available>
<source>
</source>
<target>
<path>/var/kvm/images</path>
<permissions>
<mode>0700</mode>
<owner>-1</owner>
<group>-1</group>
</permissions>
</target>
</pool>
# any name you like
<name>disk01</name>
<capacity>0</capacity>
<allocation>0</allocation>
<available>0</available>
<source>
</source>
<target>
# specify a pool directory
<path>/var/kvm/images</path>
<permissions>
<mode>0700</mode>
<owner>-1</owner>
<group>-1</group>
</permissions>
</target>
</pool>
# define the pool
[root@dlp ~]# virsh pool-define /etc/libvirt/storage/disk01.xml
Pool disk01 defined from /etc/libvirt/storage/disk01.xml
# start the pool
[root@dlp ~]# virsh pool-start disk01
Pool disk01 started
# set auto-start
[root@dlp ~]# virsh pool-autostart disk01
Pool disk01 marked as autostarted
# confirm to show the pool list
[root@dlp ~]# virsh pool-list
Name State Autostart ----------------------------------------- disk01 active yes
# confirm to show the details
[root@dlp ~]# virsh pool-info disk01
Name: disk01 UUID: 2de62477-7132-4512-b5d8-003e28da105c State: running Persistent: yes Autostart: yes Capacity: 197.17 GiB Allocation: 2.90 GiB Available: 194.27 GiB
|
If you installed Desktop Environment,it's possible to create a Virtual machine on GUI.This example shows to install Windows Server 2012 R2 on GUI.
|
|
| [1] | Install virt-manager first. |
| [root@dlp ~]#
yum -y install virt-manager
|
| [2] | Start Desktop and run 'Virtual Machine Manager'. |
 |
| [3] | Click 'New' button (it's just the PC-icon on upper-left) and open a wizard to create a new Virtual Machine. |
| [4] | Specify the name of virtual machine and installation source. This example selects local media. |
 |
| [5] | Select Installation media or ISO image, and specify OS type and version. Windows Server 2012 in not listed, but it's possible to install it to select Windows 2008. |
 |
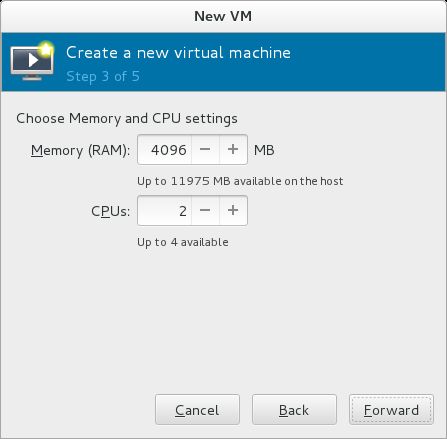
| [6] | Specify the amount of memories and number of virtual CPUs. |
 |
| [7] | Specify the amount of disks. |
 |
| [8] | Open 'Advanced options' and make sure the settings for networking or architecture are correct. |
 |
| [9] | Windows Server 2012 R2 Installation starts. |
 |
| [10] | Installation finished and Windows Server 2012 R2 is running. |
|
Basic Operarions with virsh command
|
|
| [1] | Start Virtual Machine |
|
[root@dlp ~]# virsh start centos7
[root@dlp ~]# virsh start centos7 --console
# Start Virtual Machine 'centos7'
# start and connect to console of 'centos7'
Connected to domain centos7 |
| [2] | Stop Virtual Machine |
|
[root@dlp ~]# virsh shutdown centos7
[root@dlp ~]# virsh destroy centos7
# Stop Virtual Machine 'centos7'
Domain centos7 is being shutdown
# Stop fourcely Virtual Machine 'centos7'
Domain centos7 destroyed |
| [3] | Set auto-start for Virtual Machines |
|
[root@dlp ~]# virsh autostart centos7
[root@dlp ~]# virsh autostart --disable centos7
# Enable auto-start for 'centos7'
# Disable auto-start for 'centos7'
|
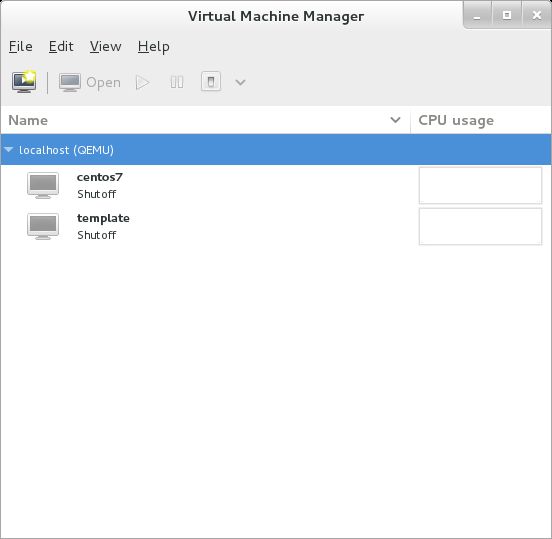
| [4] | List all Virtual Machines |
| [root@dlp ~]# virsh list
# List all active Virtual Machines
Id Name State ---------------------------------------- 2 centos7 running[root@dlp ~]# virsh list --all
# List all Virtual Machines included inactives
Id Name State ---------------------------------------- - centos7 shut off - template shut off - Win2k12 shut off |
| [5] | Switch console Move to GuestOS to HostOS with Ctrl + ] key. Move to HostOS to GuestOS with a command 'virsh console (name of virtual machine)'. |
| [root@dlp ~]# virsh console centos7
# connect to 'centos7'
Connected to domain centos7
Escape character is ^] # Enter
CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
Kernel 3.10.0-123.el7.x86_64 on an x86_64
localhost login:
Password:
# just switched on Guest
Last login: Sat Jul 12 20:51:10 2014 [root@localhost ~]# # Ctrl + ] key [root@dlp ~]# # just switched on Host |
| [6] | For Other options below, there are many options, please try to execute them. |
[root@dlp ~]# virsh --help
virsh [options]... [<command_string>]
virsh [options]... <command> [args...]
options:
-c | --connect=URI hypervisor connection URI
-r | --readonly connect readonly
-d | --debug=NUM debug level [0-4]
-h | --help this help
-q | --quiet quiet mode
-t | --timing print timing information
-l | --log=FILE output logging to file
-v short version
-V long version
--version[=TYPE] version, TYPE is short or long (default short)
