LZW编码
LZW(Lempel-Ziv & Welch)编码又称字串表编码,是Welch将Lemple和Ziv所提出来的无损压缩技术改进后的压缩方法。GIF图像文件采用的是一种改良的LZW压缩算法,通常称为GIF-LZW压缩算法。下面简要介绍GIF-LZW的编码与解码方法。
例 现有来源于二色系统的图像数据源(假设数据以字符串表示):aabbbaabb,试对其进行LZW编码及解码。
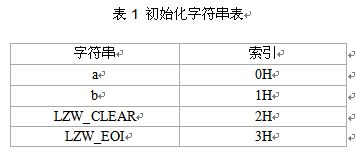
解:1)根据图像中使用的颜色数初始化一个字串表(如表1),字串表中的每个颜色对应一个索引。在初始字串表的LZW_CLEAR和LZW_EOI分别为字串表初始化标志和编码结束标志。设置字符串变量S1、S2并初始化为空。
2)输出LZW_CLEAR在字串表中的索引3H(见表2第一行)。
3)从图像数据流中第一个字符开始,读取一个字符a,将其赋给字符串变量S2。判断S1+S2=“a”在字符表中,则S1=S1+S2=“a”(见表2第二行)。
4)读取图像数据流中下一个字符啊,将其赋给字符串变量S2。判断S1+S2=“aa”不在字符串表中,输出S1=“a”在字串表中的索引0H,并在字串表末尾为S1+S2="aa"添加索引4H,且S1=S2=“a”(见表2第三行)。
5)读下一个字符b赋给S2。判断S1+S2=“ab”不在字符串表中,输出S1=“a”在字串表中的索引0H,并在字串表末尾为S1+S2=“ab”添加索引5H,且S1=S2=“b”(见表2第四行)。
6)读下一个字符b赋给S2。S1+S2=“bb”不在字串表中,输出S1=“b”在字串表中的索引1H,并在字串表末尾为S1+S2=“bb”添加索引6H,且S1=S2=“b”(见表2第五行)。
7)读字符b赋给S2。S1+S2=“bb”在字串表中,则S1=S1+S2=“bb”(见表2第六行)。
8)读字符a赋给S2。S1+S2=“bba”不在字串表中,输出S1=“bb”在字串表中的索引6H,并在字串表末尾为S1+S2=“bba”添加索引7H,且S1=S2=“a”(见表2第七行)。
9)读字符a赋给S2。S1+S2=“aa”在字串表中,则S1=S1+S2=“aa”(见表2第八行)。
10)读字符b赋给S2。S1+S2=“aab”不在字串表中,输出S1=“aa”在字串表中的索引4H,并在字串表末尾为S1+S2=“aab”添加索引8H,且S1=S2=“b”(见表2第九行)。
11)读字符b赋给S2。S1+S2=“bb”,在字串表中,则S1=S1+S2=“b”(见表2第十行)。
12)输出S1中的字符串"b"在字串表中的索引1H(见表2第十一行)。
13)输出结束标志LZW_EOI的索引3H,编码完毕。
最后的编码结果为"30016463“。
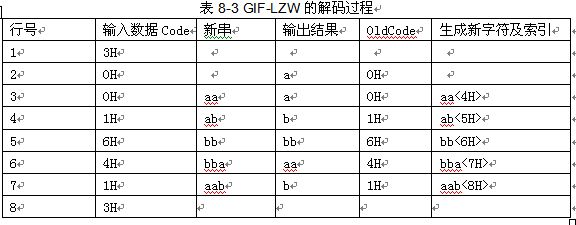
下面对上述编码结果"30016463"进行解码。同样先初始化字符串表,结果如表1所示。
1)首先读取第一个编码Code=3H,由于它为LZW_CLEAR,无输出(见表3第一行)。
2)读入下一个编码Code=0H,由于字符串表中存在该索引,因此输出字符串表中0H对应的字符串"a",同时使OldCode=Code=0H(见表3第二行)。
3)读下一个编码Code=0H,字符串表中存在该索引,输出0H所对应的字符串"a",然后将OldCode=0H所对应的字符串"a"加上Code=0H所对应的字符串的第一个字符"a",即"aa"添加到字串表中,其索引为4H,同时使OldCode=Code=0H(见表3第三行)。
4)读下一个编码Code=1H,字串表中存在该索引,输出1H所对应的字符串"b",然后将OldCode=0H所对应的字符串"a"加上Code=1H所对应的字符串的第一个字符"b",即"ab"添加到字串表中,其索引为5H,同时使OldCode=Code=1H(见表3第四行)。
5)读入下一个编码Code=6H,由于字串表中不存在该索引,因此输出OldCode=1H所对应的字符串"b"加上OldCode的第一个字符"b“,即"bb",同时将"bb"添加到字符串表中,其索引为6H,同时使OldCode=Code=6H(见表3第五行)。
6)读下一个编码Code=4H,字串表中存在该索引,输出4H所对应的字符串"aa",然后将OldCode=6H所对应的字符串"bb"加上Code=4H所对应的字符串的第一个字符"a",即"bba"添加到字串表中,其索引为7H,同时使OldCode=Code=4H(见表3第六行)。
7)读下一个编码Code=6H,字串表中存在该索引,输出6H所对应的字符串"bb",然后将OldCode=4H所对应的字符串"aa"加上Code=6H所对应的字符串的第一个字符"b",即"aab"添加到字串表中,其索引为8H,同时使OldCode=Code=6H(见表3第七行)。
8)读下一个编码Code=3H,它等于LZW_EOI,数据解码完毕(见表3第八行)。
最后的解码结果为aabbbaabb。
由此可见,LZW编码算法在编码与解码过程中所建立的字符串表是一样的,都是动态生成的,因此在压缩文件中不必保存字符串表。
/***********************************************************************************************************
LZW.c
本演示程序提供了LZW编码法的压缩和解压缩函数,并实现了对图象
文件的压缩和解压缩
**********************************************************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define BITS 12 /* Setting the number of bits to 12, 13*/
#define HASHING_SHIFT BITS-8 /* or 14 affects several constants. */
#define MAX_VALUE (1 << BITS) - 1 /* Note that MS-DOS machines need to */
#define MAX_CODE MAX_VALUE - 1 /* compile their code in large model if*/
/* 14 bits are selected. */
#if BITS == 14
#define TABLE_SIZE 18041 /* The string table size needs to be a */
#endif /* prime number that is somewhat larger*/
#if BITS == 13 /* than 2**BITS. */
#define TABLE_SIZE 9029
#endif
#if BITS <= 12
#define TABLE_SIZE 5021
