NoSQL标准性能测试
1 概述
随着IT技术的不断发展和革新,近年来,一种称之为“NoSQL”的技术渐渐成为业界的新宠,在很多不同的行业和应用领域能够替代传统的关系型数据库,提供更敏捷的开发效率与执行效率。NoSQL技术通过弱化一部分关系型数据库的特性,例如一致性和关系模型等,来提升其可扩展性以及高可用性,弥补了关系型数据库在很多互联网类应用中的不足。
在本篇测试报告中,我们使用Yahoo发布的标准YCSB测试规则,对包括几款国外的NoSQL数据库产品和SequoiaDB进行对比,并尝试给出每种不同产品所适用的应用场景。在测试配置中,我们尽可能对全部产品做到高可用配置,而在一致性级别上则使用最终一致性。
在测试中我们会对两种类型的NoSQL数据库做横向对比,包括Document-Oriented文档类数据库、以及Big-Table宽表类数据库。由于每种类型的数据库具有很多自己独特的特性,我们不能将每种特性一一表现在该测评结果中。本测试主要针对数据库在不同任务类型下的性能指标进行,且仅依赖YCSB所提供的标准测试流程。
本测试由SequoiaDB开发团队完成,并在文档中详细列出本测试的物理环境以及配置信息,以便于读者能够使用自己的环境独立验证结果。
2 测试概要
2.1 测试产品
本测试主要对比两种类型的NoSQL数据库,包括四款不同的产品:
- MongoDB (文档类,V2.6.1)
- SequoiaDB (文档类,V1.8)
- HBase (宽表类,V0.94.6-CDH4.5.0)
- Cassandra (宽表类,V1.1.12)
其中MongoDB作为当前市场占有率最高的数据库,可能是众多读者所关心的产品,提供丰富的数据库功能,号称是最接近关系型数据库的NoSQL产品;而SequoiaDB作为我国新兴的文档类数据库产品,由前IBM DB2团队的研发人员创建,据称在性能和功能上能够与MongoDB做正面抗衡,同样提供很多MongoDB所提供的功能(例如分片、多索引等特性)。
HBase则是Hadoop框架的一员,也已经被广大企业和互联网用户所接受,我们使用的版本0.94.6是跟随CDH 4.5.0安装包的版本;而Cassandra则是与HBase类似的产品,由Facebook研发并进行开源,同样拥有广大的用户市场。
我们的测试使用由Yahoo!研究院发布的Yahoo Cloud Serving Benchmark (YCSB)基准测试,并将接口对各自产品的最新版进行了修改和适配。我们在正文后的附录中也提供了SequoiaDB的YCSB测试接口。
需要重新强调的是,每种不同的产品都有各自的应用场景。YCSB测试尽管是Yahoo!研究院提供的测试框架,但是在很多场景下并不能完全发挥出每个产品各自的特点。在本测试中,我们尝试使用YCSB框架给出最为客观的评估结果。如果对于该测试结果或配置存在疑问,我们欢迎广大读者根据自身需要重新调整,并将结果共享给我们SequoiaDB的开发团队作为参考。
2.2 测试场景
YCSB测试框架提供了丰富的场景配置机制,允许用户根据需要选择需要导入的数据量和增删改查之间相应的比例。在本测试中,我们导入一亿条数据,并对如下场景进行对比。
| 场景编号 |
场景分类 |
描述 |
| 1 |
单条记录导入 |
单条记录导入 |
| 2 |
批量记录导入 |
批量记录导入 |
| 3 |
单纯查询 |
100%查询 |
| 4 |
查询导入平衡 |
50%导入,50%查询 |
| 5 |
更新为主 |
95%更新,5%查询 |
| 6 |
查询为主 |
95%查询,5%更新 |
| 7 |
查询最新 |
95%查询,5%导入 |
对于数据导入的场景,我们对单条记录插入和批量插入两个场景进行了区分。对于一些数据库来说,默认配置会在客户端将一批记录打包并统一发送给服务器,对于这类产品,尽管其接口为单条记录操作,我们依然将其归类为批量记录导入模式。
写入和查询的数据模拟典型日志记录的长度,具有以下特性:
| 特性 |
描述 |
| 字段数 |
10字段 |
| 字段名长度 |
6字节 |
| 记录总大小 |
100Bytes |
| 全部字段类型 |
字符串 |
| 主键长度 |
23字节 |
| 总记录数 |
1亿条 |
| 总裸数据量 |
大约100GB |
| 数据副本份数 |
3 |
其中,SequoiaDB与MongoDB的分片均配置为一主两从;HBase所在的HDFS设置复制份数为3;Cassandra建表时使用参数replication_factor=2。
一致性级别上,我们使用最弱的最终一致性,读写的write concern均设置为1。
2.3 测试环境
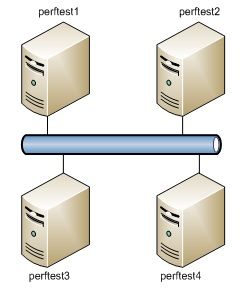
本测试中,测试环境总共包含4台Dell R520物理机作为数据存储。生成数据的YCSB程序与数据库运行在同一物理环境。
注:如使用独立服务器进行YCSB的数据生成,会导致千兆网瓶颈。
整个集群的拓扑结构如图1所示:
图1:测试集群拓扑
2.3.1 服务器环境
本测试数据库服务器使用4台Dell R520物理机环境,每台物理机配置如下:
| 类型 |
参数 |
| CPU |
Intel(R) Xeon® CPU E5-2420 1.9GHZ (6 core) |
| 内存 |
DDR3 48GB |
| 磁盘 |
6块内置SATA硬盘,2TB/块 |
| 网络 |
千兆以太网 |
| 操作系统 |
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 6.4 kernel-release:2.6.32-358.e16.x86_64 |
| JDK |
Oracle JDK 1.6 |
2.4 测试方法
本测试使用YCSB标准,基于四台物理机执行。对于每种不同产品的测试流程如下:
1 安装软件
2 基于四节点部署集群,配置时尽可能基于以下准则:
- 高可用配置
- 最终一致性
- 功能与单节点环境保持一致
- 充分利用硬件资源
3 在四台物理机中部署YCSB集群,向本地集群写入读取数据
4 进行数据操作时通过YCSB产生记录的统计数量
5 根据结果生成Excel文件
6 针对其他场景重复以上步骤
并发性方面则基于以下规则:
- 单条记录插入每服务器24条线程
- 批量记录插入每服务器8条线程
- 其他所有操作每服务器36条线程
3 测试结果
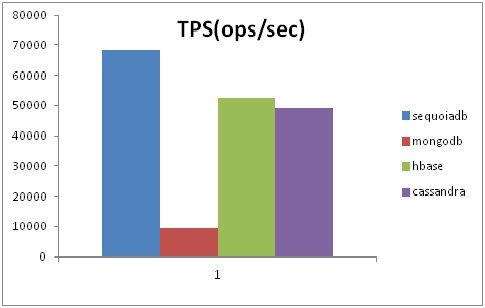
3.1 场景1:单条记录导入
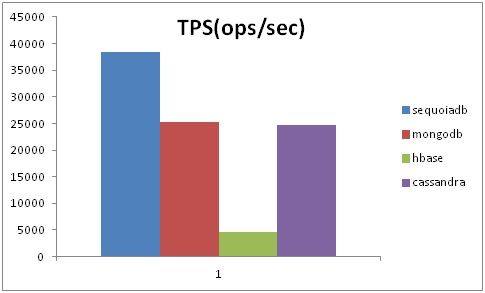
图2:单条记录导入场景
在单条记录导入场景中,SequoiaDB与MongoDB使用insert方法,writeConcern设置为Normal;HBase则设置客户端缓冲区为2KB。而在错误检验方式上,由于是单条记录插入,所以MongoDB必须在每次操作后检测返回值是否成功,因此不可以使用异步插入方式。
在图2的结果中可以看到,单条记录导入操作SequoiaDB最高,总吞吐量可以达到每秒钟近7万。而HBase与Cassandra则比较接近,在5-6万之间。MongoDB在该场景中表现较差,总吞吐量不到每秒1万。
在该场景中,YCSB在4台服务器上各启动24条线程,总共并发量为96线程。3.2 场景2:批量记录导入
图3:批量记录导入场景
批量记录导入场景的结果见图3。在该场景中,SequoiaDB与MongoDB使用各自提供的bulk insert方法;HBase则设置client buffer为4MB;Cassandra不提供批量数据导入方式。
在该测试中,批量导入数据为每批次3000条记录,每节点启动8条线程,总数32线程。
测试结果显示,SequoiaDB可以达到每秒钟近19万的导入速度,而MongoDB则与单线程导入的性能接近(1万左右),HBase也没有本质提升。
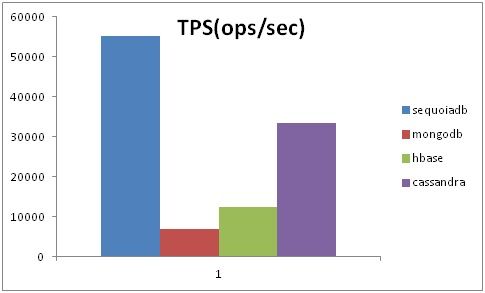
3.3 场景3:单纯查询
图4:单纯查询场景
图4显示单纯随机查询的场景。在该场景中MongoDB表现最为突出,整体吞吐量达到每秒钟8万以上。SequoiaDB和Cassandra类似,大约为MongoDB的一半,在4万至5万之间徘徊。而HBase表现最差,未达到每秒1万的指标。