-e | --escape <char> set escape sequence for console
commands (non interactive mode):
Domain Management (help keyword 'domain')
attach-device attach device from an XML file
attach-disk attach disk device
attach-interface attach network interface
autostart autostart a domain
blkdeviotune Set or query a block device I/O tuning parameters.
blkiotune Get or set blkio parameters
blockcommit Start a block commit operation.
blockcopy Start a block copy operation.
blockjob Manage active block operations
blockpull Populate a disk from its backing image.
blockresize Resize block device of domain.
change-media Change media of CD or floppy drive
console connect to the guest console
cpu-baseline compute baseline CPU
cpu-compare compare host CPU with a CPU described by an XML file
cpu-stats show domain cpu statistics
create create a domain from an XML file
define define (but don't start) a domain from an XML file
desc show or set domain's description or title
destroy destroy (stop) a domain
detach-device detach device from an XML file
detach-disk detach disk device
detach-interface detach network interface
domdisplay domain display connection URI
domfstrim Invoke fstrim on domain's mounted filesystems.
domhostname print the domain's hostname
domid convert a domain name or UUID to domain id
domif-setlink set link state of a virtual interface
domiftune get/set parameters of a virtual interface
domjobabort abort active domain job
domjobinfo domain job information
domname convert a domain id or UUID to domain name
dompmsuspend suspend a domain gracefully using power management functions
dompmwakeup wakeup a domain from pmsuspended state
domuuid convert a domain name or id to domain UUID
domxml-from-native Convert native config to domain XML
domxml-to-native Convert domain XML to native config
dump dump the core of a domain to a file for analysis
dumpxml domain information in XML
edit edit XML configuration for a domain
inject-nmi Inject NMI to the guest
send-key Send keycodes to the guest
send-process-signal Send signals to processes
lxc-enter-namespace LXC Guest Enter Namespace
managedsave managed save of a domain state
managedsave-remove Remove managed save of a domain
maxvcpus connection vcpu maximum
memtune Get or set memory parameters
migrate migrate domain to another host
migrate-setmaxdowntime set maximum tolerable downtime
migrate-compcache get/set compression cache size
migrate-setspeed Set the maximum migration bandwidth
migrate-getspeed Get the maximum migration bandwidth
numatune Get or set numa parameters
qemu-attach QEMU Attach
qemu-monitor-command QEMU Monitor Command
qemu-agent-command QEMU Guest Agent Command
reboot reboot a domain
reset reset a domain
restore restore a domain from a saved state in a file
resume resume a domain
save save a domain state to a file
save-image-define redefine the XML for a domain's saved state file
save-image-dumpxml saved state domain information in XML
save-image-edit edit XML for a domain's saved state file
schedinfo show/set scheduler parameters
screenshot take a screenshot of a current domain console and store it into a file
setmaxmem change maximum memory limit
setmem change memory allocation
setvcpus change number of virtual CPUs
shutdown gracefully shutdown a domain
start start a (previously defined) inactive domain
suspend suspend a domain
ttyconsole tty console
undefine undefine a domain
update-device update device from an XML file
vcpucount domain vcpu counts
vcpuinfo detailed domain vcpu information
vcpupin control or query domain vcpu affinity
emulatorpin control or query domain emulator affinity
vncdisplay vnc display
Domain Monitoring (help keyword 'monitor')
domblkerror Show errors on block devices
domblkinfo domain block device size information
domblklist list all domain blocks
domblkstat get device block stats for a domain
domcontrol domain control interface state
domif-getlink get link state of a virtual interface
domiflist list all domain virtual interfaces
domifstat get network interface stats for a domain
dominfo domain information
dommemstat get memory statistics for a domain
domstate domain state
list list domains
Host and Hypervisor (help keyword 'host')
capabilities capabilities
freecell NUMA free memory
hostname print the hypervisor hostname
node-memory-tune Get or set node memory parameters
nodecpumap node cpu map
nodecpustats Prints cpu stats of the node.
