ARM——操作系统—最小操作系统
自己动手写最小的ARM操作系统。能够看到自己的代码,真的控制着硬件启动起来,心情是不一样的。
ARM是嵌入式设备,想写个操作系统就需要了解硬件。在X86时代有BIOS帮我们,大部分东西简化了。在ARM时代,最小的操作系统,是设置好串口。通过串口打印字符。
最小的PC,也是有键盘,显示器和主机。
最小的嵌入式设备,无键盘,无显示器,只有主机,最通用的就是串口了。所以最小的操作系统,也只能通过这里输出。
我们要做的工作,(目前没有使用中断,从最小系统的角度,已经够了,理解就好。):
1.阅读SOC的芯片手册,找到如何设置UART寄存器。
2.往串口写数据。
.org 0x0000
@
@ UART initialisation (38400 8N1)
@
ldr r0, =0x1c090000 @ UART base (Versatile Express)
mov r1, #0x10 @ ibrd
str r1, [r0, #0x24]
mov r1, #0xc300
orr r1, #0x0001 @ cr
str r1, [r0, #0x30]
mov r1, #'f'
str r1, [r0, #0x0]
mov r1, #'o'
str r1, [r0, #0x0]
mov r1, #'r'
str r1, [r0, #0x0]
mov r1, #'e'
str r1, [r0, #0x0]
mov r1, #'s'
str r1, [r0, #0x0]
mov r1, #'t'
str r1, [r0, #0x0]
mov r1, #'c'
str r1, [r0, #0x0]
mov r1, #'e'
str r1, [r0, #0x0]
mov r1, #'l'
str r1, [r0, #0x0]
mov r1, #'l'
str r1, [r0, #0x0]
mov r1, #0x0A
str r1, [r0, #0x0]
b .
Makefile
# Build an ELF linux image IMAGE = boot.bin BOOTLOADER = boot.S CROSS_COMPILE = arm-none-linux-gnueabi- AS = $(CROSS_COMPILE)as LD = $(CROSS_COMPILE)ld all:$(IMAGE) clean: rm -f $(IMAGE) $(IMAGE): $(BOOTLOADER) $(AS) -o $@ $<
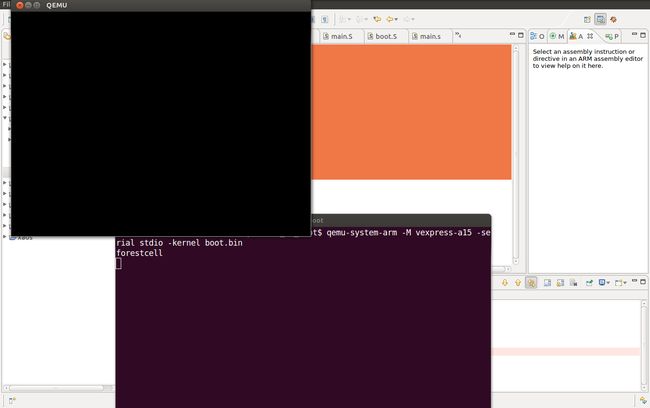
qemu模拟运行的截图