该场景每台物理服务器使用36条客户端线程,总数144条线程。3.4 场景4:查询导入平衡
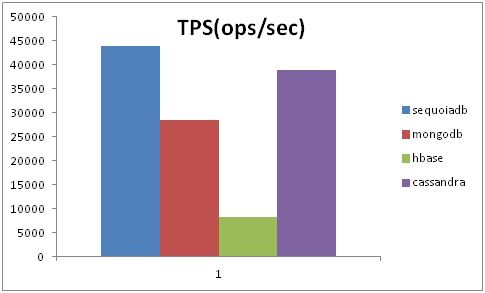
图5:查询导入平衡场景
该场景主要模拟50%的插入和50%的查询业务(图5)。其中插入业务使用单条记录插入。
最终的结果显示,SequoiaDB的整体表现最优,平均达到每秒钟超过14000TPS,而MongoDB/HBase/Cassandra则比较接近,各自不到10000TPS。3.5 场景5:更新为主
图6:更新为主场景
如图6所示,更新为主场景模拟95%更新与5%查询的场景。该场景中,SequoiaDB表现最优,结果介于5万到6万之间每秒。
而MongoDB表现相对较弱,大约在5千每秒左右的数量级。
3.6 场景6:查询为主
图7:查询为主场景
在查询为主的场景中,模拟95%查询+5%更新。在该测试中,SequoiaDB与Cassandra的性能接近单纯查询的场景,而更新操作对MongoDB的损耗相对较大,使其性能仅不到3万每秒。
HBase在随机读为主的场景下相对较慢。
3.7 场景7:查询最新
图8:查询最新场景
查询最新场景为95%读+5%插入,并且读取的数据尽可能是刚刚写入的数据。
从图8中可以看出,SequoiaDB对于刚刚写入至内存中便读取的场景性能最佳,达到近4万每秒。
而MongoDB和Cassandra则相比场景6有明显下降,HBase依然性能较低。
4 结论
从第三部分的各个场景对比中可以看出,SequoiaDB数据库在数据插入场景中表现最为突出,甚至超过本身以插入性能著称的Cassandra。而业界普及率最高的MongoDB则在单纯读取性能上最为抢眼,远远超过HBase和Cassandra。
总体来看,SequoiaDB在性能表现上较为出色,与其他主流NoSQL数据库相比在多个指标上明显胜出,并且不存在明显的短板。
HBase与Cassandra虽然在写入性能上远高于MongoDB,但是和SequoiaDB相比仍然逊色一筹;而在主键随机读操作方面,Cassandra的新版本和之前的版本比起来性能大幅度上升,基本做到和MongoDB/SequoiaDB处于同一水平线,而HBase则远不能和其他产品相比。
当然,这些比较也仅仅局限于YCSB所做的测试,而文档类数据库能够提供的二级索引等机制并非是YCSB所测试的。因此,文档类数据库能够提供比宽表类数据库更多的应用场景。
如此看来,对于宽表类数据库来说,如果在其最有优势的主场都败给了SequoiaDB文档类数据库,这是否意味着,HBase和Cassandra最大的优势已经不再,文档类数据库会在各个领域的性能表现超越宽表呢?5 附录A:配置信息
5.1 MongoDB
mongodb的分片分布如图9,不同颜色代表不同的分片,我们采用的是多个副本的分片。
图9:MongoDB环境部署
mongodb的部署脚本如下(deploy.sh):
#!/bin/bash
sshperftest-1 "mongod --configsvr --logpath/data/disk1/mongodb-cfg/configsvr.log --dbpath /data/disk1/mongodb-cfg/ --port37019 --journal --fork"
sshperftest-2 "mongod --configsvr --logpath /data/disk1/mongodb-cfg/configsvr.log--dbpath /data/disk1/mongodb-cfg/ --port 37019 --journal --fork"
sshperftest-3 "mongod --configsvr --logpath/data/disk1/mongodb-cfg/configsvr.log --dbpath /data/disk1/mongodb-cfg/ --port37019 --journal --fork"
sshperftest-1 "mongos --configdb perftest-0:37019,perftest-1:37019,perftest-2:37019--logpath /data/disk1/mongodb-data/mongos.log --fork"
sshperftest-2 "mongos --configdbperftest-0:37019,perftest-1:37019,perftest-2:37019 --logpath/data/disk1/mongodb-data/mongos.log --fork"
sshperftest-3 "mongos --configdbperftest-0:37019,perftest-1:37019,perftest-2:37019 --logpath/data/disk1/mongodb-data/mongos.log --fork"
sshperftest-4 "mongos --configdbperftest-0:37019,perftest-1:37019,perftest-2:37019 --logpath/data/disk1/mongodb-data/mongos.log --fork"
hostno=0
hosts=("perftest-1""perftest-2" "perftest-3" "perftest-4")
disknos=(11 1 1)
port=37017
for((i=0;i<8;++i))
do
for ((j=0;j<3;++j))
do
ssh ${hosts[$hostno]} "mongod--replSet dg$i --logpath /data/disk${disknos[$hostno]}/mongodb-data/mongd.log--dbpath /data/disk${disknos[$hostno]}/mongodb-data/ --logappend --quiet --port$port --fork"
letdisknos[$hostno]=${disknos[$hostno]}+1
let hostno=hostno+1
if [ $hostno -eq ${#hosts[@]} ];then
let hostno=0
fi
done
let port=port+10
done
mongodb的分片添加脚本如下(addshard.js):
varport=37017
varhosts=[" perftest-1"," perftest-2"," perftest-3","perftest-4"];
var hostid=0;
for(i=0;i<8;++i)
{
var conf = new Object();
conf._id = 'dg'+i;
conf.members = new Array();
for (j=0;j<3;++j)
{
var member = new Object();
member._id = j;
member.host = hosts[hostid] +":" + port;
conf.members[j] = member;
hostid=hostid+1;
if (hostid == hosts.length)
{
hostid = 0;
}
}
var db = connect(conf.members[0].host+"/test");
rs.initiate(conf);
rs.conf();
port =port + 10
var db2 = connect(conf.members[0].host +'/test');
sh.addShard('dg'+i+'/'+conf.members[0].host )
}
mongodb的集合创建脚本如下(createcl.sh):
mongo<<EOF
sh.stopBalancer();
useycsb;
db.dropDatabase();
useadmin;
db.runCommand({enableSharding:"ycsb"});
useadmin;
db.runCommand({shardcollection:"ycsb.usertable",key:{_id:'hashed'},numInitialChunks:4096});