#endif
/* 函数原型 */
int LZW_Compression(char *in_filename, char *out_filename);
int LZW_Decompression(char *in_filename, char *out_filename);
/* 内部函数 */
int find_match(int hash_prefix,unsigned int hash_character);
char *decode_string(unsigned char *buffer,unsigned int code);
unsigned int input_code(FILE *input);
void output_code(FILE *output,unsigned int code);
/* 全局变量,编码/解码使用的内存缓冲区 */
int *code_value; /* This is the code value array */
unsigned int *prefix_code; /* This array holds the prefix codes */
unsigned char *append_character; /* This array holds the appended chars */
unsigned char decode_stack[4000]; /* This array holds the decoded string */
/* 主程序 */
void main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
printf("LZW compression and decompression utility/n");
if (4 != argc)
{
printf("/nUsage : lzw -c|d sourcefilename targetfilename/n");
exit(0);
}
if (! strcmp(argv[1], "-c"))
LZW_Compression(argv[2], argv[3]);
else if (! strcmp(argv[1], "-d"))
LZW_Decompression(argv[2], argv[3]);
else
printf("/nUnknow command./n");
}
/**************************************************************************************************
LZW_Compression()
本函数用LZW算法压缩指定的文件,并将结构存储到新的文件中
***************************************************************************************************/
int LZW_Compression(char *in_filename, char *out_filename)
{
unsigned int next_code;
unsigned int character;
unsigned int string_code;
unsigned int index;
int i;
FILE *input;
FILE *output;
/* allocate memory for compression */
code_value=malloc(TABLE_SIZE*sizeof(unsigned int));
prefix_code=malloc(TABLE_SIZE*sizeof(unsigned int));
append_character=malloc(TABLE_SIZE*sizeof(unsigned char));
if (code_value==NULL || prefix_code==NULL || append_character==NULL)
{
printf("Fatal error allocating table space!/n");
return 0;
}
/* open files */
input=fopen(in_filename,"rb");
output=fopen(out_filename,"wb");
if (input==NULL || output==NULL)
{
printf("Fatal error opening files./n");
return 0;
};
/* compressing... */
next_code=256; /* Next code is the next available string code*/
for (i=0;i<TABLE_SIZE;i++) /* Clear out the string table before starting */
code_value[i]=-1;
i=0;
printf("Compressing.../n");
string_code=getc(input); /* Get the first code */
/*
** This is the main loop where it all happens. This loop runs util all of
** the input has been exhausted. Note that it stops adding codes to the
** table after all of the possible codes have been defined.
*/
while ((character=getc(input)) != (unsigned)EOF)
{
if (++i==1000) /* Print a * every 1000 */
{ /* input characters. This */
i=0; /* is just a pacifier. */
printf(".");
}
index=find_match(string_code,character);/* See if the string is in */
if (code_value[index] != -1) /* the table. If it is, */
string_code=code_value[index]; /* get the code value. If */
else /* the string is not in the*/
{ /* table, try to add it. */
if (next_code <= MAX_CODE)
{
code_value[index]=next_code++;
prefix_code[index]=string_code;
append_character[index]=character;
