Hadoop MapReduce之MapTask任务执行(一)
前面我们介绍了作业的提交(客户端和服务端)、任务分解和调度、任务的启动,这些操作完成之后就是任务执行了,在hadoop中一个任务的执行是包含在一个单独的JVM中的,在任务启动阶段会生成一个shell(taskjvm.sh),然后会通过ShellCommandExecutor类来执行这个脚本,底层通过ProcessBuiler来实现进程启动,那么在启动之后就是任务执行的部分,在执行时hadoop要了解当前任务的执行情况,这里使用了IPC通信的机制,在Child JVM中会创建一个TaskUmbilicalProtocol的代理用于和父进程通信。任务会创建两个日志刷新线程,一个用于周期性的刷新新产生的日志,另一个用于在JVM关闭时最后一次刷新日志。
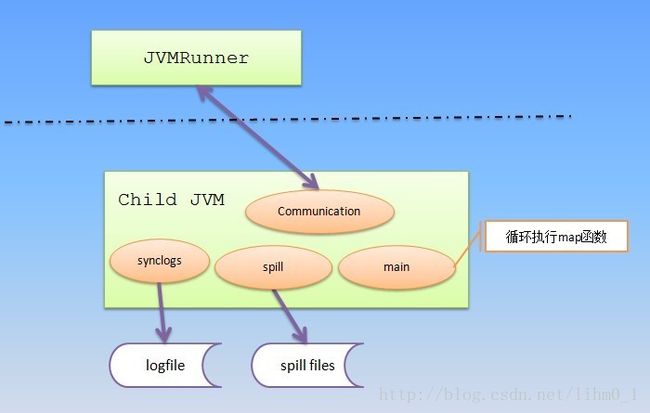
Child JVM通过TaskUmbilicalProtocol与父进程进行周期性通信,来报告作业状态,这个任务是由一个线程实现的(communication thread),作业的执行由RunJar开始,启动某个具体任务由Child启动,中间会经过复杂的任务分配调度,关于任务的提交、调度、JT和TT的通信前面已经介绍过了,我们这里重点分析任务执行,以map任务为例,这个也是和我们业务代码联系较紧密的部分,其中涉及到map如何读取KV、输出KV,排序、合并、分组、写磁盘文件等操作,这些操作是作业中比较耗费资源的操作,关系到我们作业的性能。我们先看任务启动的main函数:

Child JVM通过TaskUmbilicalProtocol与父进程进行周期性通信,来报告作业状态,这个任务是由一个线程实现的(communication thread),作业的执行由RunJar开始,启动某个具体任务由Child启动,中间会经过复杂的任务分配调度,关于任务的提交、调度、JT和TT的通信前面已经介绍过了,我们这里重点分析任务执行,以map任务为例,这个也是和我们业务代码联系较紧密的部分,其中涉及到map如何读取KV、输出KV,排序、合并、分组、写磁盘文件等操作,这些操作是作业中比较耗费资源的操作,关系到我们作业的性能。我们先看任务启动的main函数:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
LOG.debug("Child starting");
//与父进程通信的地址端口信息,用于创建代理
final JobConf defaultConf = new JobConf();
String host = args[0];
int port = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
final InetSocketAddress address = NetUtils.makeSocketAddr(host, port);
//作业ID
final TaskAttemptID firstTaskid = TaskAttemptID.forName(args[2]);
//日志位置
final String logLocation = args[3];
final int SLEEP_LONGER_COUNT = 5;
int jvmIdInt = Integer.parseInt(args[4]);
JVMId jvmId = new JVMId(firstTaskid.getJobID(),firstTaskid.isMap(),jvmIdInt);
//检测任务类型
String prefix = firstTaskid.isMap() ? "MapTask" : "ReduceTask";
//获取工作目录
cwd = System.getenv().get(TaskRunner.HADOOP_WORK_DIR);
if (cwd == null) {
throw new IOException("Environment variable " +
TaskRunner.HADOOP_WORK_DIR + " is not set");
}
// file name is passed thru env
String jobTokenFile =
System.getenv().get(UserGroupInformation.HADOOP_TOKEN_FILE_LOCATION);
Credentials credentials =
TokenCache.loadTokens(jobTokenFile, defaultConf);
LOG.debug("loading token. # keys =" +credentials.numberOfSecretKeys() +
"; from file=" + jobTokenFile);
Token<JobTokenIdentifier> jt = TokenCache.getJobToken(credentials);
SecurityUtil.setTokenService(jt, address);
UserGroupInformation current = UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser();
current.addToken(jt);
UserGroupInformation taskOwner
= UserGroupInformation.createRemoteUser(firstTaskid.getJobID().toString());
taskOwner.addToken(jt);
// Set the credentials
defaultConf.setCredentials(credentials);
//获得与父进行通信代理
final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical =
taskOwner.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<TaskUmbilicalProtocol>() {
@Override
public TaskUmbilicalProtocol run() throws Exception {