nodeinfo node information
nodememstats Prints memory stats of the node.
nodesuspend suspend the host node for a given time duration
sysinfo print the hypervisor sysinfo
uri print the hypervisor canonical URI
version show version
Interface (help keyword 'interface')
iface-begin create a snapshot of current interfaces settings,
which can be later committed (iface-commit) or restored (iface-rollback)
iface-bridge create a bridge device and attach an existing network device to it
iface-commit commit changes made since iface-begin and free restore point
iface-define define (but don't start) a physical host interface from an XML file
iface-destroy destroy a physical host interface (disable it / "if-down")
iface-dumpxml interface information in XML
iface-edit edit XML configuration for a physical host interface
iface-list list physical host interfaces
iface-mac convert an interface name to interface MAC address
iface-name convert an interface MAC address to interface name
iface-rollback rollback to previous saved configuration created via iface-begin
iface-start start a physical host interface (enable it / "if-up")
iface-unbridge undefine a bridge device after detaching its slave device
iface-undefine undefine a physical host interface (remove it from configuration)
Network Filter (help keyword 'filter')
nwfilter-define define or update a network filter from an XML file
nwfilter-dumpxml network filter information in XML
nwfilter-edit edit XML configuration for a network filter
nwfilter-list list network filters
nwfilter-undefine undefine a network filter
Networking (help keyword 'network')
net-autostart autostart a network
net-create create a network from an XML file
net-define define (but don't start) a network from an XML file
net-destroy destroy (stop) a network
net-dumpxml network information in XML
net-edit edit XML configuration for a network
net-info network information
net-list list networks
net-name convert a network UUID to network name
net-start start a (previously defined) inactive network
net-undefine undefine an inactive network
net-update update parts of an existing network's configuration
net-uuid convert a network name to network UUID
Node Device (help keyword 'nodedev')
nodedev-create create a device defined by an XML file on the node
nodedev-destroy destroy (stop) a device on the node
nodedev-detach detach node device from its device driver
nodedev-dumpxml node device details in XML
nodedev-list enumerate devices on this host
nodedev-reattach reattach node device to its device driver
nodedev-reset reset node device
Secret (help keyword 'secret')
secret-define define or modify a secret from an XML file
secret-dumpxml secret attributes in XML
secret-get-value Output a secret value
secret-list list secrets
secret-set-value set a secret value
secret-undefine undefine a secret
Snapshot (help keyword 'snapshot')
snapshot-create Create a snapshot from XML
snapshot-create-as Create a snapshot from a set of args
snapshot-current Get or set the current snapshot
snapshot-delete Delete a domain snapshot
snapshot-dumpxml Dump XML for a domain snapshot
snapshot-edit edit XML for a snapshot
snapshot-info snapshot information
snapshot-list List snapshots for a domain
snapshot-parent Get the name of the parent of a snapshot
snapshot-revert Revert a domain to a snapshot
Storage Pool (help keyword 'pool')
find-storage-pool-sources-as find potential storage pool sources
find-storage-pool-sources discover potential storage pool sources
pool-autostart autostart a pool
pool-build build a pool
pool-create-as create a pool from a set of args
pool-create create a pool from an XML file
pool-define-as define a pool from a set of args
pool-define define (but don't start) a pool from an XML file
pool-delete delete a pool
pool-destroy destroy (stop) a pool
pool-dumpxml pool information in XML
pool-edit edit XML configuration for a storage pool
pool-info storage pool information
pool-list list pools
pool-name convert a pool UUID to pool name
pool-refresh refresh a pool
pool-start start a (previously defined) inactive pool
pool-undefine undefine an inactive pool
pool-uuid convert a pool name to pool UUID
Storage Volume (help keyword 'volume')
vol-clone clone a volume.