exit
EOF
所有的writeConcern都为normal。
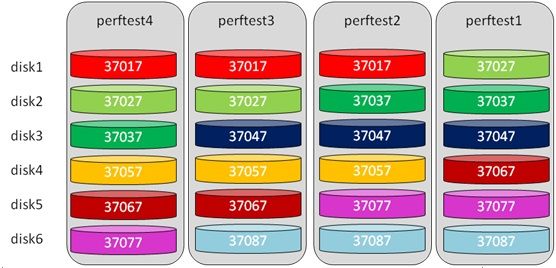
5.2 SequoiaDB
sequoiadb的数据组分布情况如图10,其中不同颜色代表不同的分片。

图10:SequoiaDB部署架构图
sequoiadb的部署脚本如下(deploy.js):
try
{
var db = new Sdb();
db.createCataRG('perftest-1',11820,'/opt/sequoiadb/database/cata/11820');
db.getRG(1).createNode('perftest-2',11820,'/opt/sequoiadb/database/cata/11820');
db.getRG(1).createNode('perftest-3',11820,'/opt/sequoiadb/database/cata/11820');
db.getRG(1).getNode('perftest-2',11820).start();
db.getRG(1).getNode('perftest-3',11820).start();
// group number is 8
var port=11830;
var hostid = 0;
var diskno = 1;
var diskids = [1,1,1,1];
for(i=0;i<8;++i)
{
db.createRG('dg'+i);
// 3 nodes of per group
for (j=0;j<3;++j)
{
db.getRG('dg'+i).createNode('perftest-'+( hostid+1), port,'/data/disk' +diskids[hostid] + '/sequoiadb/database/data'+port);
diskids[hostid] += 1;
hostid += 1;
if (hostid > 3)
{
hostid = 0;
}
}
db.getRG('dg'+i).start();
port += 10;
}
}catch(e)
{
throw e;
}
创建分区集合的脚本如下(createcl.js):
try
{
var db = new Sdb()
db.dropCS('ycsb')
}catch(e)
{
if (e != -34)
{
throw "drop cs failure" + e;
}
}
try
{
db.createCS('ycsb')
db.ycsb.createCL('usertable',{ShardingType:'hash',ShardingKey:{_id:1},EnsureShardingIndex:false})
var snapshot8 =db.snapshot(8,{Name:'ycsb.usertable'}).toArray();
var obj = eval ( "(" +snapshot8[0] + ")" );
var srcgroup =obj["CataInfo"][0]["GroupName"];
var partition = obj["Partition"];
var groupnames = new Array()
var groups = db.list(7).toArray();
for(i=0;i<groups.length;++i)
{
var group = eval("(" +groups[i] + ")");
if (group["GroupName"] =="SYSCatalogGroup")
{
continue;
}
groupnames.push(group["GroupName"]);
}
var remainderpart = partition %groupnames.length ;
var part = (partition - remainderpart) /groupnames.length
for(i=0;i<groupnames.length;++i)
{
if (groupnames[i] == srcgroup )
{
continue;
}
println("spliting from " +srcgroup + " to " + groupnames[i]+ "........");
db.ycsb.usertable.split(srcgroup,groupnames[i], {Partition: (i*part)},{Partition:(i+1)*part});
if (remainderpart > 1)
{
db.ycsb.usertable.split(srcgroup,groupnames[i], {Partition: endpart},{Partition: (endpart + 1)})
endpart += 1;
remainderpart -= 1;
}
}
}catch(e)
{
throw e;
}
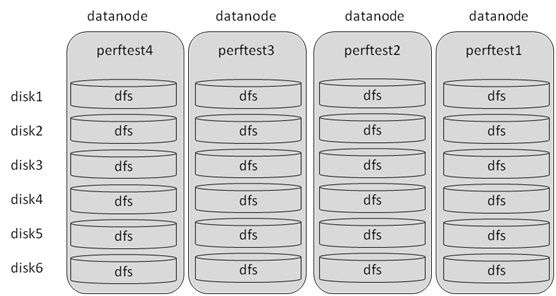
5.3 HBase
HBase的数据分布情况如图11:
图11:HBase部署架构图
创始表语句使用:
create'usertable', 'cf', {SPLITS => ['user1', 'user2', 'user3', 'user4', 'user5', 'user6','user7', 'user8', 'user9' ]}
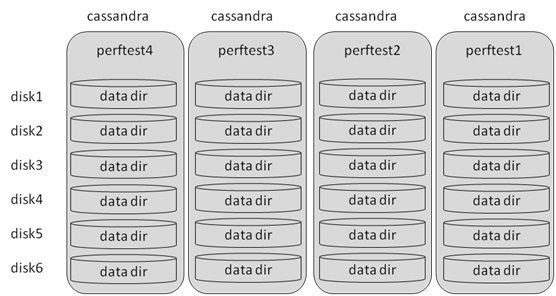
5.4 Cassandra
图12是一个Cassandra四节点集群。我们采用使用二十四块硬盘同时处理数据和提交日志。
图12:Cassandra部署架构图
与测试的其他数据库不同,Cassandra在配置中使用环形拓扑,节点需要被明确地视为“种子”节点(这有助于它们加入到环中)。在配置时,必须指定哪些令牌将映射到哪些实例。
我们使用了https://raw.github.com/riptano/ComboAMI/2.2/tokentoolv2.py提供的令牌生成工具来创建节点配置。
$ ./tokentoolv2.py 4
{
"0":{
"0":0,
"1":42535295865117307932921825928971026432,
"2":85070591730234615865843651857942052864,
"3":127605887595351923798765477786913079296
}
}
Cassandra 的一致性级别可以调节。每次读取和写入都可以明确地说明该操作需要什么级别的数据库一致性。由于这是一个基准测试项目,因此我们使用了最弱和最快的一致性级别(ONE)来进行读取和写入。
对于所有数据库,我们使用的复制因子都是 2。其他主要设置为:
| 内容 |
值 |
| 分区工具 |
RandomPartitioner |
| 初始令牌空间 |
2^127 / 4 |
| 内存表空间 |
4GB |
| 并发读取 |
48 |
| 并发写入 |
48 |
| 压缩 |
SnappyCompressor |
| 提交日志同步 |
10000 ms |
以下内容为 conf/cassandra.yaml的设置:
cluster_name:'Test'
initial_token:0
hinted_handoff_enabled:true
max_hint_window_in_ms:3600000 # one hour
hinted_handoff_throttle_delay_in_ms:1
authenticator:org.apache.cassandra.auth.AllowAllAuthenticator
authority:org.apache.cassandra.auth.AllowAllAuthority
partitioner:org.apache.cassandra.dht.RandomPartitioner
data_file_directories:
- /data/disk1/cassandra-data
- /data/disk2/cassandra-data
- /data/disk3/cassandra-data
- /data/disk4/cassandra-data
-/data/disk5/cassandra-data
- /data/disk6/cassandra-data
commitlog_directory:
/data/disk1/cassandra-log/,/data/disk2/cassandra-log/,/data/disk3/cassandra-log/,/data/disk4/cassandra-log/
,/data/disk5/cassandra-log/,/data/disk6/cassandra-log/
saved_caches_directory:/data/disk1/apache-cassandra/saved_caches
commitlog_sync:periodic
commitlog_sync_period_in_ms:10000
seed_provider:
- class_name:org.apache.cassandra.locator.SimpleSeedProvider
parameter s:
- seeds: "192.168.30.62,192.168.30.64,192.168.30.65,192.168.30.67"
flush_largest_memtables_at:0.75
reduce_cache_sizes_at:0.85
reduce_cache_capacity_to:0.6
concurrent_reads:48
concurrent_writes:48
memtable_flush_queue_size:4
sliced_buffer_size_in_kb:64
storage_port:7000
ssl_storage_port:7001
listen_address:192.168.30.62
rpc_address:0.0.0.0
rpc_port:9160
rpc_keepalive:true
rpc_server_type:sync
thrift_framed_transport_size_in_mb:15
thrift_max_message_length_in_mb:16
incremental_backups:false
snapshot_before_compaction:false
column_index_size_in_kb:64
in_memory_compaction_limit_in_mb:64
multithreaded_compaction:false
compaction_throughput_mb_per_sec:16
compaction_preheat_key_cache:true
rpc_timeout_in_ms:10000
endpoint_snitch:org.apache.cassandra.locator.SimpleSnitch
dynamic_snitch_update_interval_in_ms:100
dynamic_snitch_reset_interval_in_ms:600000
dynamic_snitch_badness_threshold:0.1
request_scheduler:org.apache.cassandra.scheduler.NoScheduler
index_interval:128
encryption_options:
internode_encryption: none
keystore: conf/.keystore
keystore_password: cassandra
truststore: conf/.truststore
truststore_password: cassandra
使用以下命令对数据库进行初始化:
CREATE KEYSPACE usertable
WITH placement_strategy ='org.apache.cassandra.locator.SimpleStrategy' AND strategy_options ={replication_factor:2};
use usertable;
CREATE COLUMN FAMILY data WITHcomparator = UTF8Type
AND key_validation_class = UTF8Type
6 附录B:YCSB调整
6.1 驱动调整
6.1.1 MongoDB
- 默认没有采用连接池的形式实现,调整为连接池形式
- 默认不支持批量插入,增加支持批量插入
- 默认不支持选择查询接口,增加支持选择查询接口
- 默认不支持选择readpreference,增加支持选择readpreference
- 为适应2.12.1版本的driver作了些调整
详细调整如下:
void init()
{
...
Properties props = getProperties();
String url =props.getProperty("mongodb.url",
"mongodb://localhost:27017");
database =props.getProperty("mongodb.database", "ycsb");
StringwriteConcernType = props.getProperty("mongodb.writeConcern",
"safe").toLowerCase();
//final StringmaxConnections = props.getProperty(
// "mongodb.maxconnections","100");
insertmode =props.getProperty("mongodb.insertmode", "single");
readpreference =props.getProperty("mongodb.readpreference",
"primary");
bulknumber=Integer.parseInt(props.getProperty("mongodb.bulknumber",
"5000"));
final String find =props.getProperty("mongodb.usefindinterface",
"false");
if (replWriteNum != 1){
writeConcern= new WriteConcern(replWriteNum);
}
try {
// strip out prefix since Javadriver doesn't currently support
// standard connection formatURL yet
//http://www.mongodb.org/display/DOCS/Connections
/* if(url.startsWith("mongodb://")) {
url = url.substring(10);
}*/
// need to append db to url.
url += "/" +database;
System.out.println("newdatabase url = " + url);
MongoClientURI uri = new MongoClientURI(url);
mongo =new MongoClient(uri);
mongo.setReadPreference(ReadPreference.valueOf(readpreference));
mongo.setWriteConcern(writeConcern);
System.out.println("mongoconnection created with " + url);
}
catch (Exception e1) {
System.err
.println("Couldnot initialize MongoDB connection pool for Loader: "
+ e1.toString());
