Android之gallery 常见2种使用方法和3D效果总结
我们有时候在iPhone手机上或者Windows上面看到动态的图片,可以通过鼠标或者手指触摸来移动它,产生动态的图片滚动效果,还可以根据你的点击或者触摸触发其他事件响应。同样的,在Android中也提供这这种实现,这就是通过Gallery在UI上实现缩略图浏览器。
一般情况下,我们在Android中要用到类似这种图片容器的控件,都需要为它指定一个适配器,让它可以把内容按照我们定义的方式来显示,因此我们来给它加一个适配器,至于这个适配器如何实现,后面接着来操作,这里只需知道这个适配器的类叫ImageGalleryAdapter 。 gallery.setAdapter(new ImageGalleryAdapter (this));
下面介绍常用2种用法:
第一种方法:
第一步:设计xml布局文件
代码如下:main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Gallery
android:id="@+id/myGallery"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:spacing="3px"
android:text="@string/hello" />
</LinearLayout>
package net.loonggg.gallery;
import android.content.Context;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.widget.Gallery;
import android.widget.ImageView;
public class ImageGalleryAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private Context context;
// 里面所有的方法表示的是可以根据指定的显示图片的数量,进行每个图片的处理
private int[] image = new int[] { R.drawable.ispic_a, R.drawable.ispic_b,
R.drawable.ispic_c, R.drawable.ispic_d, R.drawable.ispic_e };
public ImageGalleryAdapter(Context context) {
this.context = context;
}
public int getCount() { // 取得要显示内容的数量
return image.length;
}
public Object getItem(int position) { // 每个资源的位置
return image[position];
}
public long getItemId(int position) { // 取得每个项的ID
return image[position];
}
// 将资源设置到一个组件之中,很明显这个组件是ImageView
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
ImageView iv = new ImageView(context);
iv.setBackgroundColor(0xFFFFFFFF);
iv.setImageResource(image[position]);// 给ImageView设置资源
iv.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.CENTER);// 设置对齐方式
iv.setLayoutParams(new Gallery.LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
return iv;
}
}
第三步:主方法:
package net.loonggg.gallery;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
import android.widget.Gallery;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class GalleryActivity extends Activity {
private Gallery myGallery;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
myGallery = (Gallery) findViewById(R.id.myGallery);
myGallery.setAdapter(new ImageGalleryAdapter(this));
myGallery.setOnItemClickListener(new OnItemClickListenerImpl());
}
private class OnItemClickListenerImpl implements OnItemClickListener {
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position,
long id) {
Toast.makeText(GalleryActivity.this, String.valueOf(position),
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
}
第二种方法
第一步:设计xml布局文件<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:gravity="bottom"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ImageSwitcher
android:id="@+id/is"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
</ImageSwitcher>
<Gallery
android:id="@+id/myGallery"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:spacing="3px" />
</LinearLayout>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#FFFFFF"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/iv"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:scaleType="center" />
</LinearLayout>
package net.loonggg.gallery2;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
import android.widget.Gallery;
import android.widget.ImageSwitcher;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
import android.widget.ViewSwitcher.ViewFactory;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private ImageSwitcher is;
private Gallery gallery;
private SimpleAdapter adapter;
private List<Map<String, Integer>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String, Integer>>();
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
is = (ImageSwitcher) findViewById(R.id.is);
is.setFactory(new ViewFactoryImpl());
initAdapter();
gallery = (Gallery) findViewById(R.id.myGallery);
gallery.setAdapter(adapter); // 为gallery设置合适的适配器
gallery.setOnItemClickListener(new OnItemClickListenerImpl());
}
public class OnItemClickListenerImpl implements OnItemClickListener { // gallery的点击事件
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position,
long id) {
Map<String, Integer> map = (Map<String, Integer>) parent
.getAdapter().getItem(position);
is.setImageResource(map.get("image"));
}
}
public void initAdapter() { // 这个方法的功能是:从R.java文件中获取图片资源的id,如果资源图片数量比较多,用数组的方法一一定义,就不太合适,这种方法最好了。
Field[] fields = R.drawable.class.getDeclaredFields();
for (int x = 0; x < fields.length; x++) {
if (fields[x].getName().startsWith("ispic_")) { // 根据图片的名称取出想要的图片
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
try {
map.put("image", fields[x].getInt(R.drawable.class));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
list.add(map);
}
}
adapter = new SimpleAdapter(MainActivity.this, list,
R.layout.grid_item, new String[] { "image" },
new int[] { R.id.iv });
}
public class ViewFactoryImpl implements ViewFactory {
@Override
public View makeView() {
ImageView iv = new ImageView(MainActivity.this);
iv.setBackgroundColor(0xFFFFFFFF);
iv.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.CENTER);
iv.setLayoutParams(new ImageSwitcher.LayoutParams(
LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
return iv;
}
}
}
一,创建倒影效果
这个基本思路是:
1,创建一个源图一样的图,利用martrix将图片旋转180度。这个倒影图的高是源图的一半。
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
// 1表示放大比例,不放大也不缩小。
// -1表示在y轴上相反,即旋转180度。
matrix.preScale(1, -1);
Bitmap reflectionBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(
srcBitmap,
0,
srcBitmap.getHeight() / 2, // top为源图的一半
srcBitmap.getWidth(), // 宽度与源图一样
srcBitmap.getHeight() / 2, // 高度与源图的一半
matrix,
false);
2,创建一个最终效果的图,即源图 + 间隙 + 倒影。
final int REFLECTION_GAP = 5;
Bitmap bitmapWithReflection = Bitmap.createBitmap(
reflectionWidth,
srcHeight + reflectionHeight + REFLECTION_GAP,
Config.ARGB_8888);
3,依次将源图、倒影图绘制在最终的bitmap上面。
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(bitmapWithReflection);
// Draw the original bitmap.
