Visual Representation of SQL Joins
Introduction
This is just a simple article visually explaining SQL JOINs.
Background
I'm a pretty visual person. Things seem to make more sense as a picture. I looked all over the Internet for a good graphical representation of SQL JOINs, but I couldn't find any to my liking. Some had good diagrams but lacked completeness (they didn't have all the possible JOINs), and some were just plain terrible. So, I decided to create my own and write an article about it.
Using the code
I am going to discuss seven different ways you can return data from two relational tables. I will be excluding cross Joins and self referencing Joins. The seven Joins I will discuss are shown below:
INNER JOINLEFT JOINRIGHT JOINOUTER JOINLEFT JOIN EXCLUDING INNER JOINRIGHT JOIN EXCLUDING INNER JOINOUTER JOIN EXCLUDING INNER JOIN
For the sake of this article, I'll refer to 5, 6, and 7 as LEFT EXCLUDING JOIN, RIGHT EXCLUDING JOIN, and OUTER EXCLUDING JOIN, respectively. Some may argue that 5, 6, and 7 are not really joining the two tables, but for simplicity, I will still refer to these as Joins because you use a SQL Join in each of these queries (but exclude some records with a WHERE clause).
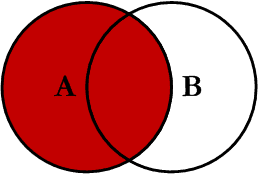
Inner JOIN
This is the simplest, most understood Join and is the most common. This query will return all of the records in the left table (table A) that have a matching record in the right table (table B). This Join is written as follows:
SELECT <select_list> FROM Table_A A INNER JOIN Table_B B ON A.Key = B.Key
Left JOIN
This query will return all of the records in the left table (table A) regardless if any of those records have a match in the right table (table B). It will also return any matching records from the right table. This Join is written as follows:
SELECT <select_list> FROM Table_A A LEFT JOIN Table_B B ON A.Key = B.Key
Right JOIN
This query will return all of the records in the right table (table B) regardless if any of those records have a match in the left table (table A). It will also return any matching records from the left table. This Join is written as follows:
SELECT <select_list> FROM Table_A A RIGHT JOIN Table_B B ON A.Key = B.Key
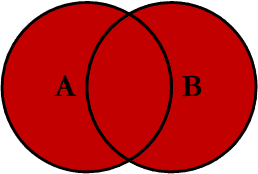
Outer JOIN
This Join can also be referred to as a FULL OUTER JOIN or a FULL JOIN. This query will return all of the records from both tables, joining records from the left table (table A) that match records from the right table (table B). This Join is written as follows:
SELECT <select_list> FROM Table_A A FULL OUTER JOIN Table_B B ON A.Key = B.Key
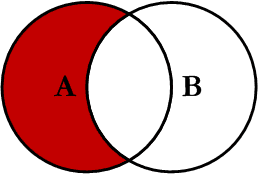
Left Excluding JOIN
This query will return all of the records in the left table (table A) that do not match any records in the right table (table B). This Join is written as follows:
SELECT <select_list> FROM Table_A A LEFT JOIN Table_B B ON A.Key = B.Key WHERE B.Key IS NULL
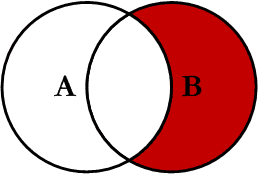
Right Excluding JOIN
This query will return all of the records in the right table (table B) that do not match any records in the left table (table A). This Join is written as follows:
SELECT <select_list> FROM Table_A A RIGHT JOIN Table_B B ON A.Key = B.Key WHERE A.Key IS NULL
Outer Excluding JOIN
This query will return all of the records in the left table (table A) and all of the records in the right table (table B) that do not match. I have yet to have a need for using this type of Join, but all of the others, I use quite frequently. This Join is written as follows:
SELECT <select_list> FROM Table_A A FULL OUTER JOIN Table_B B ON A.Key = B.Key WHERE A.Key IS NULL OR B.Key IS NULL