e1.printStackTrace();
return;
}
}
publicint insert(String table, String key,
HashMap<String, ByteIterator>values) {
com.mongodb.DB db = null;
try {
db = mongo.getDB(database);
if (!outputclientflag){
CommandResult commandResult =db.command("buildInfo");
if(commandResult.containsField("tokumxVersion")){
System.out.println("tokumx");
}
else{
System.out.println("mongodb");
}
outputclientflag= true;
}
db.requestStart();
DBCollection collection =db.getCollection(table);
DBObject r = newBasicDBObject().append("_id", key);
for (String k : values.keySet()) {
r.put(k,values.get(k).toArray());
}
//WriteResult res = null;
if(insertmode.equals("bulk")){
objs.add(r);
//bulkwrite.insert(r);
if (objs.size() == bulknumber){
//res =
collection.insert(objs);
objs.clear();
//return 0;
}
}else{
//res =
collection.insert(r);
}
//return res.getN() == replWriteNum? 0:1;
return 0;
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 1;
}
finally {
if (db != null) {
db.requestDone();
}
}
}
publicint read(String table, String key, Set<String> fields,
HashMap<String, ByteIterator>result) {
com.mongodb.DB db = null;
DBCursor cursor = null;
try {
db = mongo.getDB(database);
db.requestStart();
//getCollection(table);
DBCollection collection =db.getCollection(table);
DBObject q = newBasicDBObject().append("_id", key);
DBObject fieldsToReturn = newBasicDBObject();
DBObject queryResult = null;
//DBCursor cursor = null;
if (fields != null) {
Iterator<String> iter =fields.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
fieldsToReturn.put(iter.next(), INCLUDE);
}
if(findone){
queryResult = collection.findOne(q,fieldsToReturn);
}
else{
cursor = collection.find(q,fieldsToReturn);
}
}
else {
if(findone){
queryResult= collection.findOne(q);
}
else{
cursor= collection.find(q).setReadPreference(ReadPreference.secondaryPreferred());
}
}
if (cursor != null &&cursor.hasNext()){
queryResult= cursor.next();
}
if (queryResult != null) {
result.putAll(queryResult.toMap());
}
return queryResult != null ? 0 : 1;
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println(e.toString());
return 1;
}
finally {
if (db != null) {
db.requestDone();
}
if (cursor != null){
cursor.close();
}
}
}
6.1.2 HBase
1 支持通过参数控制WriteBufferSize
2 适应驱动做微调
详细如下:
publicvoid init() throws DBException
{
if ((getProperties().getProperty("debug")!=null) &&
(getProperties().getProperty("debug").compareTo("true")==0))
{
_debug=true;
}
_columnFamily =getProperties().getProperty("columnfamily");
if (_columnFamily == null)
{
System.err.println("Error,must specify a columnfamily for HBase table");
throw new DBException("Nocolumnfamily specified");
}
_columnFamilyBytes =Bytes.toBytes(_columnFamily);
clientbufsize =Integer.parseInt(getProperties().getProperty("clientbuffersize"));
}
publicvoid getHTable(String table) throws IOException
{
synchronized (tableLock) {
_hTable = new HTable(config,table);
//2 suggestions fromhttp://ryantwopointoh.blogspot.com/2009/01/performance-of-hbase-importing.html
_hTable.setAutoFlush(false);
_hTable.setWriteBufferSize(clientbufsize*1024);
//return hTable;
}
}
6.2 统计数据收集
从原有的Measurements派生出ExcelMeasurementsExporter用于将生成的统计数据导出到excel文件中,ExcelMeasurementsExporter调用jxl.jar开源库实现。
统计数据由Overalloperresult、Overallresult,Periodresult这几个类存储,为了保存统计数据原来的Measurements,StatusThread都相应作了些调整。
6.3 预热
增加如下xml配置文件:
<?xmlversion="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Test>
<load>
<transactionname="bulkload_concurrent" />
<!--transactionname="bulkload" /-->
<transactionname="singleload_concurrent" />
<!--transactionname="singleload" /-->
