android与服务端交互(二)
上一节中我们通过http协议,采用HttpClient向服务器端action请求数据。当然调用服务器端方法获取数据并不止这一种。WebService也可以为我们提供所需数据,那么什么是webService呢?,它是一种基于SAOP协议的远程调用标准,通过webservice可以将不同操作系统平台,不同语言,不同技术整合到一起。
我们在PC机器java客户端中,需要一些库,比如XFire,Axis2,CXF等等来支持访问WebService,但是这些库并不适合我们资源有限的android手机客户端,做过JAVA ME的人都知道有KSOAP这个第三方的类库,可以帮助我们获取服务器端webService调用,当然KSOAP已经提供了基于android版本的jar包了,那么我们就开始吧:
首先下载KSOAP包:ksoap2-android-assembly-2.5.2-jar-with-dependencies.jar包
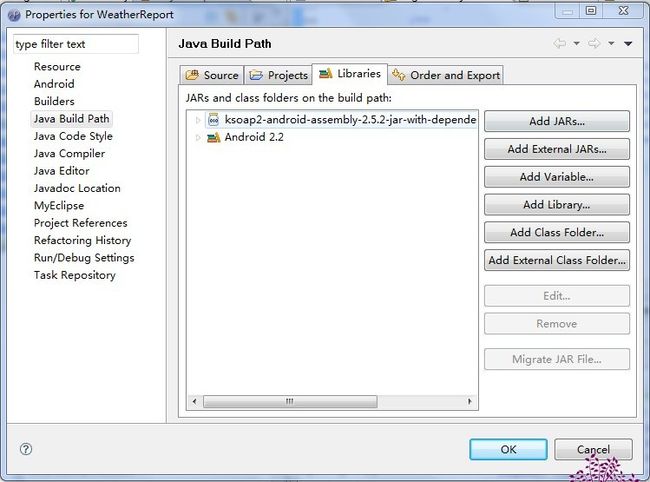
然后新建android项目:并把下载的KSOAP包放在android项目的lib目录下:右键->build path->configure build path--选择Libraries,如图:
以下分为七个步骤来调用WebService方法:
第一:实例化SoapObject 对象,指定webService的命名空间(从相关WSDL文档中可以查看命名空间),以及调用方法名称。如:
//
命名空间
private
static
final String serviceNameSpace
=
"
http://WebXml.com.cn/
"
;
//
调用方法(获得支持的城市)
private
static
final String getSupportCity
=
"
getSupportCity
"
;
//
实例化SoapObject对象
SoapObject request
=
new
SoapObject(serviceNameSpace, getSupportCity);
request.addProperty( " 参数名称 " , " 参数值 " );
第三步:设置SOAP请求信息(参数部分为SOAP协议版本号,与你要调用的webService中版本号一致):
// 获得序列化的Envelope
SoapSerializationEnvelope envelope = new SoapSerializationEnvelope(SoapEnvelope.VER11);
envelope.bodyOut = request;
第四步:注册Envelope:
( new MarshalBase64()).register(envelope);
第五步:构建传输对象,并指明WSDL文档URL:
// 请求URL
private static final String serviceURL = " http://www.webxml.com.cn/webservices/weatherwebservice.asmx " ;
// Android传输对象
AndroidHttpTransport transport = new AndroidHttpTransport(serviceURL);
transport.debug = true ;
第六步:调用WebService(其中参数为1:命名空间+方法名称,2:Envelope对象):
transport.call(serviceNameSpace + getWeatherbyCityName, envelope);
第七步:解析返回数据:
if (envelope.getResponse() != null ){
return parse(envelope.bodyIn.toString());
}
/** ************
* 解析XML
* @param str
* @return
*/
private static List < String > parse(String str){
String temp;
List < String > list = new ArrayList < String > ();
if (str != null && str.length() > 0 ){
int start = str.indexOf( " string " );
int end = str.lastIndexOf( " ; " );
temp = str.substring(start, end - 3 );
String []test = temp.split( " ; " );
for ( int i = 0 ;i < test.length;i ++ ){
if (i == 0 ){
temp = test[i].substring( 7 );
} else {
temp = test[i].substring( 8 );
}
int index = temp.indexOf( " , " );
list.add(temp.substring( 0 , index));
}
}
return list;
}
这样就成功啦。那么现在我们就来测试下吧,这里有个地址提供webService天气预报的服务的,我这里只提供获取城市列表:
// 命名空间
private static final String serviceNameSpace = " http://WebXml.com.cn/ " ;
// 请求URL
private static final String serviceURL = " http://www.webxml.com.cn/webservices/weatherwebservice.asmx " ;
// 调用方法(获得支持的城市)
private static final String getSupportCity = " getSupportCity " ;
// 调用城市的方法(需要带参数)
private static final String getWeatherbyCityName = " getWeatherbyCityName " ;
// 调用省或者直辖市的方法(获得支持的省份或直辖市)
private static final String getSupportProvince = " getSupportProvince " ;
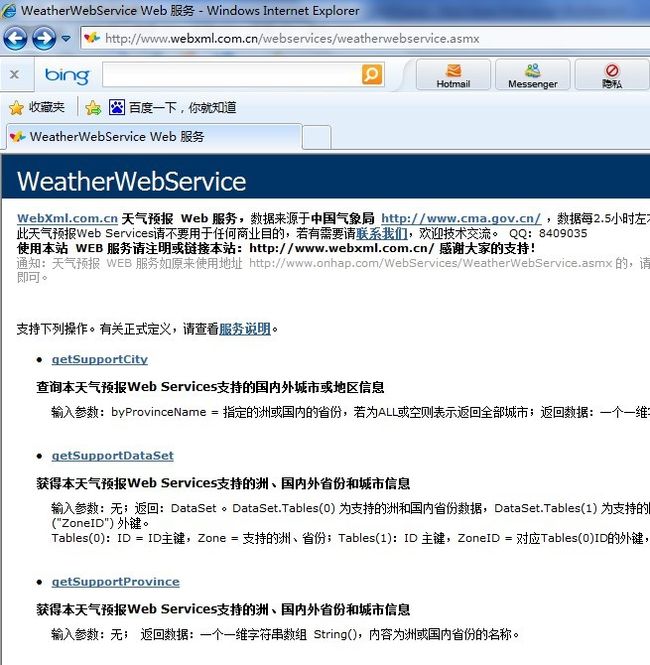
然后你可以在浏览器中输入地址(WSDL):serviceURL,你会看到一些可供调用的方法:
我们选择获取国内外主要城市或者省份的方法吧:getSupportProvice,然后调用,你会发现浏览器返回给我们的是xml文档:
<? xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
- < ArrayOfString xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns ="http://WebXml.com.cn/" >
< string > 直辖市 </ string >
< string > 特别行政区 </ string >
< string > 黑龙江 </ string >
< string > 吉林 </ string >
< string > 辽宁 </ string >
< string > 内蒙古 </ string >
< string > 河北 </ string >
< string > 河南 </ string >
< string > 山东 </ string >
