STL笔记之优先队列
STL笔记之优先队列
在STL中队列queue是基于deque实现的,优先队列priority_queue则是基于堆实现的。所谓优先队列即元素具有优先级的队列,在最大优先级队列中,队列最前面的元素具有最高的优先级,最大优先级队列基于最大堆(max-heap)实现。
1. 堆的基本性质
二叉堆是一颗完全二叉树,可以分为最小堆和最大堆,以最大堆为例来说,对于堆中的每一个节点p,都满足条件key[p] >= key[p->left] && key[p] >= key[p->right],即以p为根的子树中,根节点p的值是最大的,堆中的所有节点都满足这个性质。
因为二叉堆是一颗完全二叉树,所以,所以根节点的索引从1开始算,则对于索引为i的节点,其左子结点的索引为2*i,右子节点的索引为2*i+1,父节点的索引为i/2,这些操作都可以基于移位运算快速实现。因为这个特性,通常使用数组存储堆的节点。
CLRS 6.1-7
对于拥有n个节点的堆而言,其叶子节点的下标为[n/2]+1, [n/2]+2, …, n。
证明:因为有n个元素,最后一个元素序号为n,那么它的parent结点应该是序号最大的parent结点,那么这个parent结点就为[n/2],其之后都是叶子结点,因而为[n/2]+1, [n/2]+2, …, n。
(也可以从二叉树节点的度与二叉树节点之间的关系进行证明,具体过程略)
max_heapify 最大堆性质的维护
如果一个节点的左右两颗子树都满足最大堆的性质,但是节点本身可能不满足最大堆的性质,这时候可以通过对该节点执行max_heapify操作来保持以该节点为根的堆的性质。max_heapify通过找出节点p,p->left,p->right三个节点中值最大的节点,然后将最大节点的值与节点i的值进行交换,然后在原有的最大节点上递归调用max_heapify来实现。
void maxheapify(int a[], int i, int heapsize)
{
int l = (i<<1);
int r = (i<<1) + 1;
int largest = i;
if (l <= heapsize && a[l] > a[largest])
{
largest = l;
}
if (r <= heapsize && a[r] > a[largest])
{
largest = r;
}
if (largest != i)
{
swap(a[largest], a[i]);
maxheapify(a, largest, heapsize);
}
}maxheapify的时间复杂度为O(lgN)
堆的建立
我们可以从后往前扫描数组,对每一个节点都进行maxheapify操作,这样就建立了一个堆。但是对于叶子节点而言,调用maxheapify操作是没有意义的。而上面的CLRS 6.1-7提到,对于拥有n个节点的堆而言,其叶子节点的下标为[n/2]+1, [n/2]+2, …, n。因此,我们可以从n/2开始往前进行maxheapify操作。
void build_heap(int a[], int n)
{
for (int i = n/2; i >= 1; --i)
{
max_heapify(a, i, n);
}
} 需要注意的一点是,建堆操作的时间复杂度看上去为O(NlgN),实际上为O(N),可以从数学上进行证明。以满二叉树为例,如下图所示:
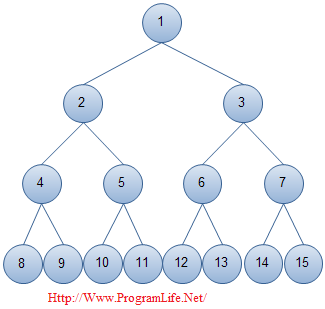
令堆所对应的二叉树的高度为h,节点的个数为n,对于满二叉树有n = 2^(h+1) – 1,对最坏情况而言,其中有2^(h-1)个结点向下访问1次,2^(h-2)个结点向下访问2次,…1个结点向下访问h次,时间复杂度推导过程如下:

堆排序
在建立好一个堆之后,堆排序就比较简单了。每次把第一个节点和最后一个节点的值交换,然后对第一个节点调用maxheapify操作,直到堆的元素个数减小到1.