</load>
<run>
<transactionname="readonly_concurrent" />
<transactionname="readheavy_concurrent" />
<transactionname="updateheavy_concurrent" />
<transactionname="insertheavy_concurrent" />
<transaction name="readlastest_concurrent"/>
</run>
</Test>
我们增加了如下python脚本用于连续运行:
#!/usr/bin/python
#!/bin/envpython
importos
importsys
importsubprocess
fromxml.etree import ElementTree
importycsb
fromycsb import (DATABASES,COMMANDS,BASE_URL,
get_ycsb_home, find_jars)
defgetloadtrans(workloadpath,root):
load = []
lst_node = root.find("load")
for node in lst_node:
load.append(workloadpath +node.attrib['name'])
return load
defgetruntrans(workloadpath,root):
run = []
lst_node = root.find("run")
for node in lst_node:
run.append(workloadpath +node.attrib['name'])
return run
defushelp():
print "Usage: %s database " % sys.argv[0]
print "\nDatabases:"
for db in sorted(DATABASES.keys()):
print " %s %s" % (db.ljust(13), BASE_URL +db.split("-")[0])
sys.exit(1)
defrunscene(trans, cmd, db_classname, pervscene):
curscene = ""
for item in trans:
curscene = os.path.basename(item)
command =COMMANDS[cmd]["command"]
options=["-s", "-P",item]
ycsb_command = ["java","-cp", ":".join(find_jars(ycsb_home, database)), \
COMMANDS[cmd]["main"], "-db", db_classname] +options
if command:
ycsb_command.append(command)
#print "".join(ycsb_command)
subprocess.call(ycsb_command)
pervscene = curscene
return pervscene
iflen(sys.argv) < 2:
ushelp()
ifsys.argv[1] not in DATABASES:
print "ERROR: Database '%s' notfound" % sys.argv[1]
ushelp()
os.chdir('..')
conffile = os.getcwd()+"/conf/workload.xml"
resultfile= os.getcwd()+"/result/report_output.xls"
resultdir = os.getcwd()+"/result/"
workloadsdir= os.getcwd()+"/workloads/"
ifFalse == os.path.exists(conffile):
print conffile + "not exist";
sys.exit(1)
root =ElementTree.parse(conffile)
loadtrans= getloadtrans(workloadsdir, root)
runtrans= getruntrans(workloadsdir, root)
os.chdir('bin')
ycsb_home= get_ycsb_home()
database= sys.argv[1]
db_classname= DATABASES[database]
runscene(loadtrans,"load", db_classname, pervscene)
runscene(runtrans,"run", db_classname, pervscene)
importtime
curtime=time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d_%H_%M_%S",time.localtime(time.time()))
newreportfile=resultdir+ "report_" + curtime +".xls"
os.rename(resultfile,newreportfile)为尽量保证后续的查询、更新操作是基于前续的load操作,以保证缓存的高命中率。
6.4 数据类型
本次测试的数据皆为字符串类型:
- fieldcount=10
- fieldlength=10
- key字段由单词"user"后面加上64位的Fowler-Noll-Vo哈希值构成
- key大小为23字节
- 所有字段的值采用zipfian算法生成
7 附录C:SequoiaDB接口
package com.yahoo.ycsb.db;
import com.yahoo.ycsb.ByteArrayByteIterator;
import com.yahoo.ycsb.ByteIterator;
import com.yahoo.ycsb.DB;
import com.yahoo.ycsb.DBException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.Vector;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import org.bson.BSONObject;
import org.bson.BasicBSONObject;
import org.bson.types.BasicBSONList;
import com.sequoiadb.base.SequoiadbOption;
import com.sequoiadb.base.SequoiadbDatasource;
import com.sequoiadb.base.CollectionSpace;
import com.sequoiadb.base.DBCollection;
import com.sequoiadb.base.DBCursor;
import com.sequoiadb.base.Sequoiadb;
public class SequoiaDBClient extends DB {
/** Used to include a field in a response. */
protected static final Integer INCLUDE = Integer.valueOf(1);
/** The key field name */
//private static final String KEY_FILED = "key";
private static final String KEY_FILED = "_id";
private static final String DEFAULT_INSERTMODE="single";
/**
* Count the number of times initialized to teardown on the last
* {@link #cleanup()}.
