EF里单个实体的增查改删以及主从表关联数据的各种增删 改查
本文目录
- EF对单个实体的增查改删
- 增加单个实体
- 查询单个实体
- 修改单个实体
- 删除单个实体
- EF里主从表关联数据的各种增删改查
- 增加(增加从表数据、增加主从表数据)
- 查询(根据主表找从表数据、根据从表找主表数据)
- 修改(修改从表的外键)
- 删除(删除主从表关系、删除主表数据、删除主从表数据、修改从表数据外键)
- 补充内容
- SaveChanges方法提交多次操作
- DbSet.Add方法返回当前实体
- 源码和系列文章导航
注:本章节多次演示了各种删除,要重复查看效果,需要解开注释初始化数据方法。
一、EF对单个实体的增查改删
增加单个实体:
/// <summary>
/// 增加单个实体
/// </summary>
private static void AddMachuPicchu()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var mauchuPicchu = new DbContexts.Model.Destination
{
Name = "Machu Picchu",
Country = "Peru"
};
context.Destinations.Add(mauchuPicchu);
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
产生的insert sql:
exec sp_executesql N'insert [baga].[Locations]([LocationName], [Country], [Description], [Photo], [TravelWarnings], [ClimateInfo]) values (@0, @1, null, null, null, null) select [LocationID] from [baga].[Locations] where @@ROWCOUNT > 0 and [LocationID] = scope_identity()',N'@0 nvarchar(200),@1 nvarchar(max) ',@0=N'Machu Picchu',@1=N'Peru'
查询单个实体:
/// <summary>
/// 查询单个实体
/// </summary>
private static void GetGreatBarrierReef()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var destination = context.Destinations.Find(4);
Console.WriteLine(destination.Name);
}
}
生成的select sql(find方法生成的查询sql略复杂点,普通的linq查询或者Lambda表达式写法就简单许多了):
exec sp_executesql N'SELECT
[Limit1].[LocationID] AS [LocationID],
[Limit1].[LocationName] AS [LocationName],
[Limit1].[Country] AS [Country],
[Limit1].[Description] AS [Description],
[Limit1].[Photo] AS [Photo],
[Limit1].[TravelWarnings] AS [TravelWarnings],
[Limit1].[ClimateInfo] AS [ClimateInfo]
FROM ( SELECT TOP (2)
[Extent1].[LocationID] AS [LocationID],
[Extent1].[LocationName] AS [LocationName],
[Extent1].[Country] AS [Country],
[Extent1].[Description] AS [Description],
[Extent1].[Photo] AS [Photo],
[Extent1].[TravelWarnings] AS [TravelWarnings],
[Extent1].[ClimateInfo] AS [ClimateInfo]
FROM [baga].[Locations] AS [Extent1]
WHERE [Extent1].[LocationID] = @p0
) AS [Limit1]',N'@p0 int',@p0=4
修改单个实体:
/// <summary>
/// 修改单个实体
/// </summary>
private static void ChangeGrandCanyon()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var canyon = (from d in context.Destinations
where d.Name == "Grand Canyon"
select d).Single();
canyon.Description = "227 mile long canyon.";
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
产生的update sql:
exec sp_executesql N'update [baga].[Locations] set [Description] = @0 where ([LocationID] = @1) ',N'@0 nvarchar(500),@1 int',@0=N'227 mile long canyon.',@1=1
删除单个实体:
/// <summary>
/// 删除单个实体
/// </summary>
private static void DeleteWineGlassBay()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var bay = (from d in context.Destinations
where d.Name == "Wine Glass Bay"
select d).Single();
context.Destinations.Remove(bay);
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
产生的delete sql:
exec sp_executesql N'delete [baga].[Locations] where ([LocationID] = @0)',N'@0 int',@0=3
删除方法这样写可能有点效率问题:要删除一个实体,只要知道它的id就可以了,但是上面的方法却先加载了这个实体到内存中,这个是多余的步骤。我们使用attach方法:
