第五章 数组与广义表
/* c5-1.h 数组的顺序存储表示 */
#include<stdarg.h> /* 标准头文件,提供宏va_start,va_arg和va_end, */
/* 用于存取变长参数表 */
#define MAX_ARRAY_DIM 8 /* 假设数组维数的最大值为8 */
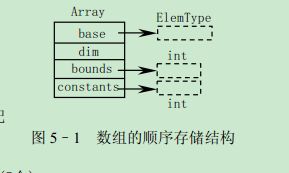
typedef struct
{
ElemType *base; /* 数组元素基址,由InitArray分配 */
int dim; /* 数组维数 */
int *bounds; /* 数组维界基址,由InitArray分配 */
int *constants; /* 数组映象函数常量基址,由InitArray分配 */
}Array;
/* bo5-1.c 顺序存储数组(存储结构由c5-1.h定义)的基本操作(5个) */
Status InitArray(Array *A,int dim,...)
{ /* 若维数dim和各维长度合法,则构造相应的数组A,并返回OK */
int elemtotal=1,i; /* elemtotal是数组元素总数,初值为1(累乘器) */
va_list ap;
if(dim<1||dim>MAX_ARRAY_DIM)
return ERROR;
(*A).dim=dim;
(*A).bounds=(int *)malloc(dim*sizeof(int));
if(!(*A).bounds)
exit(OVERFLOW);
va_start(ap,dim);
for(i=0;i<dim;++i)
{
(*A).bounds[i]=va_arg(ap,int);
if((*A).bounds[i]<0)
return UNDERFLOW; /* 在math.h中定义为4 */
elemtotal*=(*A).bounds[i];
}
va_end(ap);
(*A).base=(ElemType *)malloc(elemtotal*sizeof(ElemType));
if(!(*A).base)
exit(OVERFLOW);
(*A).constants=(int *)malloc(dim*sizeof(int));
if(!(*A).constants)
exit(OVERFLOW);
(*A).constants[dim-1]=1;
for(i=dim-2;i>=0;--i)
(*A).constants[i]=(*A).bounds[i+1]*(*A).constants[i+1];
return OK;
}
void DestroyArray(Array *A)
{ /* 销毁数组A */
if((*A).base)
free((*A).base);
if((*A).bounds)
free((*A).bounds);
if((*A).constants)
free((*A).constants);
(*A).base= (*A).bounds=(*A).constants=NULL;
(*A).dim=0;
}
Status Locate(Array A,va_list ap,int *off) /* Value()、Assign()调用此函数 */
{ /* 若ap指示的各下标值合法,则求出该元素在A中的相对地址off */
int i,ind;
*off=0;
for(i=0;i<A.dim;i++)
{
ind=va_arg(ap,int);
if(ind<0||ind>=A.bounds[i])
return OVERFLOW;
*off+=A.constants[i]*ind;
}
return OK;
}
Status Value(ElemType *e,Array A,...) /* 在VC++中,...之前的形参不能是引用类型 */
{ /* ...依次为各维的下标值,若各下标合法,则e被赋值为A的相应的元素值 */
va_list ap;
int off;
va_start(ap,A);
if(Locate(A,ap,&off)==OVERFLOW) /* 调用Locate() */
return ERROR;
*e=*(A.base+off);
return OK;
}
Status Assign(Array A,ElemType e,...) /* 变量A的值不变,故不需要* */
{ /* ...依次为各维的下标值,若各下标合法,则将e的值赋给A的指定的元素 */
va_list ap;
int off;
va_start(ap,e);
if(Locate(A,ap,&off)==OVERFLOW) /* 调用Locate() */
return ERROR;
*(A.base+off)=e;
return OK;
}
/* main5-1.c 检验bo5-1.c的主程序 */
#include"c1.h"
typedef int ElemType;
#include"c5-1.h"
#include"bo5-1.c"
void main()
{
Array A;
int i,j,k,*p,dim=3,bound1=3,bound2=4,bound3=2; /* A[3][4][2]数组 */
ElemType e,*p1;
InitArray(&A,dim,bound1,bound2,bound3); /* 构造3×4×2的3维数组A */
p=A.bounds;
printf("A.bounds=");
for(i=0;i<dim;i++) /* 顺序输出A.bounds */
printf("%d ",*(p+i));
p=A.constants;
printf("\nA.constants=");
for(i=0;i<dim;i++) /* 顺序输出A.constants */
printf("%d ",*(p+i));
printf("\n%d页%d行%d列矩阵元素如下:\n",bound1,bound2,bound3);
for(i=0;i<bound1;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<bound2;j++)
{
for(k=0;k<bound3;k++)
{
Assign(A,i*100+j*10+k,i,j,k); /* 将i×100+j×10+k赋值给A[i][j][k] */
Value(&e,A,i,j,k); /* 将A[i][j][k]的值赋给e */
printf("A[%d][%d][%d]=%2d ",i,j,k,e); /* 输出A[i][j][k] */
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
p1=A.base;
printf("A.base=\n");
for(i=0;i<bound1*bound2*bound3;i++) /* 顺序输出A.base */
{
printf("%4d",*(p1+i));
if(i%(bound2*bound3)==bound2*bound3-1)
printf("\n");
}
printf("A.dim=%d\n",A.dim);
DestroyArray(&A);
}