canvas.drawBitmap(srcBitmap, 0, 0, null);
// Draw the reflection bitmap.
canvas.drawBitmap(reflectionBitmap, 0, srcHeight + REFLECTION_GAP, null);
4,创建LinearGradient,从而给定一个由上到下的渐变色。
Paint paint = new Paint();
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
LinearGradient shader = new LinearGradient(
0,
srcHeight,
0,
bitmapWithReflection.getHeight() + REFLECTION_GAP,
0x70FFFFFF,
0x00FFFFFF,
TileMode.MIRROR);
paint.setShader(shader);
paint.setXfermode(new PorterDuffXfermode(android.graphics.PorterDuff.Mode.DST_IN));
// Draw the linear shader.
canvas.drawRect(
0,
srcHeight,
srcWidth,
bitmapWithReflection.getHeight() + REFLECTION_GAP,
paint);
二,扩展Gallery
扩展系统的gallery,我们需要重写两个方法,getChildStaticTransformation()和getChildDrawingOrder(),同时,要使这两个方法能被调用,必须执行如下两行代码,文档上面是有说明的。
// Enable set transformation. this.setStaticTransformationsEnabled(true); // Enable set the children drawing order. this.setChildrenDrawingOrderEnabled(true);
- getChildDrawingOrder的实现
@Override
protected int getChildDrawingOrder(int childCount, int i)
{
// Current selected index.
int selectedIndex = getSelectedItemPosition() - getFirstVisiblePosition();
if (selectedIndex < 0)
{
return i;
}
if (i < selectedIndex)
{
return i;
}
else if (i >= selectedIndex)
{
return childCount - 1 - i + selectedIndex;
}
else
{
return i;
}
}
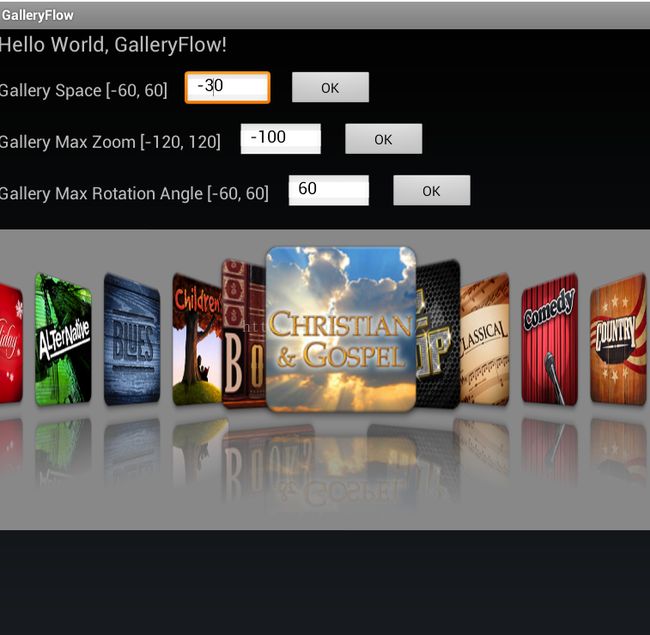
这里为什么要计算drawing order,因为从上图中看到,我们的效果是:中间左边的顺序是 0, 1, 2,右边的child覆盖左边的child,而在中间右边的顺序正好相反,左边的覆盖右边的,所以我们要重写这个方法,而gallery自身的实现,不是这种效果。
- getChildStaticTransformation的实现
@Override
protected boolean getChildStaticTransformation(View child, Transformation t)
{
super.getChildStaticTransformation(child, t);
final int childCenter = getCenterOfView(child);
final int childWidth = child.getWidth();
int rotationAngle = 0;
t.clear();
t.setTransformationType(Transformation.TYPE_MATRIX);
// If the child is in the center, we do not rotate it.