堆排序的时间复杂度为O(NlgN),因为maxheapify中,前面两个if语句(也就是从左右子节点取得最大值节点)的顺序是可以随意安排的,所以堆排序不是稳定排序。
void heap_sort(int a[], int n)
{
build_heap(a, n);
for (int i = n; i >= 2; --i)
{
swap(a[1], a[i]);
max_heapify(a, 1, i-1);
}
} 2. STL heap
SGI STL的heap的操作基本就和上面提到的差不多了,只是许多过程都是地推来实现的,而且,并没有采用下标从1开始的基数规则,而是采用从0开始。
其中adjust_heap和max_heapify操作思路有所不同,adjust_heap的实现思路是:首先把子节点往上移动,最后调用push_heap操作来实现。
// ============================================================================
// 插入新节点
// ============================================================================
// push_heap实现
// holeIndex为空洞节点的索引,最开始即为末尾待加入堆的节点的索引
// topIndex为根节点的索引
// value为待加入节点的值
template <class _RandomAccessIterator, class _Distance, class _Tp>
void
__push_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first,
_Distance __holeIndex, _Distance __topIndex, _Tp __value)
{
// 获取父节点的索引值
_Distance __parent = (__holeIndex - 1) / 2;
// 如果还没有上升到根节点,且父节点的值小于待插入节点的值
while (__holeIndex > __topIndex && *(__first + __parent) < __value) {
// 父节点下降到holeIndex
*(__first + __holeIndex) = *(__first + __parent);
// 继续往上检查
__holeIndex = __parent;
__parent = (__holeIndex - 1) / 2;
}
// 插入节点
*(__first + __holeIndex) = __value;
}
template <class _RandomAccessIterator, class _Distance, class _Tp>
inline void
__push_heap_aux(_RandomAccessIterator __first,
_RandomAccessIterator __last, _Distance*, _Tp*)
{
__push_heap(__first, _Distance((__last - __first) - 1), _Distance(0),
_Tp(*(__last - 1)));
}
// 公开接口,假定[first, last-1)已经是一个堆,此时把*(last-1)压入堆中
template <class _RandomAccessIterator>
inline void
push_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last)
{
__push_heap_aux(__first, __last,
__DISTANCE_TYPE(__first), __VALUE_TYPE(__first));
}
// ============================================================================
// 保持堆的性质
// ============================================================================
// first 起始位置
// holeIndex 要进行调整操作的位置
// len 长度
// value holeIndex新设置的值
template <class _RandomAccessIterator, class _Distance, class _Tp>
void
__adjust_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _Distance __holeIndex,
_Distance __len, _Tp __value)
{
// 当前根节点的索引值
_Distance __topIndex = __holeIndex;
// 右孩子节点的索引值
_Distance __secondChild = 2 * __holeIndex + 2;
// 如果没有到末尾
while (__secondChild < __len) {
// 如果右孩子节点的值比左孩子节点的值要小,那么secondChild指向左孩子
if (*(__first + __secondChild) < *(__first + (__secondChild - 1)))
__secondChild--;
// 子节点的往上升
*(__first + __holeIndex) = *(__first + __secondChild);
// 继续处理
__holeIndex = __secondChild;
__secondChild = 2 * (__secondChild + 1);
}
// 如果没有右子节点
if (__secondChild == __len) {
*(__first + __holeIndex) = *(__first + (__secondChild - 1));
__holeIndex = __secondChild - 1;
}
// 针对节点topIndex调用push_heap操作
__push_heap(__first, __holeIndex, __topIndex, __value);
}
// ============================================================================
// 弹出一个节点
// ============================================================================
// 区间:[first, last)
// result: 保存根节点的值
// value: 原来末尾节点的值
template <class _RandomAccessIterator, class _Tp, class _Distance>
inline void
__pop_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last,
_RandomAccessIterator __result, _Tp __value, _Distance*)
{
// 取出根节点的值
*__result = *__first;
// 对根节点调用adjust_heap
__adjust_heap(__first, _Distance(0), _Distance(__last - __first), __value);
}
template <class _RandomAccessIterator, class _Tp>
inline void
__pop_heap_aux(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last,
_Tp*)
{
__pop_heap(__first, __last - 1, __last - 1,
_Tp(*(__last - 1)), __DISTANCE_TYPE(__first));
}
// 对外接口:取出根节点的值放入到末尾节点并保持堆的性质
template <class _RandomAccessIterator>
inline void pop_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first,
_RandomAccessIterator __last)
{
