appium框架之bootstrap
原文地址:http://www.it165.net/pro/html/201407/17696.html
bootstrap结构
如图所示为bootstrap的项目结构
bootstrap作用
bootstrap在appium中是以jar包的形式存在的,它实际上是一个uiautomator写的case包,通过PC端的命令可以在手机端执行。
bootstrap源码分析
首先程序的入口为Bootstrap类。所以从该类开始一步一步解释这个项目
Bootstrap.java
01.
package io.appium.android.bootstrap;
02.
03.
import io.appium.android.bootstrap.exceptions.SocketServerException;
04.
05.
import com.android.uiautomator.testrunner.UiAutomatorTestCase;
06.
07.
/**
08.
* The Bootstrap class runs the socket server. uiautomator开发的脚本,可以直接在pc端启动
09.
*/
10.
public class Bootstrap extends UiAutomatorTestCase {
11.
12.
public void testRunServer() {
13.
SocketServer server;
14.
try {
15.
// 启动socket服务器,监听4724端口。
16.
server = new SocketServer(4724);
17.
server.listenForever();
18.
} catch (final SocketServerException e) {
19.
Logger.error(e.getError());
20.
System.exit(1);
21.
}
22.
23.
}
24.
}
该类继承自UiAutomatorTestCase。所以它才能通过adb shell uiautomator runtest AppiumBootstrap.jar -c io.appium.android.bootstrap.Bootstrap被执行。
该类很简单,就是启动线程,监听4724端口,该端口与appium通信。
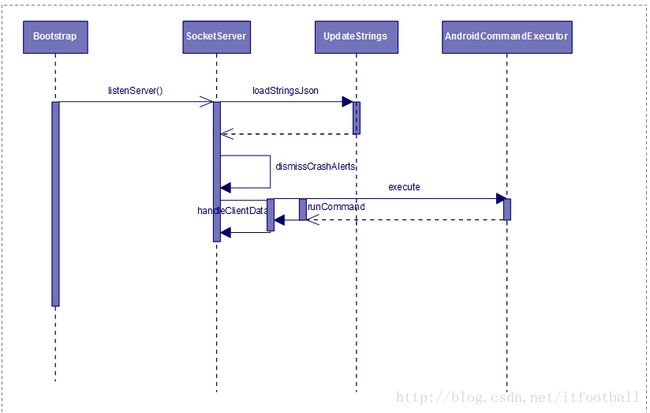
然后走server.listenForever()方法。
SocketServer.java
01.
/**
02.
* Listens on the socket for data, and calls {@link #handleClientData()} when
03.
* it's available.
04.
*
05.
* @throws SocketServerException
06.
*/
07.
public void listenForever() throws SocketServerException {
08.
Logger.debug("Appium Socket Server Ready");
09.
//读取strings.json文件的数据
10.
UpdateStrings.loadStringsJson();
11.
// 注册两种监听器:AND和Crash
12.
dismissCrashAlerts();
13.
final TimerTask updateWatchers = new TimerTask() {
14.
@Override
15.
public void run() {
16.
try {
17.
// 检查系统是否有异常
18.
watchers.check();
19.
} catch (final Exception e) {
20.
}
21.
}
22.
};
23.
// 计时器,0.1秒后开始,每隔0.1秒执行一次。
24.
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(updateWatchers, 100, 100);
25.
26.
try {
27.
client = server.accept();
28.
Logger.debug("Client connected");
29.
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(client.getInputStream(),
30.
"UTF-8"));
31.
out = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(client.getOutputStream(),
32.
"UTF-8"));
33.
while (keepListening) {
34.
// 获取客户端数据
35.
handleClientData();
36.
}
37.
in.close();
38.
out.close();
39.
client.close();
40.
Logger.debug("Closed client connection");
41.
} catch (final IOException e) {
42.
throw new SocketServerException("Error when client was trying to connect");
43.
}
44.
}
该方法中首先调用UpdateStrings.loadStringsJson();该方法如下:
UpdateStrings
01.
/**
02.
* strings.json文件保存的是apk的strings.xml里的内容,在Bootstrap启动前由appium服务器解析并push到设备端的
03.
*
04.
* @return
05.
*/
06.
public static boolean loadStringsJson() {
07.
Logger.debug("Loading json...");
08.
try {
09.
final String filePath = "/data/local/tmp/strings.json";
10.
final File jsonFile = new File(filePath);
11.
// json will not exist for apks that are only on device
12.