return (TaskUmbilicalProtocol)RPC.getProxy(TaskUmbilicalProtocol.class,
TaskUmbilicalProtocol.versionID,
address,
defaultConf);
}
});
int numTasksToExecute = -1; //-1 signifies "no limit"
int numTasksExecuted = 0;
//JVM的钩子进程,用于最后刷新日志
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread() {
public void run() {
try {
if (taskid != null) {
TaskLog.syncLogs
(logLocation, taskid, isCleanup, currentJobSegmented);
}
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
}
}
});
//周期性日志刷新进程
Thread t = new Thread() {
public void run() {
//every so often wake up and syncLogs so that we can track
//logs of the currently running task
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
if (taskid != null) {
TaskLog.syncLogs
(logLocation, taskid, isCleanup, currentJobSegmented);
}
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
} catch (IOException iee) {
LOG.error("Error in syncLogs: " + iee);
System.exit(-1);
}
}
}
};
t.setName("Thread for syncLogs");
t.setDaemon(true);
t.start();
String pid = "";
if (!Shell.WINDOWS) {
pid = System.getenv().get("JVM_PID");
}
JvmContext context = new JvmContext(jvmId, pid);
int idleLoopCount = 0;
Task task = null;
UserGroupInformation childUGI = null;
final JvmContext jvmContext = context;
//注意这里是一个循环,主要作用就是为了任务较多情况下使一个JVM运行多个任务,避免多次启动JVM带来的性能消耗
//同时需要注意的是一个JVM执行的任务是串行的,当上一个任务执行完毕后才能执行下一个,判断标准就是
//已执行的任务数量不能大于我们的设定值
try {
while (true) {
taskid = null;
currentJobSegmented = true;
//获得一个任务
JvmTask myTask = umbilical.getTask(context);
if (myTask.shouldDie()) {//任务被杀死
break;
} else {
if (myTask.getTask() == null) {
taskid = null;
currentJobSegmented = true;
//如果没有接收到任务则产生等待
if (++idleLoopCount >= SLEEP_LONGER_COUNT) {
//we sleep for a bigger interval when we don't receive
//tasks for a while
Thread.sleep(1500);
} else {
Thread.sleep(500);
}
continue;
}
}
//获取到任务
idleLoopCount = 0;
task = myTask.getTask();
task.setJvmContext(jvmContext);
taskid = task.getTaskID();
// 创建JobConf
final JobConf job = new JobConf(task.getJobFile());
currentJobSegmented = logIsSegmented(job);
isCleanup = task.isTaskCleanupTask();
// 重置文件系统统计信息
FileSystem.clearStatistics();
/**
*下面是一系列的初始化操作,例如jobconf、本地目录,证书信息
*/
// Set credentials
job.setCredentials(defaultConf.getCredentials());
//forcefully turn off caching for localfs. All cached FileSystems
//are closed during the JVM shutdown. We do certain
//localfs operations in the shutdown hook, and we don't
//want the localfs to be "closed"
job.setBoolean("fs.file.impl.disable.cache", false);
// set the jobTokenFile into task
task.setJobTokenSecret(JobTokenSecretManager.
createSecretKey(jt.getPassword()));
// setup the child's mapred-local-dir. The child is now sandboxed and
// can only see files down and under attemtdir only.