__pop_heap_aux(__first, __last, __VALUE_TYPE(__first));
}
// ============================================================================
// 建堆操作
// ============================================================================
template <class _RandomAccessIterator, class _Tp, class _Distance>
void
__make_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first,
_RandomAccessIterator __last, _Tp*, _Distance*)
{
// 只有一个元素不需要进行任何操作
if (__last - __first < 2) return;
_Distance __len = __last - __first;
_Distance __parent = (__len - 2)/2;
// 从第一个不是叶子节点的索引从后往前调用adjust_heap操作
while (true) {
__adjust_heap(__first, __parent, __len, _Tp(*(__first + __parent)));
if (__parent == 0) return;
__parent--;
}
}
// 公开接口
template <class _RandomAccessIterator>
inline void
make_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last)
{
__make_heap(__first, __last,
__VALUE_TYPE(__first), __DISTANCE_TYPE(__first));
}
// ============================================================================
// 堆排序
// ============================================================================
// 建好堆之后才能调用sort_heap
template <class _RandomAccessIterator>
void sort_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last)
{
while (__last - __first > 1)
pop_heap(__first, __last--);
} 3. STL priority_queue
priority_queue底层基于heap实现,属于配接器(adapter),所以源代码相对很简单。
template <class _Tp,
class _Sequence __STL_DEPENDENT_DEFAULT_TMPL(vector<_Tp>),
class _Compare
__STL_DEPENDENT_DEFAULT_TMPL(less<typename _Sequence::value_type>) >
class priority_queue {
typedef typename _Sequence::value_type _Sequence_value_type;
public:
typedef typename _Sequence::value_type value_type;
typedef typename _Sequence::size_type size_type;
typedef _Sequence container_type;
typedef typename _Sequence::reference reference;
typedef typename _Sequence::const_reference const_reference;
protected:
// c即底层存放数据的容器,默认使用vector<T>
_Sequence c;
// comp即为比较函数对象,默认为less<T>
_Compare comp;
public:
// 构造函数
priority_queue() : c() {}
explicit priority_queue(const _Compare& __x) : c(), comp(__x) {}
priority_queue(const _Compare& __x, const _Sequence& __s)
: c(__s), comp(__x)
{ make_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp); }
priority_queue(const value_type* __first, const value_type* __last)
: c(__first, __last) { make_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp); }
priority_queue(const value_type* __first, const value_type* __last,
const _Compare& __x)
: c(__first, __last), comp(__x)
{ make_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp); }
priority_queue(const value_type* __first, const value_type* __last,
const _Compare& __x, const _Sequence& __c)
: c(__c), comp(__x)
{
c.insert(c.end(), __first, __last);
make_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp);
}
// empty, size, top是对底层容器的包装
bool empty() const { return c.empty(); }
size_type size() const { return c.size(); }
// 注意top返回const_reference
const_reference top() const { return c.front(); }
// push操作
void push(const value_type& __x) {
__STL_TRY {
c.push_back(__x);
push_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp);
}
__STL_UNWIND(c.clear());
}
// pop操作
void pop() {
__STL_TRY {
pop_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp);
c.pop_back();
}
__STL_UNWIND(c.clear());
}
}; 4. 基于优先队列实现queue和stack
基于priority_queue可以实现queue。queue的性质为FIFO,那么如果基于最小优先队列,我们给每一个元素都设置一个优先级,每次push操作之后,优先级增加1,那么栈顶的元素总是优先级最小的元素,也就是最先入队的元素,这样就满足了FIFO性质。
template<class T>
class Queue
{
public:
Queue() : priority(0) {}
void push(const T& t)
{
q.push(Node(t, priority++));
}
bool empty()
{
return q.empty();
}
int size()
{
return q.size();
}
void pop()
{
q.pop();
}
const T& top()
{
return q.top().t;
}
private:
struct Node
{
T t;
int p;
Node(const T& _t, int _p) : t(_t), p(_p) {}
bool operator>(const Node& rhs) const