// 你的case必须写明apk的路径,如果启动设备上已有的应用而case中没有app路径,此时json文件是不存在的
13.
// because the node server can't extract the json from the apk.
14.
if (!jsonFile.exists()) {
15.
return false;
16.
}
17.
final DataInputStream dataInput = new DataInputStream(
18.
new FileInputStream(jsonFile));
19.
final byte[] jsonBytes = new byte[(int) jsonFile.length()];
20.
dataInput.readFully(jsonBytes);
21.
// this closes FileInputStream
22.
dataInput.close();
23.
final String jsonString = new String(jsonBytes, "UTF-8");
24.
// 将读取出来的信息赋给Find类中的属性,以做后用
25.
Find.apkStrings = new JSONObject(jsonString);
26.
Logger.debug("json loading complete.");
27.
} catch (final Exception e) {
28.
Logger.error("Error loading json: " + e.getMessage());
29.
return false;
30.
}
31.
return true;
32.
}
然后回到ServerSocket类的listenForever(),此时执行到dismissCrashAlerts();该方法作用是注册一些监听器,观察是否有糖出口或者AND和crash的异常。
1.
public void dismissCrashAlerts() {
2.
try {
3.
new UiWatchers().registerAnrAndCrashWatchers();
4.
Logger.debug("Registered crash watchers.");
5.
} catch (final Exception e) {
6.
Logger.debug("Unable to register crash watchers.");
7.
}
8.
}
此时listenForever()方法里执行到注册心跳程序,每隔0.1秒开始执行一遍上面注册的监听器来检查系统是否存在异常。
01.
final TimerTask updateWatchers = new TimerTask() {
02.
@Override
03.
public void run() {
04.
try {
05.
// 检查系统是否有异常
06.
watchers.check();
07.
} catch (final Exception e) {
08.
}
09.
}
10.
};
11.
// 计时器,0.1秒后开始,每隔0.1秒执行一次。
12.
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(updateWatchers, 100, 100);
然后启动数据通道,接受客户端发来的数据和返回结果给客户端。
1.
client = server.accept();
2.
Logger.debug("Client connected");
3.
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(client.getInputStream(),
4.
"UTF-8"));
5.
out = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(client.getOutputStream(),
6.
"UTF-8"));
接下来就是最重要的方法handleClientData();到此listenForever()方法的主要作用就完成了。现在来看handleClientData()方法做了啥。
01.
/**
02.
* When data is available on the socket, this method is called to run the
03.
* command or throw an error if it can't.
04.
*
05.
* @throws SocketServerException
06.
*/
07.
private void handleClientData() throws SocketServerException {
08.
try {
09.
input.setLength(0); // clear
10.
11.
String res;
12.
int a;
13.
// (char) -1 is not equal to -1.
14.
// ready is checked to ensure the read call doesn't block.
15.
while ((a = in.read()) != -1 && in.ready()) {
16.
input.append((char) a);
17.
}
18.
final String inputString = input.toString();
19.
Logger.debug("Got data from client: " + inputString);
20.
try {
21.
final <a href="http://www.it165.net/pro/ydad/" target="_blank" class="keylink">Android</a>Command cmd = getCommand(inputString);
22.
Logger.debug("Got command of type " + cmd.commandType().toString());
23.
res = runCommand(cmd);
24.
Logger.debug("Returning result: " + res);
25.
} catch (final CommandTypeException e) {
26.
res = new <a href="http://www.it165.net/pro/ydad/" target="_blank"class="keylink">Android</a>CommandResult(WDStatus.UNKNOWN_ERROR, e.getMessage())
27.
.toString();
28.
} catch (final JSONException e) {
29.
res = new AndroidCommandResult(WDStatus.UNKNOWN_ERROR,
30.
"Error running and parsing command").toString();
31.
}
32.
out.write(res);
33.
out.flush();
34.
} catch (final IOException e) {
35.
throw new SocketServerException("Error processing data to/from socket ("
36.
+ e.toString() + ")");
37.
}
38.
}
该方法中读取客户端发来的数据,利用getCommand()方法获得AndroidCommand对象,然后执行runCommand()方法,获取直接的结果。那么该方法的作用就转移到了runCommand()。所以现在就来看runCommand()方法是啥意思啦。
01.
/**
02.
* When {@link #handleClientData()} has valid data, this method delegates the
03.
* command.
04.
*
05.
* @param cmd
06.
* AndroidCommand
07.