< string > 山西 </ string >
< string > 江苏 </ string >
< string > 安徽 </ string >
< string > 陕西 </ string >
< string > 宁夏 </ string >
< string > 甘肃 </ string >
< string > 青海 </ string >
< string > 湖北 </ string >
< string > 湖南 </ string >
< string > 浙江 </ string >
< string > 江西 </ string >
< string > 福建 </ string >
< string > 贵州 </ string >
< string > 四川 </ string >
< string > 广东 </ string >
< string > 广西 </ string >
< string > 云南 </ string >
< string > 海南 </ string >
< string > 新疆 </ string >
< string > 西藏 </ string >
< string > 台湾 </ string >
< string > 亚洲 </ string >
< string > 欧洲 </ string >
< string > 非洲 </ string >
< string > 北美洲 </ string >
< string > 南美洲 </ string >
< string > 大洋洲 </ string >
</ ArrayOfString >
我们可以用 listview来显示:
那么下面我将给出全部代码:
public class WebServiceHelper {
// WSDL文档中的命名空间
private static final String targetNameSpace = " http://WebXml.com.cn/ " ;
// WSDL文档中的URL
private static final String WSDL = " http://webservice.webxml.com.cn/WebServices/WeatherWebService.asmx?wsdl " ;
// 需要调用的方法名(获得本天气预报Web Services支持的洲、国内外省份和城市信息)
private static final String getSupportProvince = " getSupportProvince " ;
// 需要调用的方法名(获得本天气预报Web Services支持的城市信息,根据省份查询城市集合:带参数)
private static final String getSupportCity = " getSupportCity " ;
// 根据城市或地区名称查询获得未来三天内天气情况、现在的天气实况、天气和生活指数
private static final String getWeatherbyCityName = " getWeatherbyCityName " ;
/* *******
* 获得州,国内外省份和城市信息
* @return
*/
public List < String > getProvince(){
List < String > provinces = new ArrayList < String > ();
String str = "" ;
SoapObject soapObject = new SoapObject(targetNameSpace,getSupportProvince);
// request.addProperty("参数", "参数值");调用的方法参数与参数值(根据具体需要可选可不选)
SoapSerializationEnvelope envelope = new SoapSerializationEnvelope(SoapEnvelope.VER11);
envelope.dotNet = true ;
envelope.setOutputSoapObject(soapObject); // envelope.bodyOut=request;
AndroidHttpTransport httpTranstation = new AndroidHttpTransport(WSDL);
// 或者HttpTransportSE httpTranstation=new HttpTransportSE(WSDL);
try {
httpTranstation.call(targetNameSpace + getSupportProvince, envelope);
SoapObject result = (SoapObject)envelope.getResponse();
// 下面对结果进行解析,结构类似json对象
// str=(String) result.getProperty(6).toString();
int count = result.getPropertyCount();
for ( int index = 0 ;index < count;index ++ ){
provinces.add(result.getProperty(index).toString());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return provinces;
}
/* *********
* 根据省份或者直辖市获取天气预报所支持的城市集合
* @param province
* @return
*/
public List < String > getCitys(String province){
List < String > citys = new ArrayList < String > ();
SoapObject soapObject = new SoapObject(targetNameSpace,getSupportCity);
soapObject.addProperty( " byProvinceName " , province);
SoapSerializationEnvelope envelope = new SoapSerializationEnvelope(SoapEnvelope.VER11);
envelope.dotNet = true ;
envelope.setOutputSoapObject(soapObject);
AndroidHttpTransport httpTransport = new AndroidHttpTransport(WSDL);
try {
httpTransport.call(targetNameSpace + getSupportCity, envelope);
SoapObject result = (SoapObject)envelope.getResponse();
int count = result.getPropertyCount();
for ( int index = 0 ;index < count;index ++ ){
citys.add(result.getProperty(index).toString());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return citys;
}
/* **************************
* 根据城市信息获取天气预报信息
* @param city
* @return