vol-create-as create a volume from a set of args
vol-create create a vol from an XML file
vol-create-from create a vol, using another volume as input
vol-delete delete a vol
vol-download download volume contents to a file
vol-dumpxml vol information in XML
vol-info storage vol information
vol-key returns the volume key for a given volume name or path
vol-list list vols
vol-name returns the volume name for a given volume key or path
vol-path returns the volume path for a given volume name or key
vol-pool returns the storage pool for a given volume key or path
vol-resize resize a vol
vol-upload upload file contents to a volume
vol-wipe wipe a vol
Virsh itself (help keyword 'virsh')
cd change the current directory
connect (re)connect to hypervisor
echo echo arguments
exit quit this interactive terminal
help print help
pwd print the current directory
quit quit this interactive terminal
(specify help <group> for details about the commands in the group)
(specify help <command> for details about the command)
|
Install useful tools for virt management.
|
|
| [1] | Install virt tools. |
| [root@dlp ~]# yum -y install libguestfs-tools virt-top |
| [2] | "ls" a directory in a virtual machine. |
[root@dlp ~]# virt-ls -l -d centos7 /roottotal 36 dr-xr-x---. 2 root root 4096 Jan 8 22:38 . drwxr-xr-x. 17 root root 4096 Jan 8 22:36 .. -rw-------. 1 root root 61 Jan 8 22:38 .bash_history -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 18 Dec 29 2013 .bash_logout -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 176 Dec 29 2013 .bash_profile -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 176 Dec 29 2013 .bashrc ... |
| [3] | "cat" a file in a virtual machine. |
[root@dlp ~]# virt-cat -d centos7 /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync ... |
| [4] | Edit a file in a virtual machine. |
[root@dlp ~]# virt-edit -d centos7 /etc/fstab
# # /etc/fstab # Created by anaconda on Thu Jan 8 13:20:43 2015 # # Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk' # See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info # /dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults 1 1 UUID=537b215f-30a1-4e82-b05d-f480aa8e1034 /boot xfs defaults 1 2 /dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults 0 0 |
| [5] | Display disk usage in a virtual machine. |
[root@dlp ~]# virt-df -d centos7
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% centos7:/dev/sda1 508588 72348 436240 15% centos7:/dev/centos/root 8910848 779252 8131596 9% |
| [6] | Mount a disk for a virtual machine. |
[root@dlp ~]# guestmount -d centos7 -i /media
total 32 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Jan 8 22:22 bin -> usr/bin dr-xr-xr-x. 4 root root 4096 Jan 8 22:37 boot drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Jan 8 22:20 dev drwxr-xr-x. 74 root root 8192 Jan 8 22:36 etc ... |
| [7] | Display the status of virtual machines. |
virt-top 22:32:virt-top14 - x86_64 4/4CPU 2801MHz 11968MB 2 domains, 1 active, 1 running, 0 sleeping, 0 paused, 1 inactive D:0 O:0 X:0 CPU: 0.2% Mem: 500 MB (500 MB by guests) ID S RDRQ WRRQ RXBY TXBY %CPU %MEM TIME NAME 6 R 0 0 0.2 4.0 0:09.14 guestfs-o7nss1p3kxvyl1r5 - (centos7)
|
This is the example to use Live Migration function for virtual machines.
This requires 2 KVM host server and a storage server like follows.
Please set DNS or hosts to resolve names or IP addresses normally, first. +----------------------+
| [ NFS Servver ] |
| nfs.srv.world |
| |
+-----------+----------+
|10.0.0.30
|
+----------------------+ | +----------------------+
| [ KVM Host #1 ] |10.0.0.21 | 10.0.0.22| [ KVM Host #2 ] |
| +----------+----------+ |
| kvm01.srv.world | | kvm02.srv.world |
+----------------------+ +----------------------+
|
| [1] |
Configure Storage server which has virtual machine images. For Storage server, it's OK to use NFS, iSCSI, GlusterFS and so on. This example uses NFS Storage server.
|
| [2] |
Configure 2 KVM host server and mount a directory provided from Storage server on the same mount point on both KVM server. This example mounts on [/var/kvm/images].
|
| [3] |
Create and start a virtual machine on a KVM host server.