/// <summary>
/// 删除单个实体attach
/// </summary>
private static void DeleteWineGlassBayAttach()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var toDelete = new DbContexts.Model.Destination { DestinationId = 2 };
context.Destinations.Attach(toDelete); //attach
context.Destinations.Remove(toDelete);
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
自然就没有了先加载实体到内存中的sql,只有一个简单的删除sql。attach方法是让EF知道DestinationId为2的实体是一个存在的实体。当然不使用attach,直接调用Remove方法删除会报一个InvalidOperationException错:无法删除此对象,因为未在 ObjectStateManager 中找到它。
attach中文意为“连接,附上”等意思,后续还有很多attach方法高富帅的用法讲解。
还有一种不加载实体到内存就可以删除实体的简单方法,用EF直接执行sql:
/// <summary>
/// 删除单个实体ExecuteSqlCommand
/// </summary>
private static void DeleteWineGlassBayExecuteSqlCommand()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
context.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand("delete from baga.Locations where LocationName = 'Hawaii'");
}
}
可见,都不需要调用上下文的SaveChanges方法了,因为是直接执行sql,所有并不需要EF跟踪任何状态然后提交到数据库。
ok,对于单个的增删改查就是这么简单,有Linq的写法,也有Lambda表达式的写法,都很简单,下面看复杂点的。
二、主从表关联数据的各种增删改查
1.增加
主从表数据的添加分为:仅添加从表数据、添加主表同时增加相关联的从表数据
仅添加从表数据:
/// <summary>
/// 添加从表数据
/// </summary>
private static void NewGrandCanyonResort()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var resort = new DbContexts.Model.Resort
{
Name = "Pete's Luxury Resort"
};
context.Lodgings.Add(resort);
var canyon = (from d in context.Destinations
where d.Name == "Grand Canyon"
select d).Single();
canyon.Lodgings.Add(resort);
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
Lodging是住宿类,有两个类继承本类,分别Resort度假村类和Hostel宿舍类。上面的方法添加了一个Grand Canyon景点的度假村,Name是Pete's Luxury Resort。这里的Grand Canyon是主表数据,Pete's Luxury Resort是从表数据。跟踪到的sql:
exec sp_executesql N'insert [dbo].[Lodgings]([Name], [Owner], [MilesFromNearestAirport], [destination_id], [PrimaryContactId], [SecondaryContactId], [Entertainment], [Activities], [MaxPersonsPerRoom], [PrivateRoomsAvailable], [Discriminator]) values (@0, null, @1, @2, null, null, null, null, null, null, @3) select [LodgingId] from [dbo].[Lodgings] where @@ROWCOUNT > 0 and [LodgingId] = scope_identity()',N'@0 nvarchar(200),@1 decimal(18,2),@2 int,@3 nvarchar(128)',@0=N'Pete''s Luxury Resort',@1=0,@2=1,@3=N'Resort'
这跟单个实体的增加区别就是这样增加出来的数据外键值是有的,不是一个独立的实体了,是一个指向主表某条数据的从表数据。并且注意看sql,最后一列是Discriminator,这个是用来区分继承类映射的列,告诉我们这个属于哪个表的数据,因为Resort度假村类跟Destination没有直接的关系,而是继承的住宿类Lodging跟Destination是多对一的关系。具体点这里了解。
添加主表数据同时添加相关联的从表数据:
/// <summary>
/// 添加主表数据同时添加相关联的从表数据
/// </summary>
private static void AddSingleAndRelatedData()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var destination = new DbContexts.Model.Destination
{
Name = "AnHui HuangShan",
Lodgings = new List<DbContexts.Model.Lodging>
{
new DbContexts.Model.Lodging {Name="HuangShan Hotel"},
new DbContexts.Model.Lodging {Name="YingKeSong Hotel"}
}
};
context.Destinations.Add(destination);
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
监控到三段sql,分别是添加主表数据,和两条添加相关联的从表数据,它们是通过外键destination_id相关联的:
exec sp_executesql N'insert [baga].[Locations]([LocationName], [Country], [Description], [Photo], [TravelWarnings], [ClimateInfo]) values (@0, null, null, null, null, null) select [LocationID] from [baga].[Locations] where @@ROWCOUNT > 0 and [LocationID] = scope_identity()',N'@0 nvarchar(200)',@0=N'AnHui HuangShan'
exec sp_executesql N'insert [dbo].[Lodgings]([Name], [Owner], [MilesFromNearestAirport], [destination_id], [PrimaryContactId], [SecondaryContactId], [Entertainment], [Activities], [MaxPersonsPerRoom], [PrivateRoomsAvailable], [Discriminator]) values (@0, null, @1, @2, null, null, null, null, null, null, @3) select [LodgingId] from [dbo].[Lodgings] where @@ROWCOUNT > 0 and [LodgingId] = scope_identity()',N'@0 nvarchar(200),@1 decimal(18,2),@2 int,@3 nvarchar(128)',@0=N'HuangShan Hotel',@1=0,@2=5,@3=N'Lodging'
exec sp_executesql N'insert [dbo].[Lodgings]([Name], [Owner], [MilesFromNearestAirport], [destination_id], [PrimaryContactId], [SecondaryContactId], [Entertainment], [Activities], [MaxPersonsPerRoom], [PrivateRoomsAvailable], [Discriminator]) values (@0, null, @1, @2, null, null, null, null, null, null, @3) select [LodgingId] from [dbo].[Lodgings] where @@ROWCOUNT > 0 and [LodgingId] = scope_identity()',N'@0 nvarchar(200),@1 decimal(18,2),@2 int,@3 nvarchar(128)',@0=N'YingKeSong Hotel',@1=0,@2=5,@3=N'Lodging'
注意看第一段sql,使用了scope_identity(),这个和ado.net里在每条insert的sql后加上;SELECT @@IDENTITY是一个意思,它会返回自增长的主键id。这里当然是需要返回主键id的,因为后面从表的数据需要用这个当外键。我们可以复制第一条sql到数据库环境里执行看看效果。
2.查找
根据主表找从表数据(显示加载:先Entry,然后Collection):
/// <summary>
/// 根据主表找从表数据(显示加载)
/// </summary>
private static void LoadRelateData()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var canyon = (from d in context.Destinations
where d.Name == "Grand Canyon"
select d).Single();
context.Entry(canyon).Collection(d => d.Lodgings).Load(); //显示加载
foreach (var lodging in context.Lodgings.Local) //遍历的是内存中Lodgings的数据
{
Console.WriteLine(lodging.Name);
}
}
}
根据从表找主表数据(显示加载:先Entry,然后Reference):
/// <summary>
/// 根据从表找主表数据(显示加载)
/// </summary>
private static void LoadPrimaryKeyData()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var lodging = context.Lodgings.First();
//context.Entry(lodging).Reference(l => l.PrimaryContact).Load();
context.Entry(lodging).Reference(l => l.Destination).Load();
foreach (var destination in context.Destinations.Local) //遍历的是内存中的Destinations数据
{
Console.WriteLine(destination.Name);
}
}
}
这是EF标准的查询关联表的数据。如果不看官方的API,我们会怎么根据主表取从表数据、根据从表取主表数据呢?我想是这样:先拿到主表主键id,然后根据id使用find方法(甚至使用ExcuteSqlCommad发送sql)去从表里查,最后得到结果集。从表查主表也一样。这样写有什么不好呢?语句多了不少,其次不是EF建议的写法,个人还是建议使用Entry配合Collection和Reference方法。
3.修改
修改从表的外键:
/// <summary>
/// 修改从表的外键
/// </summary>
private static void ChangeLodgingDestination()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var hotel = (from l in context.Lodgings
where l.Name == "Grand Hotel"
select l).Single();
var reef = (from d in context.Destinations
where d.Name == "Great Barrier Reef"
select d).Single();
hotel.Destination = reef;
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