{
return t > rhs.t;
}
};
private:
int priority;
std::priority_queue<Node, std::vector<Node>, std::greater<Node> > q;
};同样,基于priority_queue可以实现stack。stack的性质为LIFO,那么如果基于最大优先队列,我们给每一个元素都设置一个优先级,每次push操作之后,优先级增加1,那么栈顶的元素总是优先级最大的元素,也就是最后入队的元素,这样就满足了LIFO性质。每次pop操作之后,我们可以将优先级记录值减小1(注意这个对于Queue不成立)。
template<class T>
class Stack
{
public:
Stack() : priority(0) {}
void push(const T& t)
{
q.push(Node(t, priority++));
}
bool empty()
{
return q.empty();
}
int size()
{
return q.size();
}
void pop()
{
q.pop();
--priority;
}
const T& top()
{
return q.top().t;
}
private:
struct Node
{
T t;
int p;
Node(const T& _t, int _p) : t(_t), p(_p) {}
bool operator<(const Node& rhs) const
{
return t < rhs.t;
}
};
private:
int priority;
std::priority_queue<Node> q;
}; 5. 最小堆K路合并
请给出一个时间为O(nlgk)、用来将k个已排序链表合并为一个排序链表的算法,此处n为所有输入链表中元素的总数。
算法思想:
1. 从k个链表中取出每个链表的第一个元素,组成一个大小为k的数组arr,然后将数组arr转换为最小堆,那么arr[0]就为最小元素了;
2. 取出arr[0],将其放到新的链表中,然后将arr[0]元素在原链表中的下一个元素补到arr[0]处,即arr[0].next,如果 arr[0].next为空,即它所在的链表的元素已经取完了,那么将堆的最后一个元素补到arr[0]处,堆的大小自动减1,循环即可。
LeetCode提供了一个练习题Merge k Sorted Lists,我的解题代码如下:
struct ListNode
{
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
class Solution
{
private:
// 其实可以不用这个索引结构,直接通过节点的next指针即可获取下一个节点
struct Node
{
ListNode *ptr;
int index;
Node(ListNode *p, int i) : ptr(p), index(i) {}
bool operator>(const Node& rhs) const
{
return ptr->val > rhs.ptr->val;
}
};
private:
vector<Node> arr;
ListNode head;
private:
void min_heapify(int i)
{
int left = i*2;
int right = i*2 + 1;
int smallest = i;
int heapsize = arr.size()-1;
if (left <= heapsize && arr[smallest] > arr[left])
{
smallest = left;
}
if (right <= heapsize && arr[smallest] > arr[right])
{
smallest = right;
}
if (smallest != i)
{
swap(arr[smallest], arr[i]);
min_heapify(smallest);
}
}
void build_heap()
{
int heapsize = arr.size()-1;
for (int i = heapsize/2+1; i >= 1; --i)
{
min_heapify(i);
}
}
public:
Solution() : head(0) {}
ListNode *mergeKLists(vector<ListNode *> &lists)
{
int n = lists.size();
arr.clear();
arr.reserve(n+1);
arr.push_back(Node(NULL, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
if (lists[i] != NULL)
{
arr.push_back(Node(lists[i], i));
lists[i] = lists[i]->next;
}
}
ListNode *p = &head;
build_heap();
while (arr.size() > 1)
{
p->next = arr[1].ptr;
p = p->next;
int i = arr[1].index;
if (lists[i])
{
arr[1] = Node(lists[i], i);
lists[i] = lists[i]->next;
}
else
{
i = arr.size()-1;
arr[1] = arr[i];
arr.erase(arr.end()-1);
}
min_heapify(1);
}
return head.next;
}
}; 6. 输出数据集前K大的数
对于一个数组,要求输出前K大的所有数。
思路:如果采用排序之后再输出,则复杂度为O(NlgN)。如果我们先建立一个堆,然后取出前K大的数,那么复杂度就是O(N)+O(KlgN),效率更高。HDU提供了一个练习题前K大的数,我的解题代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int a[1000010];
inline void swap(int &a, int &b)
{
int tmp = a;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
void max_heapify(int i, int size)
{
int left = i * 2;
int right = left + 1;
int largest = i;
if (left <= size && a[left] > a[largest])
{
largest = left;
}
if (right <= size && a[right] > a[largest])
{
largest = right;
}
if (largest != i)
{
swap(a[largest], a[i]);
max_heapify(largest, size);
}
}
void build_heap(int n)
{
for (int i = n/2+1; i >= 1; --i)
{
max_heapify(i, n);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int n, m;
while (EOF != scanf("%d %d", &n, &m))
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
build_heap(n);
printf("%d", a[1]);
for (int i = 2; i <= m; ++i)
{
swap(a[1], a[n-i+2]);
max_heapify(1, n-i+1);
printf(" %d", a[1]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
} STL源码剖析笔记系列
1. STL笔记之空间配置器
2. STL笔记之迭代器
3. STL笔记之vector
4. STL笔记之list
5. STL笔记之优先队列
参考
http://www.cnblogs.com/shuaiwhu/archive/2011/03/20/2065081.html
http://blog.csdn.net/anonymalias/article/details/8807895
http://www.cnblogs.com/shuaiwhu/archive/2011/03/20/2065077.html
《算法导论》