* @return Result
08.
*/
09.
private String runCommand(final AndroidCommand cmd) {
10.
AndroidCommandResult res;
11.
if (cmd.commandType() == AndroidCommandType.SHUTDOWN) {
12.
keepListening = false;
13.
res = new AndroidCommandResult(WDStatus.SUCCESS, "OK, shutting down");
14.
} else if (cmd.commandType() == AndroidCommandType.ACTION) {
15.
try {
16.
res = executor.execute(cmd);
17.
} catch (final Exception e) {
18.
res = new AndroidCommandResult(WDStatus.UNKNOWN_ERROR, e.getMessage());
19.
}
20.
} else {
21.
// this code should never be executed, here for future-proofing
22.
res = new AndroidCommandResult(WDStatus.UNKNOWN_ERROR,
23.
"Unknown command type, could not execute!");
24.
}
25.
return res.toString();
26.
}
27.
}
该方法首先做了判断,判断命令数据哪种类型,主要有关机命令和动作命令,我们主要关注动作命令,因为动作有很多种。所以来关注第一个else if中的AndroidCommandExecutor.execute()方法。主线又转移到了该方法中了,切去瞅一眼。
AndroidCommandExecutor.java
01.
/**
02.
* Gets the handler out of the map, and executes the command.
03.
*
04.
* @param command
05.
* The {@link AndroidCommand}
06.
* @return {@link AndroidCommandResult}
07.
*/
08.
public AndroidCommandResult execute(final AndroidCommand command) {
09.
try {
10.
Logger.debug("Got command action: " + command.action());
11.
12.
if (map.containsKey(command.action())) {
13.
return map.get(command.action()).execute(command);
14.
} else {
15.
return new AndroidCommandResult(WDStatus.UNKNOWN_COMMAND,
16.
"Unknown command: " + command.action());
17.
}
18.
} catch (final JSONException e) {
19.
Logger.error("Could not decode action/params of command");
20.
return new AndroidCommandResult(WDStatus.JSON_DECODER_ERROR,
21.
"Could not decode action/params of command, please check format!");
22.
}
23.
}
该方法中终于要执行命令的实体啦
1.
if (map.containsKey(command.action())) {
2.
return map.get(command.action()).execute(command);
3.
} else {
4.
return new AndroidCommandResult(WDStatus.UNKNOWN_COMMAND,
5.
"Unknown command: " + command.action());
6.
}
关键是上面这几行代码,调用了map.get(command.action()).execute(command).看来要想弄懂这个命令的意思,肯定得知道map里存放的对象是哪些,那么在该类中找到map的初始化代码:
01.
static {
02.
map.put("waitForIdle", new WaitForIdle());
03.
map.put("clear", new Clear());
04.
map.put("orientation", new Orientation());
05.
map.put("swipe", new Swipe());
06.
map.put("flick", new Flick());
07.
map.put("drag", new Drag());
08.
map.put("pinch", new Pinch());
09.
map.put("click", new Click());
10.
map.put("touchLongClick", new TouchLongClick());
11.
map.put("touchDown", new TouchDown());
12.
map.put("touchUp", new TouchUp());
13.
map.put("touchMove", new TouchMove());
14.
map.put("getText", new GetText());
15.
map.put("setText", new SetText());
16.
map.put("getName", new GetName());
17.
map.put("getAttribute", new GetAttribute());
18.
map.put("getDeviceSize", new GetDeviceSize());
19.
map.put("scrollTo", new ScrollTo());
20.
map.put("find", new Find());
21.
map.put("getLocation", new GetLocation());
22.
map.put("getSize", new GetSize());
23.
map.put("wake", new Wake());
24.
map.put("pressBack", new PressBack());
25.
map.put("dumpWindowHierarchy", new DumpWindowHierarchy());
26.
map.put("pressKeyCode", new PressKeyCode());
27.
map.put("longPressKeyCode", new LongPressKeyCode());
28.
map.put("takeScreenshot", new TakeScreenshot());
29.
map.put("updateStrings", new UpdateStrings());
30.
map.put("getDataDir", new GetDataDir());
31.
map.put("performMultiPointerGesture", new MultiPointerGesture());
32.
map.put("openNotification", new OpenNotification());
33.