Grand Hotel本来的外键是LocationId为1的Grand Canyon,我们的代码把它修改成到了LocationId为4的Great Barrier Reef下。生成的sql简单明了:
exec sp_executesql N'update [dbo].[Lodgings] set [destination_id] = @0 where ([LodgingId] = @1) ',N'@0 int,@1 int',@0=4,@1=1
4.删除
删除分为:删除主从表关系、删除主表数据不删除相关联的从表数据、同时删除主从表数据(级联和不级联删除)、删除主表数据同时修改相关联的从表数据指向另一个主表实体
删除主从表关系:主从表的关系是通过从表的外键列确定的,我们只需要赋值从表外键列为null即可
/// <summary>
/// 删除主从表关系(ForeignKeys方式)
/// </summary>
private static void RemovePrimaryContactForeignKeys()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var davesDump = (from l in context.Lodgings
where l.Name == "Dave's Dump"
select l).Single();
davesDump.PrimaryContactId = null;
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
另一种方式:
/// <summary>
/// 删除主从表关系(Reference方式)
/// </summary>
private static void RemovePrimaryContactReference()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var davesDump = (from l in context.Lodgings
where l.Name == "Dave's Dump"
select l).Single();
context.Entry(davesDump).Reference(l => l.PrimaryContact).Load(); //找主表数据
davesDump.PrimaryContact = null; //清空
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
住宿类Lodging跟人类Person有一个多对一的关系,这个很好理解,一个人可以有多个酒店。Dave's Dump这个住宿的地方本来本来是PrimaryContactId为1,也就是PersionId为1的这个人的记录,上面的两个方法都是修改这个1为空,即这个Dave's Dump这个住宿的地方不属于任何人了。看看生成的sql:
exec sp_executesql N'update [dbo].[Lodgings] set [PrimaryContactId] = null where ([LodgingId] = @0) ',N'@0 int',@0=2
删除主表数据不删除相关联的从表数据:
ok,先介绍两个新的实体:
/// <summary>
/// 旅行类
/// </summary>
public class Trip
{
[Key, DatabaseGenerated(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity)]
public Guid Identifier { get; set; }
public DateTime StartDate { get; set; }
public DateTime EndDate { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public decimal CostUSD { get; set; }
[Timestamp]
public byte[] RowVersion { get; set; }
public int DestinationId { get; set; }
[Required]
public Destination Destination { get; set; }
public List<Activity> Activities { get; set; }
}
/// <summary>
/// 预约类
/// </summary>
public class Reservation
{
public Reservation()
{
Payments = new List<Payment>();
}
public int ReservationId { get; set; }
public DateTime DateTimeMade { get; set; }
public Person Traveler { get; set; }
public Trip Trip { get; set; }
public Nullable<DateTime> PaidInFull { get; set; }
public List<Payment> Payments { get; set; }
}
没有配置任何Data Annotation和Fluent API。两个实体的关系是通过Reservation类的Trip导航属性确立的。很明显,这是一个一对一的关系,且预约类Reservation的外键Trip_Identifier是可空的(为何生成的外键名是Trip_Identifier?EF默认映射是取主表实体类名字加主键列),意思很明确,就是预约表Reservations的数据可以对应到旅行表Trip,也可以不对应:
我们在两张表任何一张上右键 - 关系查看下这个主外键关系的设置。删除规则为:不执行任何操作。意思是删除主表数据,对应的从表数据不会被删除;如果打开了级联删除,那么发送一条删除主表数据的sql到数据库,数据库不仅会删除主表数据,也会自动删除对应的从表数据。如果使用Fluent API配置这个一对一的关系,那么默认会打开级联删除。要了解更多级联删除的知识请点击
看看这两张表在数据库里有的数据:
很明显,Reservations预约表的Trip_Identifier列(guid类型)指向了Trips表的主键列Identifier。我们试着删除:
/// <summary>
/// 不加载从表数据直接删除主表数据
/// </summary>
private static void DeleteTrip()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var trip = (from t in context.Trip
where t.Description == "Trip from the database"
select t).Single();