|
| [4] | It's OK all, execute Live Migration like follows on server which virtual machine is running. After finishing it, virtual machine is migrated on another KVM host like follows. |
Id Name State -------------------------------------- 3 centos7 running
[root@kvm01 ~]# virsh migrate --live centos7 qemu+ssh://10.0.0.22/system
[email protected]'s password:
[root@kvm01 ~]# virsh list
[email protected]'s password:
# root password
Id Name State --------------------------------------
# just migrated
### on another KVM Host ###
[root@kvm02 ~]# virsh list
Id Name State --------------------------------------- 1 centos7 running
# back to the KVM Host again like follows
[root@kvm02 ~]# virsh migrate --live centos7 qemu+ssh://10.0.0.21/system
[email protected]'s password:
Id Name State --------------------------------------
|
Install Desktop Virtualization "SPICE ( Simple Protocol for Independent Computing Environment )".It's possible to connect to virtual machines from remote client computer.
|
|
| [1] | Install SPICE Server if it's not installed yet. ( Normally it's already installed with KVM for dependency ) |
| [root@dlp ~]#
yum -y install spice-server spice-protocol
|
| [2] | Edit existing virtual machine's xml-file and start virtual machine with SPICE like follows.This site's example has created a virtual machine without graphics, so it's OK to change settings like follows,but if you created virtual machine with a graphics, Remove "<graphics>***" and "<video>***" sections in xml file because qxl is used for graphics. |
|
[root@dlp ~]#
virsh edit centos7
# edit the configration of "centos7"
<domain type='kvm'> <name>centos7</name> <uuid>b38a50ca-a1ae-4d37-ba10-caf1e05b43ce</uuid> <memory unit='KiB'>4194304</memory> <currentMemory unit='KiB'>4194304</currentMemory> <vcpu placement='static'>2</vcpu> . . .
# add follows
# set any password for "passwd=***" section
# specify a uniq number for "sound" section "slot='0x06'"
# the "slot='0x02'" in video section is fixed number for graphics
<graphics type='spice' port='5900' autoport='no' listen='0.0.0.0' passwd='password'>
<listen type='address' address='0.0.0.0'/>
</graphics>
<sound model='ac97'>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x06' function='0x0'/>
</sound>
<video>
<model type='qxl' ram='65536' vram='32768' heads='1'/>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x02' function='0x0'/>
</video>
<memballoon model='virtio'>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x05' function='0x0'/>
</memballoon>
</devices>
</domain>
Domain centos7 XML configuration edited.
[root@dlp ~]# virsh start centos7
# start VM
Domain centos7 started |
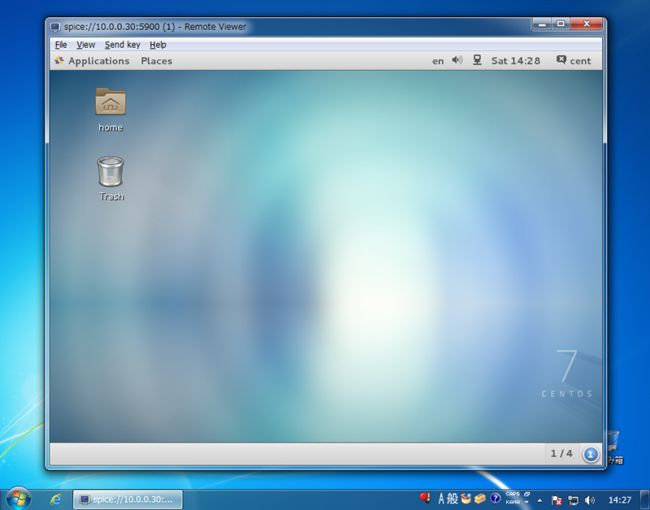
| [3] |
Configuration is all OK. See next page to connect to SPICE server from SPICE client.
|
| [4] | By the way, if you'd like to enable SPICE on initial creating of virtual machine, specify like follows. Then, it's possible to install Systems with SPICE which requires GUI like Windows without installing Desktop Environment on KVM Host computer. |
| [root@dlp ~]# virt-install \
--name Win2k12R2 \
--ram 6144 \ --disk path=/var/kvm/images/Win2k12R2.img,size=100 \ --vcpus=4 \ --os-type windows \ --os-variant=win2k8 \ --network bridge=br0 \ --graphics spice,listen=0.0.0.0,password=password \ --video qxl \ --cdrom /tmp/X64FRE_SERVER_EVAL_JA-JP-IRM_SSS_X64FREE_JA-JP_DV5.ISO |
| [5] | If Firewalld is running, allow SPICE port which you asgined to a virtual machine. |