}
output_code(output,string_code); /* When a string is found */
string_code=character; /* that is not in the table*/
} /* I output the last string*/
} /* after adding the new one*/
/*
** End of the main loop.
*/
output_code(output,string_code); /* Output the last code */
output_code(output,MAX_VALUE); /* Output the end of buffer code */
output_code(output,0); /* This code flushes the output buffer*/
printf("/n");
/* cleanup... */
fclose(input);
fclose(output);
free(code_value);
free(prefix_code);
free(append_character);
return 1;
}
/*
** This is the hashing routine. It tries to find a match for the prefix+char
** string in the string table. If it finds it, the index is returned. If
** the string is not found, the first available index in the string table is
** returned instead.
*/
int find_match(int hash_prefix,unsigned int hash_character)
{
int index;
int offset;
index = (hash_character << HASHING_SHIFT) ^ hash_prefix;
if (index == 0)
offset = 1;
else
offset = TABLE_SIZE - index;
while (1)
{
if (code_value[index] == -1)
return(index);
if ((int)prefix_code[index] == hash_prefix &&
append_character[index] == hash_character)
return(index);
index -= offset;
if (index < 0)
index += TABLE_SIZE;
}
}
/*******************************************************************
LZW_Decompression()
用LZW对文件进行解码
********************************************************************/
int LZW_Decompression(char *in_filename, char *out_filename)
{
unsigned int next_code;
unsigned int new_code;
unsigned int old_code;
int character;
int counter;
unsigned char *string;
FILE *input;
FILE *output;
/* allocate memory for decompression */
prefix_code=malloc(TABLE_SIZE*sizeof(unsigned int));
append_character=malloc(TABLE_SIZE*sizeof(unsigned char));
if (prefix_code==NULL || append_character==NULL)
{
printf("Fatal error allocating table space!/n");
return 0;
}
/* open files */
input=fopen(in_filename,"rb");
output=fopen(out_filename,"wb");
if (input==NULL || output==NULL)
{
printf("Fatal error opening files./n");
return 0;
};
/* decompress... */
next_code=256; /* This is the next available code to define */
counter=0; /* Counter is used as a pacifier. */
printf("Decompress.../n");
old_code=input_code(input); /* Read in the first code, initialize the */
character=old_code; /* character variable, and send the first */
putc(old_code,output); /* code to the output file */
/*
** This is the main expansion loop. It reads in characters from the LZW file
** until it sees the special code used to inidicate the end of the data.
*/
while ((new_code=input_code(input)) != (MAX_VALUE))
{
if (++counter==1000) /* This section of code prints out */
{ /* an asterisk every 1000 characters */
counter=0; /* It is just a pacifier. */
printf(".");
}
/*
** This code checks for the special STRING+CHARACTER+STRING+CHARACTER+STRING
** case which generates an undefined code. It handles it by decoding
** the last code, and adding a single character to the end of the decode string.
*/
if (new_code>=next_code)
{
*decode_stack=character;
string=decode_string(decode_stack+1,old_code);
}
/*
** Otherwise we do a straight decode of the new code.
*/
else
string=decode_string(decode_stack,new_code);
/*
** Now we output the decoded string in reverse order.
*/
character=*string;
while (string >= decode_stack)
putc(*string--,output);
/*
** Finally, if possible, add a new code to the string table.
*/
if (next_code <= MAX_CODE)
{
prefix_code[next_code]=old_code;
append_character[next_code]=character;
next_code++;
}
old_code=new_code;
}
printf("/n");
/* cleanup... */
fclose(input);
fclose(output);
free(prefix_code);
free(append_character);
return 1;
}
/*
** This routine simply decodes a string from the string table, storing
** it in a buffer. The buffer can then be output in reverse order by
** the expansion program.
*/
char *decode_string(unsigned char *buffer,unsigned int code)
{
int i;
i=0;
while (code > 255)
{
*buffer++ = append_character[code];
code=prefix_code[code];
if (i++>=4094)
{
printf("Fatal error during code expansion./n");
exit(0);
}
}
*buffer=code;
return(buffer);
}
/*
** The following two routines are used to output variable length
** codes. They are written strictly for clarity, and are not
** particularyl efficient.
*/
unsigned int input_code(FILE *input)
{
unsigned int return_value;
static int input_bit_count=0;
static unsigned long input_bit_buffer=0L;
while (input_bit_count <= 24)
{
input_bit_buffer |=
(unsigned long) getc(input) << (24-input_bit_count);
input_bit_count += 8;
}
return_value=input_bit_buffer >> (32-BITS);
input_bit_buffer <<= BITS;
input_bit_count -= BITS;
return(return_value);
}
void output_code(FILE *output,unsigned int code)
{
static int output_bit_count=0;
static unsigned long output_bit_buffer=0L;
output_bit_buffer |= (unsigned long) code << (32-BITS-output_bit_count);
output_bit_count += BITS;
while (output_bit_count >= 8)
{
putc(output_bit_buffer >> 24,output);
output_bit_buffer <<= 8;
output_bit_count -= 8;
}
}