context.Trip.Remove(trip);
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
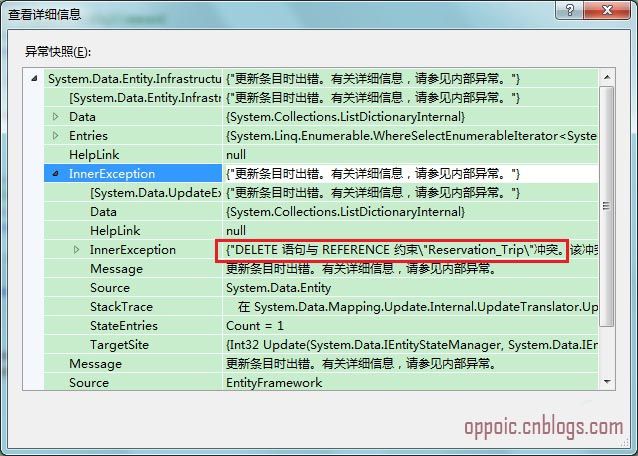
根据Description列的内容从数据库取出主表Trips的某条数据,然后直接调用上下文的Remove方法删除。程序跑起来会报一个DbUpdateException错:
违反了主外键的约束。这个很好理解:从表的某条数据指向主表的这条数据,主表的这条数据自然不能随便删除。我们修改下方法,删除主表某条数据,同时加载其关联的从表数据:
/// <summary>
/// 同时加载从表数据
/// </summary>
private static void DeleteTripLoadRelateData()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var trip = (from t in context.Trip
where t.Description == "Trip from the database"
select t).Single();
var res = (from r in context.Reservations
where r.Trip.Description == "Trip from the database"
select r).Single();
context.Trip.Remove(trip);
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
看看这几行代码生成了多少sql:
1.查出主表数据:
SELECT TOP (2) [Extent1].[Identifier] AS [Identifier], [Extent1].[StartDate] AS [StartDate], [Extent1].[EndDate] AS [EndDate], [Extent1].[Description] AS [Description], [Extent1].[CostUSD] AS [CostUSD], [Extent1].[RowVersion] AS [RowVersion], [Extent1].[DestinationId] AS [DestinationId] FROM [dbo].[Trips] AS [Extent1] WHERE N'Trip from the database' = [Extent1].[Description]
2.查出从表数据:
SELECT TOP (2) [Extent1].[ReservationId] AS [ReservationId], [Extent1].[DateTimeMade] AS [DateTimeMade], [Extent1].[PaidInFull] AS [PaidInFull], [Extent1].[Traveler_PersonId] AS [Traveler_PersonId], [Extent1].[Trip_Identifier] AS [Trip_Identifier] FROM [dbo].[Reservations] AS [Extent1] INNER JOIN [dbo].[Trips] AS [Extent2] ON [Extent1].[Trip_Identifier] = [Extent2].[Identifier] WHERE N'Trip from the database' = [Extent2].[Description]
3.更新从表的外键为null:
exec sp_executesql N'update [dbo].[Reservations] set [Trip_Identifier] = null where (([ReservationId] = @0) and ([Trip_Identifier] = @1)) ',N'@0 int,@1 uniqueidentifier',@0=1,@1='D928B2FE-C667-49C2-BEAC-E9425A12F580'
4.删除主表数据:
exec sp_executesql N'delete [dbo].[Trips] where (([Identifier] = @0) and ([RowVersion] = @1))',N'@0 uniqueidentifier,@1 binary(8)',@0='D928B2FE-C667-49C2-BEAC-E9425A12F580',@1=0x00000000000007D1
看完了你肯定会想EF删除主表数据真麻烦:同时加载主表和从表的数据,然后设置从表外键为null让它不指向主表任何数据,然后再删除主表数据。
正常的思维删除主表数据是这样的:取出主表的主键字段,然后根据主键去从表里找,看看有没有相关联的数据,有就赋值外键为null,最后删除主表数据。写出来无非就是各种find,然后update,最后delete。这是正常的思维和写法,但是缺点很明显:比上面的方法多写了很多代码。
所以,我们还是按照EF的思路来:删除主表数据,就同时加载主表和从表数据到内存中再执行删除主表数据的操作。我们只需要直接调用Remove方法就好,EF自动帮我们把从表的相关数据外键列设置为null。
删除主表数据同时删除相关联的从表数据(级联删除)
/// <summary>
/// 显示加载从表数据
/// </summary>
private static void DeleteGrandCanyonLoadRelateData()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var canyon = (from d in context.Destinations
where d.Name == "Grand Canyon"
select d).Single();
context.Entry(canyon).Collection(d => d.Lodgings).Load(); //显示加载
//不调用Load,也可以先调用Query方法,在内存中执行需要的操作再把结果集加载到内存中,效率!比如:
//context.Entry(canyon).Collection(d => d.Lodgings).Query().Where(l => l.Name.Contains("Hotel")).Load();
context.Destinations.Remove(canyon);
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
因为Destination类和Lodging类已经设置好了级联删除,所以直接找到主键删除即可,相关联的从表数据由数据库自动删除:
/// <summary>
/// 级联删除:不加载从表数据(数据库里必须设置是级联删除)