*/
private static final AtomicInteger initCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
private static int bulknum = 0;
/** Sequoiadb instance. */
private static SequoiadbDatasource sdbpools = null;
private Sequoiadb sdb = null;
/** CollectionSpace instance. */
private CollectionSpace cs = null;
private DBCollection cl = null;
private static String keyfield = null;
private static String insertmode = null;
private List<BSONObject> objs = new ArrayList<BSONObject>();
//private int callnumber =0;
private static String spacename = "ycsb";
//private DBCollection collection = null;
/**
* Initialize any state for this DB. Called once per DB instance; there is
* one DB instance per client thread.
*/
public void init() throws DBException {
initCount.incrementAndGet();
synchronized (INCLUDE) {
if (sdb != null) {
return;
}
try{
if (sdbpools != null){
sdb = sdbpools.getConnection();
cs = sdb.getCollectionSpace(spacename);
return;
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
// initialize sequoiadb driver
Properties props = getProperties();
String host = props.getProperty("sequoiadb.host", "localhost");
String port = props.getProperty("sequoiadb.port", "11810");
keyfield = props.getProperty("sequoiadb.keyfield", "_id");
int maxConnectionnum = Integer.parseInt(props.getProperty("sequoiadb.maxConnectionnum","100"));
int maxidleconnnum = Integer.parseInt(props.getProperty("sequoiadb.maxConnectionnum","10"));
int period = Integer.parseInt(props.getProperty("sequoiadb.maxConnectionnum","300"));
//String
spacename = props.getProperty("sequoiadb.space", spacename);
insertmode=props.getProperty("sequoiadb.insertmode", DEFAULT_INSERTMODE);
bulknum = Integer.parseInt(props.getProperty("sequoiadb.bulknumber","5000"));
try {
SequoiadbOption sdbOption = new SequoiadbOption();
sdbOption.setMaxConnectionNum(maxConnectionnum);
sdbOption.setMaxIdeNum(maxidleconnnum);
sdbOption.setRecheckCyclePeriod(period*1000);
sdbpools = new SequoiadbDatasource(host+":"+port,"","",sdbOption);
// need to append db to url.
//sdb = new Sequoiadb(host, Integer.parseInt(port), "", "");
sdb = sdbpools.getConnection();
if (!sdb.isCollectionSpaceExist(spacename)) {
cs = sdb.createCollectionSpace(spacename);
} else {
cs = sdb.getCollectionSpace(spacename);
}
System.out.println("sequoiadb connection created with " + host
+ ":" + port);
} catch (Exception e1) {
System.err
.println("Could not initialize Sequoiadb connection pool for Loader: "
+ e1.toString());
e1.printStackTrace();
throw new DBException(e1.toString());
}
}
}
/**
* Cleanup any state for this DB. Called once per DB instance; there is one
* DB instance per client thread.
*/
public void cleanup() throws DBException {
initCount.decrementAndGet();
try {
if (0 != objs.size()){
cl.bulkInsert(objs, DBCollection.FLG_INSERT_CONTONDUP);
}
sdbpools.close(sdb);
} catch (Exception e1) {
System.err.println("Could not close Sequoiadb connection pool: "
+ e1.toString());
e1.printStackTrace();
return;
}
}
private List<String> getAllDataGroup(){
// 获取数据组的数量
List<String> groups = new ArrayList<String>();
DBCursor cursor = sdb.getList(Sequoiadb.SDB_LIST_GROUPS, null, null, null);
while (cursor.hasNext()){
BSONObject obj = cursor.getNext();
String groupname = (String)obj.get("GroupName");
if (!groupname.equals("SYSCatalogGroup")){
groups.add(groupname);
}
}
return groups;
}
private int getPartition(String spacename, String tablename){
//获取源数据组
BSONObject condition = new BasicBSONObject();
condition.put("Name", spacename + "." + tablename);
DBCursor cr = sdb.getSnapshot(Sequoiadb.SDB_SNAP_CATALOG, condition, null, null);
int Partition = 0;
while(cr.hasNext()){
BSONObject obj = cr.getNext();
Partition = ((Integer)obj.get("Partition")).intValue();
}
return Partition;
}
private String getSrcDataGroup(String spacename, String tablename){
//获取源数据组
BSONObject condition = new BasicBSONObject();
condition.put("Name", spacename + "." + tablename);
DBCursor cr = sdb.getSnapshot(Sequoiadb.SDB_SNAP_CATALOG, condition, null, null);
String srcgroup = "";
while(cr.hasNext()){
BSONObject obj = cr.getNext();
BasicBSONList catainfo = (BasicBSONList)obj.get("CataInfo");
srcgroup=(String)((BSONObject)catainfo.get(0)).get("GroupName");
}
return srcgroup;
}
private void splitCollection(DBCollection cl, String spacename, String tablename){
// 获取数据组的数量
List<String> groups = getAllDataGroup();
int Partition = getPartition(spacename, tablename);
String srcgroup = getSrcDataGroup(spacename, tablename);
int part = Partition / groups.size();
int remainder = Partition % groups.size();
int startpart = Partition - remainder;
for (int i=0;i<groups.size();++i){
//切分
BSONObject start = new BasicBSONObject();
start.put("Partition", i*part);
BSONObject end = new BasicBSONObject();
end.put("Partition", (i+1)*part);
if (!groups.get(i).equals(srcgroup)){
cl.split(srcgroup, groups.get(i), start,end);
if (0 != remainder){
BSONObject remainderstart = new BasicBSONObject();
remainderstart.put("Partition", startpart);
BSONObject remainderend = new BasicBSONObject();
remainderend.put("Partition", startpart + 1);
cl.split(srcgroup, groups.get(i), remainderstart,remainderend);
--remainder;
}
}
}
}
private void createCollection(String table) throws DBException {
BSONObject options = new BasicBSONObject();
BSONObject subobj = new BasicBSONObject();
subobj.put(KEY_FILED, 1);
options.put("ShardingKey", subobj);
options.put("ShardingType", "hash");
options.put("EnsureShardingIndex", false);
cl = cs.createCollection(table, options);
splitCollection(cl,spacename,table);
if (0 != keyfield.compareTo("_id")){