if (childCenter == mCoveflowCenter)
{
transformImageBitmap(child, t, 0);
}
else
{
// Calculate the rotation angle.
rotationAngle = (int)(((float)(mCoveflowCenter - childCenter) / childWidth) * mMaxRotationAngle);
// Make the angle is not bigger than maximum.
if (Math.abs(rotationAngle) > mMaxRotationAngle)
{
rotationAngle = (rotationAngle < 0) ? -mMaxRotationAngle : mMaxRotationAngle;
}
transformImageBitmap(child, t, rotationAngle);
}
return true;
}
这个方法就是根据child来计算它的transformation(变换),我们需要去修改它里面的matrix,从而达到旋转的效果。根据位置和角度来计算的matrix的方法写在另外一个方法transformImageBitmap中实现。
- transformImageBitmap()的实现
private void transformImageBitmap(View child, Transformation t, int rotationAngle)
{
mCamera.save();
final Matrix imageMatrix = t.getMatrix();
final int imageHeight = child.getHeight();
final int imageWidth = child.getWidth();
final int rotation = Math.abs(rotationAngle);
// Zoom on Z axis.
mCamera.translate(0, 0, mMaxZoom);
if (rotation < mMaxRotationAngle)
{
float zoomAmount = (float)(mMaxZoom + rotation * 1.5f);
mCamera.translate(0, 0, zoomAmount);
}
// Rotate the camera on Y axis.
mCamera.rotateY(rotationAngle);
// Get the matrix from the camera, in fact, the matrix is S (scale) transformation.
mCamera.getMatrix(imageMatrix);
// The matrix final is T2 * S * T1, first translate the center point to (0, 0),
// then scale, and then translate the center point to its original point.
// T * S * T
// S * T1
imageMatrix.postTranslate((imageWidth / 2), (imageHeight / 2));
// (T2 * S) * T1
imageMatrix.preTranslate(-(imageWidth / 2), -(imageHeight / 2));
mCamera.restore();
}
这里,简单说明一个,
第一,先在Z轴上平称,其实就是得到一个缩放矩阵变换,我这里简写为 S。
第二,是利用camera这个类来生成matrix,其实mCamera.rotateY就是围绕Y轴旋转。这里生成了一个旋转矩阵,记为 R 。经过这两步,此时调用mCamera.getMatrix(imageMatrix); 从Camera中得到matrix,此时这个矩阵中包含了S * R。
第三,最关键是下面两句
// S * T1 imageMatrix.postTranslate((imageWidth / 2), (imageHeight / 2)); // (T2 * S) * T1 imageMatrix.preTranslate(-(imageWidth / 2), -(imageHeight / 2));
由于这里涉及到旋转与缩放,缩放操作其实应该是针对Child中点进行了,这里就是作一个平衡操作,我们必须是先平移,再缩放,再平移回原来位置,所以,我们最终的矩阵变换应该是这样的:
M = T * (S * R) * T1 (这里在T1表示与T相反)。
三,完整代码
GalleryFlow.java
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Camera;
import android.graphics.Matrix;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.animation.Transformation;
import android.widget.Gallery;
public class GalleryFlow extends Gallery
{
/**
* The camera class is used to 3D transformation matrix.
*/
private Camera mCamera = new Camera();
/**
* The max rotation angle.
*/
private int mMaxRotationAngle = 60;
/**
* The max zoom value (Z axis).
*/
private int mMaxZoom = -120;
/**
* The center of the gallery.
*/
private int mCoveflowCenter = 0;
public GalleryFlow(Context context)
{
this(context, null);
}
public GalleryFlow(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
{
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public GalleryFlow(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle)
{
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
// Enable set transformation.
this.setStaticTransformationsEnabled(true);
// Enable set the children drawing order.
this.setChildrenDrawingOrderEnabled(true);
}
public int getMaxRotationAngle()
{
return mMaxRotationAngle;
}
public void setMaxRotationAngle(int maxRotationAngle)
{
mMaxRotationAngle = maxRotationAngle;
}
public int getMaxZoom()
{
return mMaxZoom;
}
public void setMaxZoom(int maxZoom)
{
mMaxZoom = maxZoom;
}
@Override
protected int getChildDrawingOrder(int childCount, int i)
{
// Current selected index.