TaskRunner.setupChildMapredLocalDirs(task, job);
// setup the child's attempt directories
localizeTask(task, job, logLocation);
//setupWorkDir actually sets up the symlinks for the distributed
//cache. After a task exits we wipe the workdir clean, and hence
//the symlinks have to be rebuilt.
TaskRunner.setupWorkDir(job, new File(cwd));
//create the index file so that the log files
//are viewable immediately
TaskLog.syncLogs
(logLocation, taskid, isCleanup, logIsSegmented(job));
numTasksToExecute = job.getNumTasksToExecutePerJvm();
assert(numTasksToExecute != 0);
task.setConf(job);
// Initiate Java VM metrics
initMetrics(prefix, jvmId.toString(), job.getSessionId());
LOG.debug("Creating remote user to execute task: " + job.get("user.name"));
childUGI = UserGroupInformation.createRemoteUser(job.get("user.name"));
// Add tokens to new user so that it may execute its task correctly.
for(Token<?> token : UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser().getTokens()) {
childUGI.addToken(token);
}
// Create a final reference to the task for the doAs block
//认证通过后便开始执行任务了
final Task taskFinal = task;
childUGI.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() throws Exception {
try {
// use job-specified working directory
FileSystem.get(job).setWorkingDirectory(job.getWorkingDirectory());
taskFinal.run(job, umbilical); // 执行任务
} finally {
TaskLog.syncLogs
(logLocation, taskid, isCleanup, logIsSegmented(job));
TaskLogsTruncater trunc = new TaskLogsTruncater(defaultConf);
trunc.truncateLogs(new JVMInfo(
TaskLog.getAttemptDir(taskFinal.getTaskID(),
taskFinal.isTaskCleanupTask()), Arrays.asList(taskFinal)));
}
return null;
}
});
//判断是否超出JVM运行任务的数量,如果没有超出,则继续接受下一个任务
if (numTasksToExecute > 0 && ++numTasksExecuted == numTasksToExecute) {
break;
}
}
}
//下面对于任务异常划分的比较详细,有3种分类
catch (FSError e) { //1、文件系统异常
LOG.fatal("FSError from child", e);
umbilical.fsError(taskid, e.getMessage(), jvmContext);
} catch (Exception exception) {//2、任务执行异常
LOG.warn("Error running child", exception);
try {
if (task != null) {
// do cleanup for the task
if(childUGI == null) {
task.taskCleanup(umbilical);
} else {
final Task taskFinal = task;
childUGI.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() throws Exception {
taskFinal.taskCleanup(umbilical);
return null;
}
});
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.info("Error cleaning up", e);
}
// Report back any failures, for diagnostic purposes
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
exception.printStackTrace(new PrintStream(baos));
if (taskid != null) {
umbilical.reportDiagnosticInfo(taskid, baos.toString(), jvmContext);
}
} catch (Throwable throwable) {//3、JVM异常
LOG.fatal("Error running child : "
+ StringUtils.stringifyException(throwable));
if (taskid != null) {
Throwable tCause = throwable.getCause();
String cause = tCause == null
? throwable.getMessage()
: StringUtils.stringifyException(tCause);
umbilical.fatalError(taskid, cause, jvmContext);
}
} finally {
RPC.stopProxy(umbilical);
shutdownMetrics();
// Shutting down log4j of the child-vm...
// This assumes that on return from Task.run()
// there is no more logging done.
