apue学习第二十二天——管道与FIFO
管道与FIFO的区别,就在于 unnamed 和 named 的区别:
- 由于pipe没有名字,一个进程创建pipe之后,只有与它related(有亲缘关系)的进程才会知道这个pipe的存在,所以只能用于related的进程之间的通信;
- 而FIFO是named pipe,不同进程可以获得同一FIFO的name,所以可用于unrelated进程之间的通信。
本质上,你可以把pipe想成一个file(当然和普通文件有些区别),不同进程的通信就是通过对同一个file的read和write来完成的。那么本篇,我们来分析pipe和FIFO这两种IPC类型。
1. 管道
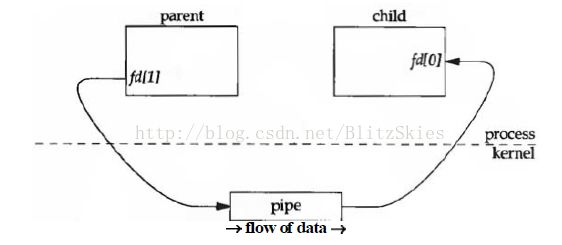
如果让一个父进程,用管道向子进程传递消息,我们想象中的情况是这样的:
当然,它是半双工的,半双工也就是数据流只能单向流动。那么如果父子进程交互传递信息呢?那么就需要两个pipe,如下图:
先不用去管图中的fd[0], fd[1],至少现在我们明白了,related processes之间,通过system call(read & write)进入kernel,对
pipe(i.e. a file)进行读写,来实现半双工或全双工的通信方式。
下面,我们看pipe创建函数,深入分析一个process是如何和一个pipe发生关系的:
#include <unistd.h>
int pipe (int fd[2]);
/* Return value: if success, return 0; if error, return -1 */
int fd[2],顾名思义,file descriptors,是两个文件描述符fd[0]和fd[1];
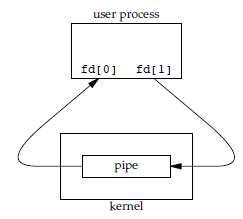
一般在程序中,我们首先定义一个int fd[2];当一个进程执行pipe(fd)时,会产生下图所示情况,
我们看,pipe执行过后,fd[0] is open for reading, fd[1] is open for writing(也就是fd[0]变成了process的input,fd[1]为output);所以我们要想从管道中读数据——read fd[0],写数据——write fd[1]即可。
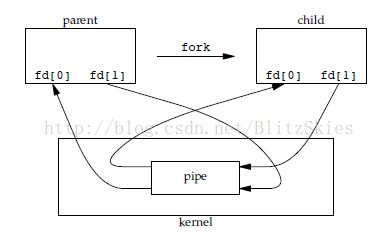
那么,pipe之后我们执行fork,看会发生什么情况:
上图的情况很容易理解,child process共享parent process打开的file descriptors。
所以,要实现刚开始的父进程向子进程传递消息,进行如下操作即可(见最上面的第一幅图):
a. 关闭parent process的fd[0];b. 关闭child process的fd[1];
当然,用两个pipe,实现全双工的通信也很容易:
a. 定义int fd1[2], fd2[2];(这样两次pipe(fd)之后就会有两个管道); b. 关闭parent process的fd1[0]和fd2[1];c. 关闭child process的fd1[1]和fd2[0];
那么,对一个一端已经关闭的pipe fd操作(read or write)时,会发生什么呢?
