hdu 5375 多校
Gray code
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 604 Accepted Submission(s): 357
Problem Description
The reflected binary code, also known as Gray code after Frank Gray, is a binary numeral system where two successive values differ in only onebit (binary digit). The reflected binary code was originally designed to prevent spurious output from electromechanical switches. Today, Gray codes are widely used to facilitate error correction in digital communications such as digital terrestrial television and some cable TV systems.
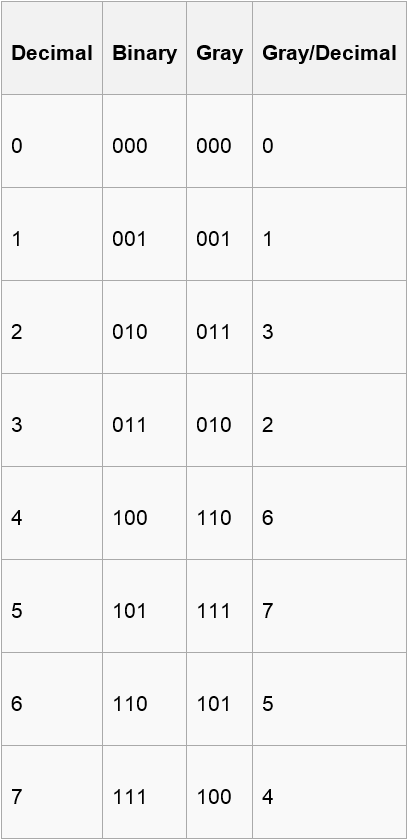
Now , you are given a binary number of length n including ‘0’ , ’1’ and ‘?’(? means that you can use either 0 or 1 to fill this position) and n integers(a1,a2,….,an) . A certain binary number corresponds to a gray code only. If the ith bit of this gray code is 1,you can get the point ai.
Can you tell me how many points you can get at most?
For instance, the binary number “00?0” may be “0000” or “0010”,and the corresponding gray code are “0000” or “0011”.You can choose “0000” getting nothing or “0011” getting the point a3 and a4.

Now , you are given a binary number of length n including ‘0’ , ’1’ and ‘?’(? means that you can use either 0 or 1 to fill this position) and n integers(a1,a2,….,an) . A certain binary number corresponds to a gray code only. If the ith bit of this gray code is 1,you can get the point ai.
Can you tell me how many points you can get at most?
For instance, the binary number “00?0” may be “0000” or “0010”,and the corresponding gray code are “0000” or “0011”.You can choose “0000” getting nothing or “0011” getting the point a3 and a4.
Input
The first line of the input contains the number of test cases T.
Each test case begins with string with ‘0’,’1’ and ‘?’.
The next line contains n (1<=n<=200000) integers (n is the length of the string).
a1 a2 a3 … an (1<=ai<=1000)
Each test case begins with string with ‘0’,’1’ and ‘?’.
The next line contains n (1<=n<=200000) integers (n is the length of the string).
a1 a2 a3 … an (1<=ai<=1000)
Output
For each test case, output “Case #x: ans”, in which x is the case number counted from one,’ans’ is the points you can get at most
Sample Input
2 00?0 1 2 4 8 ???? 1 2 4 8
Sample Output
Case #1: 12 Case #2: 15Hinthttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gray_code http://baike.baidu.com/view/358724.htm
Source
2015 Multi-University Training Contest 7
Recommend
wange2014 | We have carefully selected several similar problems for you: 5379 5378 5377 5376 5375
//#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<time.h>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define eps 1e-8
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define LL long long
#define max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
typedef pair<int , int> pii;
#define maxn 200000
int a[maxn];
char s[maxn];
int d[maxn][2];
int n;
int ans;
int main()
{
int T;
int kase = 0;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%s", s + 1);
n = strlen(s + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d", a + i);
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
d[i][0] = d[i][1] = -INF;
d[0][0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if(s[i] == '?')
{
d[i][0] = max(d[i-1][0], d[i-1][1] + a[i]);
d[i][1] = max(d[i-1][1], d[i-1][0] + a[i]);
}
else
{
int t = s[i] - '0';
d[i][t] = max(d[i-1][t], d[i-1][t^1] + a[i]);
}
}
// for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
// {
// printf("(%d---%d)\n", d[i][0], d[i][1]);
// }
ans = -INF;
ans = max(d[n][0], d[n][1]);
printf("Case #%d: %d\n", ++kase, ans);
}
return 0;
}