}
豁然开朗,该map是<String,CommandHandler>形式的map。value值对应的都是一个个的对象,这些对象都继承与CommandHandler,里面都有execute方法,该方法就是根据命令的不同调用不同的对象来执行相关代码获取结果。从map的定义可以看出,appium可以操作手机的命令还不少,我用过的有scrollTo,updateStrings,getDataDir等,上面还有截图、打开通知栏、按下等还没用过,但通过这些命令你也可以了解appium可以做哪些事。
继承CommandHandler的对象有很多,我挑一个来讲讲它具体是干嘛的,其他的我以后会挨个讲,就挑click吧。
加入现在传过来的命令后缀是click的话,那么它会调用Click对象的execute方法。
Click.java
01.
package io.appium.android.bootstrap.handler;
02.
03.
import com.android.uiautomator.core.UiDevice;
04.
import com.android.uiautomator.core.UiObjectNotFoundException;
05.
import io.appium.android.bootstrap.*;
06.
import org.json.JSONException;
07.
08.
import java.util.ArrayList;
09.
import java.util.Hashtable;
10.
11.
/**
12.
* This handler is used to click elements in the Android UI.
13.
*
14.
* Based on the element Id, click that element.
15.
*
16.
*/
17.
public class Click extends CommandHandler {
18.
19.
/*
20.
* @param command The {@link AndroidCommand}
21.
*
22.
* @return {@link AndroidCommandResult}
23.
*
24.
* @throws JSONException
25.
*
26.
* @see io.appium.android.bootstrap.CommandHandler#execute(io.appium.android.
27.
* bootstrap.AndroidCommand)
28.
*/
29.
@Override
30.
public AndroidCommandResult execute(final AndroidCommand command)
31.
throws JSONException {
32.
if (command.isElementCommand()) {
33.
try {
34.
final AndroidElement el = command.getElement();
35.
el.click();
36.
return getSuccessResult(true);
37.
} catch (final UiObjectNotFoundException e) {
38.
return new AndroidCommandResult(WDStatus.NO_SUCH_ELEMENT,
39.
e.getMessage());
40.
} catch (final Exception e) { // handle NullPointerException
41.
return getErrorResult("Unknown error");
42.
}
43.
} else {
44.
final Hashtable<String, Object> params = command.params();
45.
final Double[] coords = { Double.parseDouble(params.get("x").toString()),
46.
Double.parseDouble(params.get("y").toString()) };
47.
final ArrayList<Integer> posVals = absPosFromCoords(coords);
48.
final boolean res = UiDevice.getInstance().click(posVals.get(0),
49.
posVals.get(1));
50.
return getSuccessResult(res);
51.
}
52.
}
53.
}
该类就一个execute方法这根独苗,execute方法中会先判断传入的参数对象是坐标值还是元素值,如果是元素值那么直接调用AndroidElement中的click方法,一会我们再去看这个方法。如果是坐标的话,它会干什么呢。它会调用UiDevice的click方法,用过UiAutomator的人都知道它是uiautomator包中的类。所以说appium在api16以上的机器上使用的uiautomator机制。貌似有人觉得这好像easy了点。那好吧,我们再分析一个touchDown命令,如果传过来的命令后缀是touchDown,那么它会调用TouchDown对象的execute方法。
1.
map.put("touchDown", new TouchDown());
这个类里面的execute方法就有点意思啦。
TouchDown.java
01.
package io.appium.android.bootstrap.handler;
02.
03.
import com.android.uiautomator.common.ReflectionUtils;
04.
import com.android.uiautomator.core.UiObjectNotFoundException;
05.
import io.appium.android.bootstrap.Logger;
06.
07.
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
08.
09.
/**
10.
* This handler is used to perform a touchDown event on an element in the
11.
* Android UI.
12.
*
13.
*/
14.
public class TouchDown extends TouchEvent {
15.
16.
@Override
17.
protected boolean executeTouchEvent() throws UiObjectNotFoundException {
18.
printEventDebugLine("TouchDown");
19.
try {
20.
final ReflectionUtils utils = new ReflectionUtils();
21.
final Method touchDown = utils.getControllerMethod("touchDown", int.class,
22.
int.class);
23.
return (Boolean) touchDown.invoke(utils.getController(), clickX, clickY);
24.
} catch (final Exception e) {
25.
Logger.debug("Problem invoking touchDown: " + e);
26.
return false;
27.
}
28.
}
29.
}
该方法里用到了反射,调用uiautomator里的隐藏api来执行按下操作。就不具体讲了,后面会挨个说一遍的。
总结
说了这么多废话,尝试着用流程图描述一遍吧。