Examples
Suppose we have two tables, Table_A and Table_B. The data in these tables are shown below:
TABLE_A PK Value ---- ---------- 1 FOX 2 COP 3 TAXI 6 WASHINGTON 7 DELL 5 ARIZONA 4 LINCOLN 10 LUCENT TABLE_B PK Value ---- ---------- 1 TROT 2 CAR 3 CAB 6 MONUMENT 7 PC 8 MICROSOFT 9 APPLE 11 SCOTCH
The results of the seven Joins are shown below:
-- INNER JOIN
SELECT A.PK AS A_PK, A.Value AS A_Value,
B.Value AS B_Value, B.PK AS B_PK
FROM Table_A A
INNER JOIN Table_B B
ON A.PK = B.PK
A_PK A_Value B_Value B_PK
---- ---------- ---------- ----
1 FOX TROT 1
2 COP CAR 2
3 TAXI CAB 3
6 WASHINGTON MONUMENT 6
7 DELL PC 7
(5 row(s) affected)
-- LEFT JOIN SELECT A.PK AS A_PK, A.Value AS A_Value, B.Value AS B_Value, B.PK AS B_PK FROM Table_A A LEFT JOIN Table_B B ON A.PK = B.PK A_PK A_Value B_Value B_PK ---- ---------- ---------- ---- 1 FOX TROT 1 2 COP CAR 2 3 TAXI CAB 3 4 LINCOLN NULL NULL 5 ARIZONA NULL NULL 6 WASHINGTON MONUMENT 6 7 DELL PC 7 10 LUCENT NULL NULL (8 row(s) affected)
-- RIGHT JOIN SELECT A.PK AS A_PK, A.Value AS A_Value, B.Value AS B_Value, B.PK AS B_PK FROM Table_A A RIGHT JOIN Table_B B ON A.PK = B.PK A_PK A_Value B_Value B_PK ---- ---------- ---------- ---- 1 FOX TROT 1 2 COP CAR 2 3 TAXI CAB 3 6 WASHINGTON MONUMENT 6 7 DELL PC 7 NULL NULL MICROSOFT 8 NULL NULL APPLE 9 NULL NULL SCOTCH 11 (8 row(s) affected)
-- OUTER JOIN SELECT A.PK AS A_PK, A.Value AS A_Value, B.Value AS B_Value, B.PK AS B_PK FROM Table_A A FULL OUTER JOIN Table_B B ON A.PK = B.PK A_PK A_Value B_Value B_PK ---- ---------- ---------- ---- 1 FOX TROT 1 2 COP CAR 2 3 TAXI CAB 3 6 WASHINGTON MONUMENT 6 7 DELL PC 7 NULL NULL MICROSOFT 8 NULL NULL APPLE 9 NULL NULL SCOTCH 11 5 ARIZONA NULL NULL 4 LINCOLN NULL NULL 10 LUCENT NULL NULL (11 row(s) affected)
-- LEFT EXCLUDING JOIN SELECT A.PK AS A_PK, A.Value AS A_Value, B.Value AS B_Value, B.PK AS B_PK FROM Table_A A LEFT JOIN Table_B B ON A.PK = B.PK WHERE B.PK IS NULL A_PK A_Value B_Value B_PK ---- ---------- ---------- ---- 4 LINCOLN NULL NULL 5 ARIZONA NULL NULL 10 LUCENT NULL NULL (3 row(s) affected)
-- RIGHT EXCLUDING JOIN SELECT A.PK AS A_PK, A.Value AS A_Value, B.Value AS B_Value, B.PK AS B_PK FROM Table_A A RIGHT JOIN Table_B B ON A.PK = B.PK WHERE A.PK IS NULL A_PK A_Value B_Value B_PK ---- ---------- ---------- ---- NULL NULL MICROSOFT 8 NULL NULL APPLE 9 NULL NULL SCOTCH 11 (3 row(s) affected)
-- OUTER EXCLUDING JOIN SELECT A.PK AS A_PK, A.Value AS A_Value, B.Value AS B_Value, B.PK AS B_PK FROM Table_A A FULL OUTER JOIN Table_B B ON A.PK = B.PK WHERE A.PK IS NULL OR B.PK IS NULL A_PK A_Value B_Value B_PK ---- ---------- ---------- ---- NULL NULL MICROSOFT 8 NULL NULL APPLE 9 NULL NULL SCOTCH 11 5 ARIZONA NULL NULL 4 LINCOLN NULL NULL 10 LUCENT NULL NULL (6 row(s) affected)
Note on the OUTER JOIN that the inner joined records are returned first, followed by the right joined records, and then finally the left joined records (at least, that's how my Microsoft SQL Server did it; this, of course, is without using any ORDER BY statement).
You can visit the Wikipedia article for more info here (however, the entry is not graphical).
I've also created a cheat sheet that you can print out if needed. If you right click on the image below and select "Save Target As...", you will download the full size image.
History
- Initial release -- 02/03/2009.
- Version 1.0 -- 02/04/2009 -- Fixed cheat sheet and minor typos.
License
This article, along with any associated source code and files, is licensed under The Code Project Open License (CPOL)
About the Author
C.L. Moffatt
原文链接:http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/33052/Visual-Representation-of-SQL-Joins