LogManager.shutdown();
}
}
通过上面的分析我们知道,任务执行部分taskFinal.run(job, umbilical)是真正执行map操作的,我们进入这个函数
public void run(final JobConf job, final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
this.umbilical = umbilical;
// 进度报告器创建
TaskReporter reporter = new TaskReporter(getProgress(), umbilical,
jvmContext);
//启动线程并与Parent进程进行通信
reporter.startCommunicationThread();
//判断是否使用新的API
boolean useNewApi = job.getUseNewMapper();
initialize(job, getJobID(), reporter, useNewApi);
// 下面三个判断根据不同作业类型进入不同分支,前面的文章中也提到过setup cleanup任务
//当然这里主要分析useNewApi的部分,因为这里面会调用我们自己的代码逻辑
if (jobCleanup) {
runJobCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (jobSetup) {
runJobSetupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (taskCleanup) {
runTaskCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (useNewApi) {
//下面的代码中会分析这个函数
runNewMapper(job, splitMetaInfo, umbilical, reporter);
} else {
runOldMapper(job, splitMetaInfo, umbilical, reporter);
}
done(umbilical, reporter);
}
现在主要看runNewMapper这个分支,这是MapTask的类的一个函数,注释中介绍的也比较详细了,其中包含了获得任务上下文、获得mapper类(这个是我们自己定义的那个)、输入格式、split信息等操作
private <INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>
void runNewMapper(final JobConf job,
final TaskSplitIndex splitIndex,
final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical,
TaskReporter reporter
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException,
InterruptedException {
// make a task context so we can get the classes
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext taskContext =
new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext(job, getTaskID());
// 这里返回我们自定义mapper的实例
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE> mapper =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getMapperClass(), job);
// 获得输入格式,处理文本时通常用TextInputFormat,当然也可以自定义
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE> inputFormat =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getInputFormatClass(), job);
// 重建split
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit split = null;
split = getSplitDetails(new Path(splitIndex.getSplitLocation()),
splitIndex.getStartOffset());
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE> input =
new NewTrackingRecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE>
(split, inputFormat, reporter, job, taskContext);
job.setBoolean("mapred.skip.on", isSkipping());
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter output = null;
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>.Context
mapperContext = null;
try {
//构建MapperContext
Constructor<org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper.Context> contextConstructor =
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper.Context.class.getConstructor
(new Class[]{org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper.class,
Configuration.class,
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptID.class,
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader.class,
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter.class,
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.OutputCommitter.class,
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.StatusReporter.class,
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit.class});
// get an output object
if (job.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) {
output =
new NewDirectOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter);
} else {//创建输出采集器,用于接收KV的输出
output = new NewOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter);
}
mapperContext = contextConstructor.newInstance(mapper, job, getTaskID(),
input, output, committer,
reporter, split);
//读取动作初始化,确定从哪个位置度,读多少
input.initialize(split, mapperContext);
//开始执行map操作,这里是个循环操作,因为每次处理一对KV值,下面会继续分析这个部分
mapper.run(mapperContext);
//关闭输入
input.close();
output.close(mapperContext);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new IOException("Can't find Context constructor", e);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new IOException("Can't create Context", e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new IOException("Can't invoke Context constructor", e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new IOException("Can't invoke Context constructor", e);
}
}
下面到了与我们自定义mapper交互的时候了,其实这个流程对于熟悉MR的朋友应该比较了解了,当一个map执行的时候,会遵循以下步骤setup 、循环map、cleanup三个操作,这部分代码也是可以在继承Mapper的时候被覆盖的,该部分代码在Mapper类中,因为我的MR中使用的新API,所以我们就分析Mapper类。
public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
setup(context);//熟悉吗?
while (context.nextKeyValue()) {
map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context);//这里调用我们自己的,终于亲切了一回
}
cleanup(context);//眼熟吗?
}
这里贴一段我们自己的map代码,上面这个map执行的时候,会进入自定义代码部分
public class WordCountMapper extends
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
// 计数器
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
// key输出
private Text word = new Text();
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws java.io.IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(line);
while (st.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(st.nextToken());
context.write(word, one);//对于本实例,context类型实际是:TaskInputOutputContext
}
};
}下面的文章中我们会继续跟中任务的执行流程,因为一个map任务在输出后,到reduce执行前还是经历了很多操作的,比如sort、spill,conbine、partitioner等。下回再见。