- read一个write端被关闭的pipe:所有数据都被读完后return 0,表示文件结束;
- write一个read端被关闭的pipe:产生SIGPIPE信号。
下面我们看apue书中的15-6,这段程序的作用是:父进程将argv[1]文件通过管道传给子程序,子程序调用分页显示程序将argv[1]文件显示出来。
具体需要注意的有如下地方:
- 父进程将argv[1]文件写入pipe;
- 如果父进程不wait,子进程将成为zombie(具体看代码中的注释);
- 子进程的STDIN_FILENO(标准输入)成为管道读端(即STDIN_FILENO与fd[0]指向同一文件);
- 看环境变量environ的应用之一,调用分页显示程序;
#include "apue.h"
#include <sys/wait.h>
#define DEF_PAGER "/bin/more"
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int n;
int fd[2];
pid_t pid;
char *pager, *argv0;
char line[MAXLINE];
FILE *fp;
if(argc != 2)
err_quit("usage: a.out <pathname>");
if((fp = fopen(argv[1], "r")) == NULL)
err_sys("can't open %s", argv[1]);
/* create a pipe */
if(pipe(fd) < 0)
err_sys("pipe error");
/* fork */
if((pid = fork()) < 0)
err_sys("fork error");
else if(pid > 0) {
close(fd[0]); /* parent process close read end */
/* parent read argv[1] and write to pipe */
while (fgets(line, MAXLINE, fp) != NULL) {
n = strlen(line);
if(write(fd[1], line, n) != n)
err_sys("write error to pipe");
}
if(ferror(fp))
err_sys("fgets error");
close(fd[1]); /* close write end of pipe for reader */
/* wait until the child process terminate, if not wait, system will not release
the resources associated with the child, and the child of course will become a "zombie". */
if(waitpid(pid, NULL, 0) < 0)
err_sys("waitpid error");
exit(0);
} else {
close(fd[1]); /* child process close write end */
/* duplicate the read end to STDIN_FILENO */
if(fd[0] != STDIN_FILENO)
{
/* duplicate from the old fd to new fd */
if(dup2(fd[0], STDIN_FILENO) != STDIN_FILENO)
err_sys("dup2 error to stdin");
close(fd[0]); /* we don't need this after dup2 */
}
/* From this section, we can see how to use the "environ" to call the page program. */
/* get arguments for execl() */
if((pager = getenv("PAGER")) == NULL)
pager = DEF_PAGER;
if((argv0 = strrchr(pager, '/')) != NULL)
argv0++; /* step past rightmost slash */
else
argv0 = pager; /* no slash in pager */
if(execl(pager, argv0, (char *)0) < 0)
err_sys("execl error for %s", pager);
}
exit(0);
}
程序很长,但无论怎样应该好好看看。
pipe就那么多吗?当然不!pipe是system call,放在<unistd.h>中,下面我们看两个C库函数的使用,这使管道的使用没上面的那么麻烦:
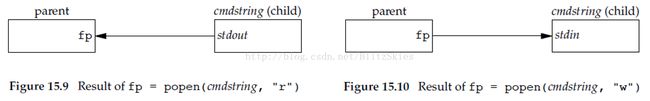
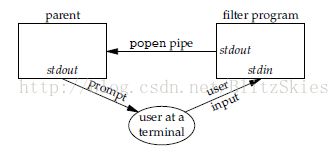
#include <stdio.h> FILE *popen(const char *cmdstring, const char *type); /* Returns: file pointer if OK, NULL on error */ int pclose(FILE *fp); /* Returns: termination status of cmdstring, or −1 on error */(1)popen函数
启动另外一个进程,去执行cmdstring这个shell命令;这里,调用popen的是父进程,启动的是子进程,子进程执行shell命令;在父子进程之间,popen函数还创建了一个管道,用于进程通信;通信的方式由type决定:
- type == "r",父进程read子进程的stdout(标准输出);
- type == "w",父进程write子进程的stdin(标准输入);
下面这幅图可以帮助我们更好的理解popen:
(2)pclose函数
关闭标准I/O流,等待命令终止,然后返回shell的终止状态(termination status,waitpid可以获得,关于终止状态更多信息,上网查吧)。
函数说明白了,如果还是不理解,那么就通过下面的示例来了解吧,毕竟程序是理解函数最佳的途径:
本程序为apue书中15-14,15-15,目的是在主程序中插入一个filter program来对输入进行变换处理,两个进程由主程序popen创建的管道相连,具体见下图,
filter program如下:
/* This is a filter program that transform upper characters to the lowers */
#include "apue.h"
#include <ctype.h>
int
main(void)
{
int c;
while((c = getchar()) != EOF)
{
if(isupper(c))
c = tolower(c);
if(putchar(c) == EOF)
err_sys("output error");
if(c == '\n')
fflush(stdout);
}
exit(0);
}
将filter program编译成可执行文件filter,主程序通过popen调用它。主程序如下:
/* This is the program that calls popen */
#include "apue.h"
#include <sys/wait.h>
int
main(void)
{
char line[MAXLINE];
FILE *fpin;
/* call popen function to create a pipe and execute filter program */
if((fpin = popen("./filter", "r")) == NULL)
err_sys("popen error");
for(; ;)
{
fputs("prompt> ", stdout);
fflush(stdout);
if(fgets(line, MAXLINE, fpin) == NULL) /* read from pipe */
break;
if(fputs(line, stdout) == EOF)
err_sys("fputs error to pipe");
}
/* close the pipe */
if(pclose(fpin) == -1)
err_sys("pclose error");
putchar('\n');
exit(0);
}
程序运行时,将输入的大写转换为小写,遇到EOF(ctrl+D)时结束。
下面我们介绍coprocess(协同进程)的概念。
UNIX系统过滤程序从标准输入读取数据,向标准输出写数据(过滤程序是接受输入,处理后输出的程序)。A filter becomes a coprocess when the same program generates the filter's input and reads the filter's output.(当一个程序产生某个过滤程序的输入,同时又读取该过滤程序的输出时,则该过滤程序就成为协同进程(coprocess)。)
那么,我们上面程序的示例是coprocess吗?不是!上面的程序popen创建的是单向的管道,而coprocess需要标准输入和标准输出各连接一个单向管道:一个接到标准输入,一个接到标准输出。
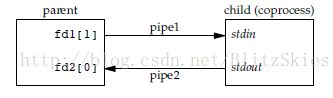
实例:下面的程序中,子进程是coprocess,它从pipe1中读入int1和int2两个数,进行相加后,把结果写入pipe2,
下面是child(coprocess)的程序:
#include "apue.h"
int
main(void)
{
int n, int1, int2;
char line[MAXLINE];
while ((n = read(STDIN_FILENO, line, MAXLINE)) > 0) /* read from STDIN_FILENO */
{
line[n] = 0; /* note: null terminate */
if(sscanf(line, "%d%d", &int1, &int2) == 2) /* read int1, int2 from line[MAXLINE] */
{
sprintf(line, "%d\n", int1 + int2); /* write sum of int1 and int2 to line[MAXLINE] */
n = strlen(line);
if(write(STDOUT_FILENO, line, n) != n) /* write line[MAXLINE] to STDOUT_FILENO */
err_sys("write error");
} else {
if(write(STDOUT_FILENO, "invalid args\n", 13) != 13)
err_sys("write error");
}
}
}
上面的程序中,read后的line[n]=0需要注意,其余4种读写的方式了解一下;
至于parent的程序,这里只给出大体思路:
- 1)创建两个pipe:fd1[2]和fd2[2];
- 2)fork一个子程序;
- 3)子程序中,关闭fd1[1], fd2[0];为了使标准输入输出连接到pipe,调用dup2将STDIN_FILENO连接到fd1[0],STDOUT_FILENO连接到fd2[1],execl运行child程序;(此处注意,子程序的标准输入输出是必须连接到管道,不能用于键盘输入和显示器输出)
- 4)父进程中,关闭fd1[0], fd2[1],用fgets(line, MAXLINE, stdin)读取数据,write fd1[1]写入管道,fd2[0]从管道读,fputs(line, stdout)输出数据。
以上就是一个简单的coprocess的工作过程,但有以下需要注意:
- 过滤程序中读写用read和write这两个底层UNIX system call,而没有用标准库函数,为什么呢?因为标准库默认全缓冲机制,如果read和write换成fgets和printf,那么由于全缓冲,当child process读阻塞时,parent process也会读阻塞,那么会产生死锁!!!这一点在设计coprocess程序(或者其它双向输入输出程序)的时候要格外注意!
到这里,关于pipe我们已经说的差不多了,还有一点要注意一下:在历史上,pipe是半双工的,虽然某些系统提供全双工的pipe,但为了更好的移植性,我们绝不应预先假设系统支持全双工pipe。
2. FIFO
了解pipe之后,FIFO就很简单了。FIFO指的是first in,first out;前面说过,FIFO也是named pipe,用于unrelated processes之间通信,是一种文件类型,这在stat结构中的st_mode可以查看FIFO文件类型。
下面,我们使用FIFO,实现两个unrelated processes之间的通信:
看看是不是和全双工pipe很像,看程序fifo.h, server.c和client.c:
/* fifo.h */ #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <sys/stat.h> /* FIFO is a type of file; this header includes mkfifo function */ #include <fcntl.h> #include <errno.h> //#include <unistd.h> #define FIFO1 "/tmp/fifo.1" #define FIFO2 "/tmp/fifo.2" #define FILE_MODE (S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH)
/* server.c */
#include "fifo.h"
void server(int readfd, int writefd)
{
/* ... */
}
int
main(void)
{
int readfd, writefd;
/* create two FIFOs; OK if they already exist */
if((mkfifo(FIFO1, FILE_MODE) < 0) && (errno != EEXIST))
{
printf("can't create %s\n", FIFO1);
exit(1);
}
if((mkfifo(FIFO2, FILE_MODE) < 0) && (errno != EEXIST))
{
unlink(FIFO1);
printf("can't create %s\n", FIFO2);
exit(1);
}
/* we don't handle the errors in the following. */
if((readfd = open(FIFO1, O_RDONLY, 0)) < 0)
{
perror("open FIFO1 failed");
unlink(FIFO1);
exit(1);
}
if((writefd = open(FIFO2, O_WRONLY, 0)) < 0)
{
perror("open FIFO2 failed");
unlink(FIFO2);
exit(1);
}
server(readfd, writefd);
exit(0);
}
/* client.c */
#include "fifo.h"
void client(int readfd, int writefd)
{
/* ... */
}
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int readfd, writefd;
/* not handle errors in the following. */
writefd = open(FIFO1, O_WRONLY, 0);
readfd = open(FIFO2, O_RDONLY, 0);
client(readfd, writefd);
close(readfd);
close(writefd);
unlink(FIFO1);
unlink(FIFO2);
exit(0);
}
以上程序为简洁起见,没有进行充分的错误检查(尤其是client.c),这里需要注意以下几点:
fifo.h中的头文件;
- FIFO必须先mkfifo,再open(和文件不一样);
- 类似于管道,若write一个尚无进程为读打开的FIFO,返回SIGPIPE;若最后一个write进程关闭了FIFO,则read它时返回EOF;
下面说FIFO的两种用途:
(1)shell命令使用FIFO将数据从一条管道送到另一条时,无需创建中间临时文件。
Example — 用FIFO复制输出流:
pipe和FIFO都可以避免数据写向中间磁盘文件,但不同的是,pipe由于unnamed所以只能线性连接,FIFO可以非线性连接;
mkfifo fifo1 prog3 < fifo1 & prog1 < infile | tee fifo1 | prog2
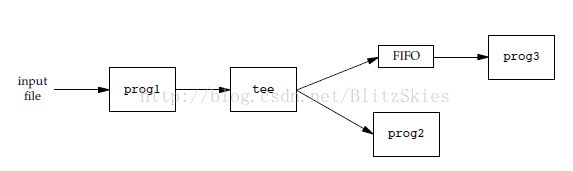
- mkfifo fifo1创建FIFO;
- prog3 < fifo1 & 后台运行prog3,并将标准输入重定向为fifo1;
- prog1 < infile | tee fifo1 | prog2,prog1的标准输入重定向到infile,标准输出通过管道连接tee的标准输入,tee程序的参数是fifo1(程序内部可以向FIFO写),然后tee的标准输出通过管道连接到prog2的标准输入。
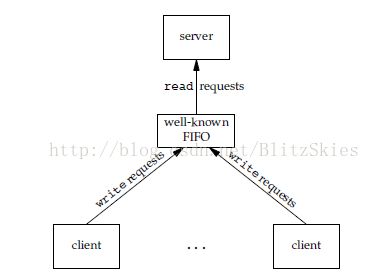
(2)使用FIFO进行client process-server process通信
首先看下图,well-known FIFO是server和所有client都知道FIFO的路径名,
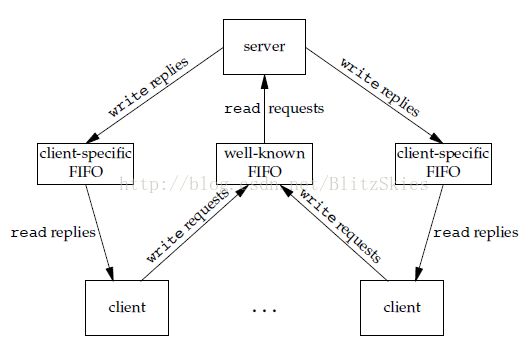
client写,server读,但如果server要相应client该怎么办呢?我们又添了些东西:client发请求的时候顺带发送自己的pid,server根据client pid来创建一个FIFO专门用来和该client process通信(例如命名为/tmp/serv1.XXXX XXXX为client pid),这样就得到了下图的形式:
这样问题似乎得到了解决,但考虑以下情况:
- client请求完后崩溃了怎么办?那么client-specific FIFO的读端被关闭,所以server写的时候就会返回SIGPIPE信号,server必须处理这种信号。
那么这样看来,这种方法也不尽合理。apue书上说的以read-write方式打开well-known FIFO现在还没怎么理解(存疑)。
还有最后几点要说明的是,
(1)FIFO只适用于单机系统;如果在NFS上(网络文件系统,“容许不同客户端及服务端通过一组RPC分享相同的文件系统”),肯定是不行的;
(2)上述的简单服务器是“迭代服务器(iterative server)”,也就是server在完全处理完一个client请求后,在处理下一个;另外一种设计是“并发服务器(concurrent server)”,UNIX下常见的one-child-per-client server就是,即为每个客户分配一个进程(或线程);
(3)迭代服务器存在的一个问题是DoS(拒绝服务型攻击),如上图,client只发送请求但并不读为自己创建的FIFO,这样会使server阻塞;解决办法是:设阻塞时钟,或改为并发服务器,虽然并发服务器面临大量DoS时也许会因为fork达到上限而无法继续fork,但总比迭代服务器好些。
本篇到此结束。