int selectedIndex = getSelectedItemPosition() - getFirstVisiblePosition();
if (selectedIndex < 0)
{
return i;
}
if (i < selectedIndex)
{
return i;
}
else if (i >= selectedIndex)
{
return childCount - 1 - i + selectedIndex;
}
else
{
return i;
}
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh)
{
mCoveflowCenter = getCenterOfCoverflow();
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
}
private int getCenterOfView(View view)
{
return view.getLeft() + view.getWidth() / 2;
}
@Override
protected boolean getChildStaticTransformation(View child, Transformation t)
{
super.getChildStaticTransformation(child, t);
final int childCenter = getCenterOfView(child);
final int childWidth = child.getWidth();
int rotationAngle = 0;
t.clear();
t.setTransformationType(Transformation.TYPE_MATRIX);
// If the child is in the center, we do not rotate it.
if (childCenter == mCoveflowCenter)
{
transformImageBitmap(child, t, 0);
}
else
{
// Calculate the rotation angle.
rotationAngle = (int)(((float)(mCoveflowCenter - childCenter) / childWidth) * mMaxRotationAngle);
// Make the angle is not bigger than maximum.
if (Math.abs(rotationAngle) > mMaxRotationAngle)
{
rotationAngle = (rotationAngle < 0) ? -mMaxRotationAngle : mMaxRotationAngle;
}
transformImageBitmap(child, t, rotationAngle);
}
return true;
}
private int getCenterOfCoverflow()
{
return (getWidth() - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight()) / 2 + getPaddingLeft();
}
private void transformImageBitmap(View child, Transformation t, int rotationAngle)
{
mCamera.save();
final Matrix imageMatrix = t.getMatrix();
final int imageHeight = child.getHeight();
final int imageWidth = child.getWidth();
final int rotation = Math.abs(rotationAngle);
// Zoom on Z axis.
mCamera.translate(0, 0, mMaxZoom);
if (rotation < mMaxRotationAngle)
{
float zoomAmount = (float)(mMaxZoom + rotation * 1.5f);
mCamera.translate(0, 0, zoomAmount);
}
// Rotate the camera on Y axis.
mCamera.rotateY(rotationAngle);
// Get the matrix from the camera, in fact, the matrix is S (scale) transformation.
mCamera.getMatrix(imageMatrix);
// The matrix final is T2 * S * T1, first translate the center point to (0, 0),
// then scale, and then translate the center point to its original point.
// T * S * T
// S * T1
imageMatrix.postTranslate((imageWidth / 2), (imageHeight / 2));
// (T2 * S) * T1
imageMatrix.preTranslate(-(imageWidth / 2), -(imageHeight / 2));
mCamera.restore();
}
}
BitmapUtil.java
package com.lee.gallery3d.utils;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.Bitmap.Config;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.LinearGradient;
import android.graphics.Matrix;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.PixelFormat;
import android.graphics.PorterDuffXfermode;
import android.graphics.Shader.TileMode;
import android.graphics.drawable.Drawable;
public class BitmapUtil
{
public static Bitmap createReflectedBitmap(Bitmap srcBitmap)
{
if (null == srcBitmap)
{
return null;
}
// The gap between the reflection bitmap and original bitmap.
final int REFLECTION_GAP = 4;
int srcWidth = srcBitmap.getWidth();
int srcHeight = srcBitmap.getHeight();
int reflectionWidth = srcBitmap.getWidth();
int reflectionHeight = srcBitmap.getHeight() / 2;
if (0 == srcWidth || srcHeight == 0)
{
return null;
}
// The matrix
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
matrix.preScale(1, -1);
try
{
// The reflection bitmap, width is same with original's, height is half of original's.
Bitmap reflectionBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(
srcBitmap,
0,
srcHeight / 2,
srcWidth,
srcHeight / 2,
matrix,
false);
if (null == reflectionBitmap)
{
return null;
}
// Create the bitmap which contains original and reflection bitmap.
Bitmap bitmapWithReflection = Bitmap.createBitmap(
reflectionWidth,
srcHeight + reflectionHeight + REFLECTION_GAP,
Config.ARGB_8888);
if (null == bitmapWithReflection)
{
return null;
}
// Prepare the canvas to draw stuff.
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(bitmapWithReflection);
// Draw the original bitmap.
canvas.drawBitmap(srcBitmap, 0, 0, null);
// Draw the reflection bitmap.
canvas.drawBitmap(reflectionBitmap, 0, srcHeight + REFLECTION_GAP, null);
Paint paint = new Paint();
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
LinearGradient shader = new LinearGradient(
0,
srcHeight,
0,
bitmapWithReflection.getHeight() + REFLECTION_GAP,
0x70FFFFFF,
0x00FFFFFF,
TileMode.MIRROR);
paint.setShader(shader);
paint.setXfermode(new PorterDuffXfermode(android.graphics.PorterDuff.Mode.DST_IN));
// Draw the linear shader.
canvas.drawRect(
0,
srcHeight,
srcWidth,
bitmapWithReflection.getHeight() + REFLECTION_GAP,
paint);
return bitmapWithReflection;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}