cl.createIndex("index",
"{" + keyfield + ":1}", true, true);
}
}
private DBCollection getCollection(String table){
if (sdb == null){
try{
sdb = sdbpools.getConnection();
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
if (cs == null){
try{
cs = sdb.getCollectionSpace(spacename);
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
if (cl == null){
try {
boolean bExist = cs.isCollectionExist(table);
if (!bExist) {
synchronized (INCLUDE) {
if (cs.isCollectionExist(table)) {
cl = cs.getCollection(table);
} else {
createCollection(table);
}
}
} else {
cl = cs.getCollection(table);
}
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
cl = null;
sdbpools.close(sdb);
sdb = null;
return getCollection(table);
}
}
return cl;
}
@Override
public int read(String table, String key, Set<String> fields,
HashMap<String, ByteIterator> result) {
DBCursor cursor = null;
DBCollection collection = null;
try {
collection = getCollection(table);
if (collection == null) {
System.out.println("Failed to get collection " + table);
}
BSONObject query = new BasicBSONObject().append(keyfield, key);
BSONObject fieldsToReturn = null;
if (fields != null) {
fieldsToReturn = new BasicBSONObject();
Iterator<String> iter = fields.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
fieldsToReturn.put(iter.next(), "");
}
}
cursor = collection.query(query, fieldsToReturn, null, null);
if (cursor != null && cursor.hasNext()) {
HashMap<String, ByteIterator> resultMap = new HashMap<String, ByteIterator>();
fillMap(resultMap, cursor.getNext());
result.putAll(resultMap);
return 0;
} else {
return 1;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println(e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
return 1;
} finally {
if (cursor != null) {
cursor.close();
}
}
}
/**
* TODO - Finish
*
* @param resultMap
* @param obj
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected void fillMap(HashMap<String, ByteIterator> resultMap,
BSONObject obj) {
Map<String, Object> objMap = obj.toMap();
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : objMap.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue() instanceof byte[]) {
resultMap.put(entry.getKey(), new ByteArrayByteIterator(
(byte[]) entry.getValue()));
}
}
}
@Override
public int scan(String table, String startkey, int recordcount,
Set<String> fields, Vector<HashMap<String, ByteIterator>> result) {
DBCursor cursor = null;
try {
DBCollection collection = getCollection(table);
BSONObject scanRange = new BasicBSONObject().append("$gte",
startkey);
BSONObject query = new BasicBSONObject().append(keyfield,
scanRange);
BSONObject fieldsToReturn = null;
if (fields != null) {
fieldsToReturn = new BasicBSONObject();
Iterator<String> iter = fields.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
fieldsToReturn.put(iter.next(), "");
}
}
cursor = collection.query(query, fieldsToReturn, null, null, 0,
recordcount);
while (cursor.hasNext()) {
// toMap() returns a Map, but result.add() expects a
// Map<String,String>. Hence, the suppress warnings.
HashMap<String, ByteIterator> resultMap = new HashMap<String, ByteIterator>();
BSONObject obj = cursor.getNext();
fillMap(resultMap, obj);
result.add(resultMap);
}
return 0;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println(e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
return 1;
} finally {
if (cursor != null) {
cursor.close();
}
}
}
@Override
public int update(String table, String key,
HashMap<String, ByteIterator> values) {
try {
DBCollection collection = getCollection(table);
if (collection == null) {
System.out.println("Failed to get collection " + table);
return -1;
}
BSONObject query = new BasicBSONObject().append(keyfield, key);
BSONObject update = new BasicBSONObject();
BSONObject fieldsToSet = new BasicBSONObject();
Iterator<String> keys = values.keySet().iterator();
while (keys.hasNext()) {
String tmpKey = keys.next();
fieldsToSet.put(tmpKey, values.get(tmpKey).toArray());
}
update.put("$set", fieldsToSet);
collection.update(query, update, null);
return 0;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println(e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
return 1;
}
}
@Override
public int insert(String table, String key,
HashMap<String, ByteIterator> values) {
try {
DBCollection collection = getCollection(table);
BSONObject record = new BasicBSONObject().append(keyfield, key);
for (String k : values.keySet()) {
record.put(k, values.get(k).toArray());
}
if (insertmode.equals(DEFAULT_INSERTMODE)){
collection.insert(record);
}
else{
if (objs.size() != bulknum){
objs.add(record);
}
if (objs.size() == bulknum){
collection.bulkInsert(objs,DBCollection.FLG_INSERT_CONTONDUP);
objs.clear();
}
}
return 0;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println(e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
return 1;
}
}
@Override
public int delete(String table, String key) {
try {
DBCollection collection = getCollection(table);
BSONObject record = new BasicBSONObject().append(keyfield, key);
collection.delete(record);
return 0;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println(e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
return 1;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("sequoiadb.host", "192.168.30.63");
props.setProperty("sequoiadb.port", "11810");
props.setProperty("sequoiadb.space", "test");
SequoiaDBClient client = new SequoiaDBClient();
client.setProperties(props);
try{
client.init();
client.getCollection("usertable");
}catch(DBException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}