************************** */
public WeatherBean getWeatherByCity(String city){
WeatherBean bean = new WeatherBean();
SoapObject soapObject = new SoapObject(targetNameSpace,getWeatherbyCityName);
soapObject.addProperty( " theCityName " ,city); // 调用的方法参数与参数值(根据具体需要可选可不选)
SoapSerializationEnvelope envelope = new SoapSerializationEnvelope(SoapEnvelope.VER11);
envelope.dotNet = true ;
envelope.setOutputSoapObject(soapObject); // envelope.bodyOut=request;
AndroidHttpTransport httpTranstation = new AndroidHttpTransport(WSDL);
// 或者HttpTransportSE httpTranstation=new HttpTransportSE(WSDL);
try {
httpTranstation.call(targetNameSpace + getWeatherbyCityName, envelope);
SoapObject result = (SoapObject)envelope.getResponse();
// 下面对结果进行解析,结构类似json对象
bean = parserWeather(result);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bean;
}
/* *
* 解析返回的结果
* @param soapObject
*/
protected WeatherBean parserWeather(SoapObject soapObject){
WeatherBean bean = new WeatherBean();
List < Map < String,Object >> list = new ArrayList < Map < String,Object >> ();
Map < String,Object > map = new HashMap < String,Object > ();
// 城市名
bean.setCityName(soapObject.getProperty( 1 ).toString());
// 城市简介
bean.setCityDescription(soapObject.getProperty(soapObject.getPropertyCount() - 1 ).toString());
// 天气实况+建议
bean.setLiveWeather(soapObject.getProperty( 10 ).toString() + " \n " + soapObject.getProperty( 11 ).toString());
// 其他数据
// 日期,
String date = soapObject.getProperty( 6 ).toString();
// ---------------------------------------------------
String weatherToday = " 今天: " + date.split( " " )[ 0 ];
weatherToday += " \n天气: " + date.split( " " )[ 1 ];
weatherToday += " \n气温: " + soapObject.getProperty( 5 ).toString();
weatherToday += " \n风力: " + soapObject.getProperty( 7 ).toString();
weatherToday += " \n " ;
List < Integer > icons = new ArrayList < Integer > ();
icons.add(parseIcon(soapObject.getProperty( 8 ).toString()));
icons.add(parseIcon(soapObject.getProperty( 9 ).toString()));
map.put( " weatherDay " , weatherToday);
map.put( " icons " ,icons);
list.add(map);
// -------------------------------------------------
map = new HashMap < String,Object > ();
date = soapObject.getProperty( 13 ).toString();
String weatherTomorrow = " 明天: " + date.split( " " )[ 0 ];
weatherTomorrow += " \n天气: " + date.split( " " )[ 1 ];
weatherTomorrow += " \n气温: " + soapObject.getProperty( 12 ).toString();
weatherTomorrow += " \n风力: " + soapObject.getProperty( 14 ).toString();
weatherTomorrow += " \n " ;
icons = new ArrayList < Integer > ();
icons.add(parseIcon(soapObject.getProperty( 15 ).toString()));
icons.add(parseIcon(soapObject.getProperty( 16 ).toString()));
map.put( " weatherDay " , weatherTomorrow);
map.put( " icons " ,icons);
list.add(map);
// --------------------------------------------------------------
map = new HashMap < String,Object > ();
date = soapObject.getProperty( 18 ).toString();
String weatherAfterTomorrow = " 后天: " + date.split( " " )[ 0 ];
weatherAfterTomorrow += " \n天气: " + date.split( " " )[ 1 ];
weatherAfterTomorrow += " \n气温: " + soapObject.getProperty( 17 ).toString();
weatherAfterTomorrow += " \n风力: " + soapObject.getProperty( 19 ).toString();
weatherAfterTomorrow += " \n " ;
icons = new ArrayList < Integer > ();
icons.add(parseIcon(soapObject.getProperty( 20 ).toString()));
icons.add(parseIcon(soapObject.getProperty( 21 ).toString()));