/// </summary>
private static void DeleteGrandCanyonWithoutLoadRelateData()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var canyon = (from d in context.Destinations
where d.Name == "Grand Canyon"
select d).Single();
context.Destinations.Remove(canyon);
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
删除主表数据同时删除相关联的从表数据(非级联删除)
标注每个从表的数据为删除状态,然后调用数据库上下文的SaveChanges方法:
/// <summary>
/// 普通删除:删除主表数据,同时标注从表数据为删除状态(数据库关闭了级联删除的情况,可以手动去数据库的外键关系修改,也可以Fluent API配置关闭级联删除)
/// </summary>
private static void DeleteGrandCanyonAndMarkChildEntitiesDeletion()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var canyon = (from d in context.Destinations
where d.Name == "Grand Canyon"
select d).Single();
foreach (var lodging in canyon.Lodgings.ToList())
{
context.Lodgings.Remove(lodging); //先标记相关的从表数据为删除状态
}
context.Destinations.Remove(canyon); //再标记主表数据为删除装填
context.SaveChanges(); //执行上面的所有标记
}
}
删除主表数据同时修改相关联的从表数据指向另一个主表实体:
/// <summary>
/// 普通删除:删除主表数据,同时设置从表数据指向另一个主键(数据库默认打开关闭级联删除都可以)
/// </summary>
private static void DeleteGrandCanyonAndChangeChildEntitiesPrimaryKey()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
//找到要删除的主表数据
var canyon = (from d in context.Destinations
where d.Name == "Grand Canyon"
select d).Single();
//找到和主表数据相关的从表数据并修改其主键值,让这些相关的从表数据指向另一个存在的主表数据
var hawaii = context.Destinations.Find(2); //hawaii此时在数据库的主键是2(find方法生成的sql稍复杂,建议使用下面的普通写法)
//var hawaii = (from d in context.Destinations
// where d.DestinationId == 2
// select d).Single();
foreach (var lodging in canyon.Lodgings.ToList())
{
lodging.Destination = hawaii;
}
//最后删除主表数据,可以此时只是单独的删除主表数据,它已经没有了相关的从表数据了
context.Destinations.Remove(canyon);
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
补充内容:以上所有演示我们调用SaveChanges都是提交一个更改,我们试着提交多个操作:
/// <summary>
/// 一次提交多个修改
/// </summary>
private static void MakeMultipleChanges()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var niagaraFalls = new DbContexts.Model.Destination
{
Name = "Niagara Falls",
Country = "USA"
};
context.Destinations.Add(niagaraFalls);
var wineGlassBay = (from d in context.Destinations
where d.Name == "Wine Glass Bay"
select d).Single();
wineGlassBay.Description = "Picturesque bay with beaches";
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
增加一个Destinations表对象,又修改了一个对象,跟踪下sql发现很明确的是一条insert,一条update的sql。SaveChanges也是一个事务,如果一个不成功,那么所有都提交不成功。
仔细看上面的DbSet.Add方法可知,DbSet.Add方法返回的对象就是我们添加的实体对象,上面的Add方法返回的就是DbContexts.Model.Destination。这个给我们编码提供了很好的便利性,我们看一个方法:
/// <summary>
/// 有就查询,没有就添加并查询
/// </summary>
private static void FindOrAddPerson()
{
using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext())
{
var ssn = 123456789;
var person = context.People.Find(ssn) ?? context.People.Add(new DbContexts.Model.Person
{
SocialSecurityNumber = ssn,
FirstName = "Phelps",
LastName = "Michael"
});
Console.WriteLine(person.FirstName);
}
}
??表示前者如果为null就使用后者。很明显,库里不存在ssn为123456789的人,那么程序添加一个新的ssn为123456789的人,添加完毕,这个person对象就是我们刚调用Add方法添加的person。这里并没有调用SaveChanges方法,如果调用SaveChanges方法通过调用person.PersonId还可以获取自增长的主键id。