map.put( " weatherDay " , weatherAfterTomorrow);
map.put( " icons " ,icons);
list.add(map);
// --------------------------------------------------------------
bean.setList(list);
return bean;
}
// 解析图标字符串
private int parseIcon(String data){
// 0.gif,返回名称0,
int resID = 32 ;
String result = data.substring( 0 , data.length() - 4 ).trim();
// String []icon=data.split(".");
// String result=icon[0].trim();
// Log.e("this is the icon", result.trim());
if ( ! result.equals( " nothing " )){
resID = Integer.parseInt(result.trim());
}
return resID;
// return ("a_"+data).split(".")[0];
}
}
以及帮助类:
public class WebServiceUtil {
// 命名空间
private static final String serviceNameSpace = " http://WebXml.com.cn/ " ;
// 请求URL
private static final String serviceURL = " http://www.webxml.com.cn/webservices/weatherwebservice.asmx " ;
// 调用方法(获得支持的城市)
private static final String getSupportCity = " getSupportCity " ;
// 调用城市的方法(需要带参数)
private static final String getWeatherbyCityName = " getWeatherbyCityName " ;
// 调用省或者直辖市的方法(获得支持的省份或直辖市)
private static final String getSupportProvince = " getSupportProvince " ;
/* ************
* @return城市列表
************ */
public static List < String > getCityList(){
// 实例化SoapObject对象
SoapObject request = new SoapObject(serviceNameSpace, getSupportCity);
// 获得序列化的Envelope
SoapSerializationEnvelope envelope = new SoapSerializationEnvelope(SoapEnvelope.VER11);
envelope.bodyOut = request;
( new MarshalBase64()).register(envelope);
// Android传输对象
AndroidHttpTransport transport = new AndroidHttpTransport(serviceURL);
transport.debug = true ;
// 调用
try {
transport.call(serviceNameSpace + getWeatherbyCityName, envelope);
if (envelope.getResponse() != null ){
return parse(envelope.bodyIn.toString());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null ;
}
public static List < String > getProviceList(){
// 实例化SoapObject对象
SoapObject request = new SoapObject(serviceNameSpace, getSupportProvince);
// 获得序列化的Envelope
SoapSerializationEnvelope envelope = new SoapSerializationEnvelope(SoapEnvelope.VER11);
envelope.bodyOut = request;
( new MarshalBase64()).register(envelope);
// Android传输对象
AndroidHttpTransport transport = new AndroidHttpTransport(serviceURL);
transport.debug = true ;
// 调用
try {
transport.call(serviceNameSpace + getWeatherbyCityName, envelope);
if (envelope.getResponse() != null ){
return null ;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null ;
}
/* ************
* @param cityName
* @return
************ */
public static String getWeather(String cityName){
return "" ;
}
/* *************
* 解析XML
* @param str
* @return
*/
private static List < String > parse(String str){
String temp;
List < String > list = new ArrayList < String > ();
if (str != null && str.length() > 0 ){
int start = str.indexOf( " string " );
int end = str.lastIndexOf( " ; " );
temp = str.substring(start, end - 3 );
String []test = temp.split( " ; " );
for ( int i = 0 ;i < test.length;i ++ ){
if (i == 0 ){
temp = test[i].substring( 7 );
} else {
temp = test[i].substring( 8 );
}
int index = temp.indexOf( " , " );
list.add(temp.substring( 0 , index));
}
}
return list;
}
/* ********
* 获取天气
* @param soapObject
*/
private void parseWeather(SoapObject soapObject){
// String date=soapObject.getProperty(6);
}
}
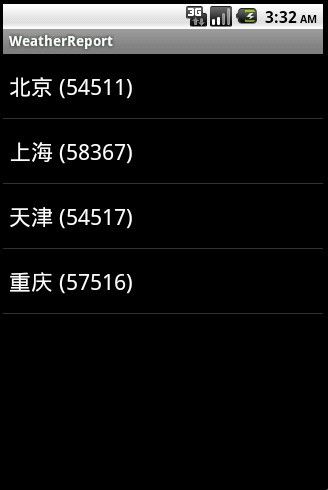
以上就是我所作的查询天气预报的全部核心代码了,读者可以根据注释以及本文章了解下具体实现,相信很快就搞明白了,运行结果如下: