通过 Health Center API 监视 Java 应用程序,第 1 部分
您是否曾经遇到过没有明确原因的应用程序服务器挂起或者 Java 应用程序变得没有响应?您的应用程序是否内存不足或者运行情况欠佳?使用 Health Center,您就可以更轻松地解决这些问题。
使用 Health Center 监视和诊断问题
Health Center 是一款适用于 Java 的 IBM® 监视和诊断工具,是一个免费的低开销诊断工具和 API,用于监视在 IBM Java 虚拟机 (JVM) 上运行的应用程序。借助 Health Center,您可以通过提供信息来快速评估正在运行的 Java 应用程序的状态,从而确定问题并帮助解决问题。您可以:
- 确定是否存在本机或堆内存泄露
- 发现哪些方法需要使用较长的运行时间
- 确定 I/O 瓶颈
- 使垃圾收集可视化并进行调优
- 查看所有锁争用
- 分析异常的 WebSphere® Real Time 事件
- 监视应用程序的线程活动
- 检测死锁条件
- 收集类的直方图数据
最新版本的 Health Center 是一个功能强大的全新 API,您可以使用它编写自己的监视工具。令人烦恼的难于查找问题的时代马上就要结束了。
在本文中,我们将学习编写一个用于检查应用程序死锁条件的监视工具,然后,应用这些原则来编写更深入的工具、查询从垃圾收集活动到方法分析的所有问题,并确定应用程序将其 CPU 周期花费在了哪些地方。
系统要求
Health Center API 包至少需要安装 Eclipse 3.4 或 Eclipse 4.x。
将 API 程序包安装到 Eclipse 中
IBM 监视和诊断工具通常安装在 IBM 支持助手 (ISA) 中,要将 Health Center 嵌入您的应用程序并使用 API 对其进行编码,首先需要将它安装到您的 Eclipse 环境中。为此,请执行以下步骤:
- 启动 Eclipse 开发环境。
- 转到 Help -> Install New Software。
- 添加 ISA 更新网站作为一个新网站。
- 单击 Add。
- 在名称框中输入 ISA Update 网站。
- 在位置框中输入此 URL:http://public.dhe.ibm.com/software/isa/isa410/production/。该操作会启动对所有可用工具的搜索,该搜索可能需要花费几分钟的时间。
- 在搜索框中输入 Health Center。
- 选择程序包 Health Center Core Feature 并单击 Next(参见图 1):
图 1. 将要安装的可用软件的列表
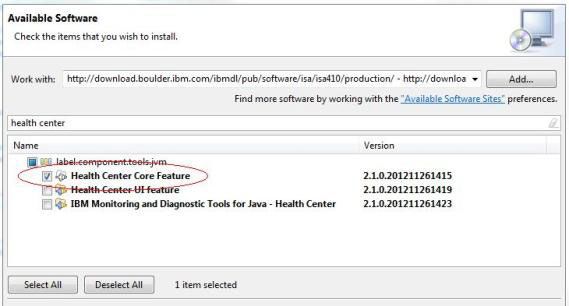
- 确认安装细节并单击 Next。
- 阅读并接受许可条款,然后单击 Finish。这些步骤会将 Health Center 核心功能安装到您的 Eclipse IDE 中。您可以准备好对此 API 进行编码。
- 确认安装细节并单击 Next。
使用此 API 编写一个简单的 rcp 来检测死锁。首先,在 Eclipse 中创建一个新的插件项目并添加 Health Center API 作为一个依赖项。为此,请执行以下步骤:
- 转到 File -> New -> Project -> Plug-in Project。
- 为该项目提供一个名称,如 HC_Deadlock。单击 Next。
- 清除 Generate an activator 复选框。当系统询问您是否想创建一个富客户端应用程序时,单击 Yes。然后单击 Next(参见图 2):
图 2. 插件项目选项
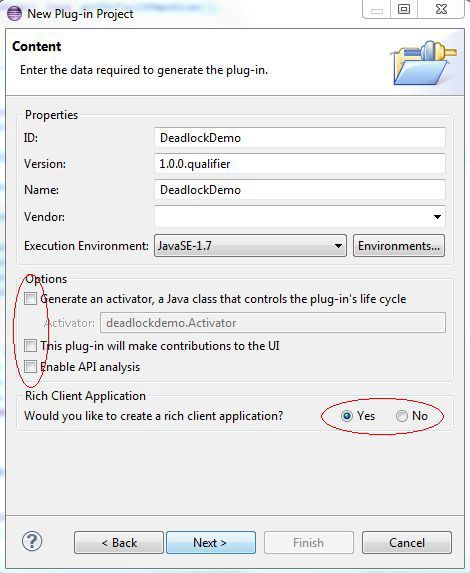
- 单击 Next。在模板屏幕上,选择 Headless Hello RCP。然后单击 Finish。
接下来,将 Health Center API 程序包作为依赖项添加到这个新项目。请遵循以下步骤:
- 要将 API 导入添加到清单中,请打开新项目中 META-INF 下的 MANIFEST.MF 文件(参见图 3):
图 3. Package Explorer 插件

- 选择 Dependencies 选项卡并单击 Add。在 Select a Plug-in 字段的搜索中键入 healthcenter.api。选择 com.ibm.java.diagnostics.healthcenter.api 插件,请注意,版本号可能有所不同(参见图 4):
图 4. Health Center API 插件选择
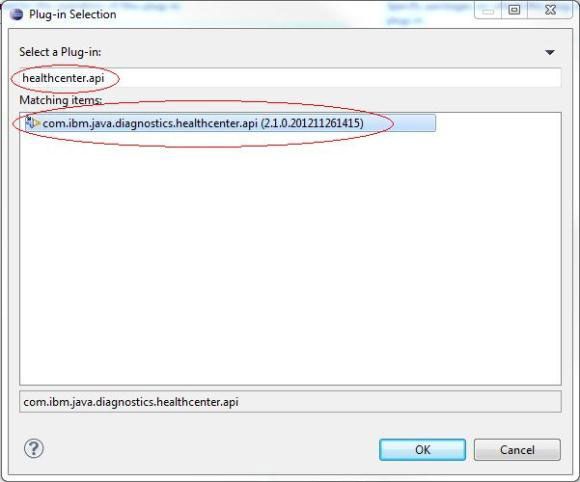
- 单击 OK。重复 选择 Dependencies 选项卡 步骤中的练习。这次,再次添加 org.eclipse.ui,版本号可能会有所不同(参见图 5):
图 5. org.eclipse.ui 的插件选择
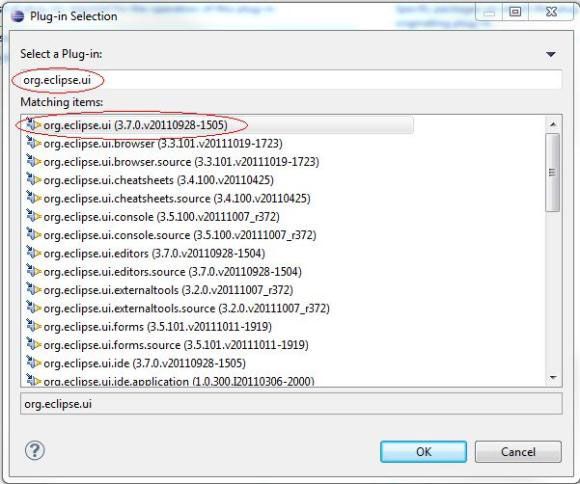
- 单击 OK,然后保存该文件。
此 API 插件现在已经包含在您的应用程序中,您可以开始对其进行编码了。
测试死锁应用程序
编写死锁监视工具之前,您可能想监视某些内容。清单 1 显示了一个获取死锁的简单应用程序的源代码:
清单 1. 一个具有死锁的简单应用程序
public class GenerateDeadlock {
AThread t1 = null;
AThread t2 = null;
AThread t3 = null;
static class AThread extends Thread {
Object hold;
Object grab;
AThread(String name, Object hold, Object grab) {
super(name);
this.hold = hold;
this.grab = grab;
}
private void delay(long time) {
try {
Thread.sleep(time);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
private void grabLocks() {
System.out.println("Thread " + this + " about to hold " + hold);
synchronized (hold) {
System.out.println(" Thread " + this + " about to grab "
+ grab);
delay(5000);
synchronized (grab) {
System.out.println(" Thread " + this
+ " got both monitors");
delay(1000000);
}
}
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("Thread " + this + " starting");
for (int i = 0; i < 200000; i++) {
grabLocks();
}
System.out.println("Thread " + this + " completed");
}
}
private void createDeadlock() {
System.out.println("Force 3 thread deadlock");
String s1 = "obj 1";
String s2 = "obj 2";
String s3 = "obj 3";
t1 = new AThread("Thread 1", s1, s2);
t2 = new AThread("Thread 2", s2, s3);
t3 = new AThread("Thread 3", s3, s1);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenerateDeadlock d = new GenerateDeadlock();
d.createDeadlock();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Press a key to exit");
try {
System.in.read();
System.exit(0);
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {
}
}
}
|
Health Center 包含两个部分,第一部分是 Health Center 代理,它与要监视的应用程序一起加载。该代理提供了对 JVM 中数据的访问,这就是随后要使用的 Health Center 的第二部分,即客户端。此 API 为您提供了访问客户端的访问权限,通常是从 ISA 开始。将此客户端嵌入您的应用程序中,以便连接到使用 Health Center 代理启动的应用程序,并获得访问 Health Center 客户端监视和显示的所有数据的权限。此 API 不提供 GUI,而是生成可在您自己的应用程序中使用的所有数据。图 6 概述了将 Health Center 客户端和代理安装到 ISA 和 JVM 中时它们所在的位置:
图 6. Health Center 客户端和代理安装在 ISA 和 JVM 中时所在的位置

启动 清单 1 中的程序及其连接的 Health Center 代理。它至少需要 IBM Java 级别的 Java 5 SR8、Java 6 SR1 或 Java 7。您可以下载 IBM 开发人员工具包。
要使用 Java 5 SR10 及其更高版本、Java 6 SR5 及更高版本和 Java 7 来启动应用程序与代理,请使用以下命令(参见图 7):
java - Xhealthcenter GenerateDeadlock |
对于 Java 5 SR9 及其早期版本或者 Java 6 SR4 及其早期版本,请使用以下命令:
java - agentlib:healthcenter - Xtrace:output=healthcenter.out GenerateDeadlock |
图 7. 运行 GenerateDeadlock 程序

Java 5 SR9 和 Java 6 SR3 自动包含此代理。有关最新版本的代理以及如何更新代理的说明,请访问 Health Center - 安装 Health Center 代理。
编写死锁监视应用程序代码
现在,您可以使用 Health Center API 修改基本的 Hello RCP World 应用程序,并将其转变成死锁检测工具。打开名为 Application.java 的文件(参见图 8):
图 8. Application.java 代码的位置

设置连接详细信息
首先,获取一个 ConnectionProperties 对象,该对象包含您要连接的应用程序的详细信息。默认的对象设置为使用 localhost 和端口 1972,但您可以在构造函数和类方法中更改这些值(和提高安全性):
ConnectionProperties hcConn = new ConnectionProperties(); |
在拥有 ConnectionProperties 对象时,可以连接到您要监视的应用程序,该应用程序已经与 Health Center 代理一起启动。调用静态的 HealthCenterFactory.connect(hcConn, true) 方法。该调用返回一个 HealthCenter 对象,此对象直接连接到 Health Center 并且允许访问 Health Center 监视的所有数据。此连接调用有效地启动了您的应用程序中的一个 Health Center 实例并开始收集数据:
HealthCenter hcMon = HealthCenterFactory.connect(hcConn,true); |
获取数据
在拥有 HealthCenter 对象之后,就可以开始查询数据。采用类似于 GUI的方式布置此 API:在获取 HealthCenter 对象之后,此 API 的第一步操作就是调用您感兴趣的数据类型。对于此示例,我们希望检查死锁,它是 ThreadsData 类的一部分。您可以在HealthCenter 对象上使用 getThreadsData() 方法进行访问,如下所示:
ThreadsData hcThreadsData = HealthCenter.getThreadsData(); |
ThreadsData 类包含一个 deadlockDetected() 方法,该方法在检测到死锁时返回 true。通过轮询该方法,就可以知道是否发生了死锁:
if(hcThreadsData.deadlockDetected()) {
do something
}
|
访问建议和分析引擎
Health Center 有一个内置的建议引擎,该引擎提供所有分析并返回结果。通常,在运行完整版的 Health Center 时,通常会在 Analysis and Recommendations 面板中看到这些结果(参见图 9):
图 9. Health Center 中的 Analysis and Recommendations 面板
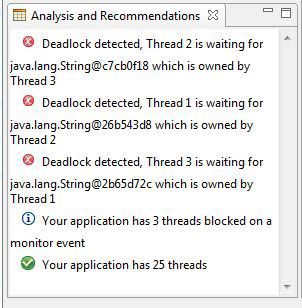
要查询任何建议,可采用一些方法。getAllRecommendations() 返回所有建议的数组,但您可以只使用getCriticalRecommendations() 调用来查询关键问题,该调用是将在 ThreadsData 对象上使用的一个调用:
String[] hcThreadsRec = hcThreadsData.getCriticalRecommendations() |
查看完整的源代码
前五个调用是在应用程序中嵌入 Health Center 以及在要监视的应用程序中检查死锁所必需的。清单 2 显示了包含所用调用的完整源代码:
清单 2. 显示了所使用的五个调用的完整源代码
package deadlockdemo;
import org.eclipse.equinox.app.IApplication;
import org.eclipse.equinox.app.IApplicationContext;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.MessageBox;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
import com.ibm.java.diagnostics.healthcenter.api.ConnectionProperties;
import com.ibm.java.diagnostics.healthcenter.api.HealthCenter;
import com.ibm.java.diagnostics.healthcenter.api.factory.HealthCenterFactory;
import com.ibm.java.diagnostics.healthcenter.api.threads.ThreadsData;
/**
* This class controls all aspects of the application's execution
*/
public class Application implements IApplication {
HealthCenter hcMon;
public Object start(IApplicationContext context) throws Exception {
ConnectionProperties hcConn = new ConnectionProperties();
hcMon = HealthCenterFactory.connect(hcConn, true);
try {
System.out
.println("Waiting for 10 seconds to allow initial data to be
parsed from the connection");
Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
checkForDeadlock();
return IApplication.EXIT_OK;
}
public void stop() {
// nothing to do
}
public void checkForDeadlock() {
while (!detectDeadlock()) {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private boolean detectDeadlock() {
ThreadsData hcthreadsData = hcMon.getThreadsData();
if (hcthreadsData == null) {
System.out.println("No threads yet");
} else {
if (hcthreadsData.deadlockDetected()) {
Display display = new Display();
Shell shell = new Shell(display);
MessageBox mb = new MessageBox(shell);
String deadlockMessage = new String();
String[] hcThreadsRec = hcthreadsData
.getCriticalRecommendations();
for (String rec : hcThreadsRec) {
deadlockMessage = deadlockMessage + rec + "\n";
}
mb.setMessage(deadlockMessage);
mb.setText("Deadlock detected");
mb.open();
display.dispose();
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
|
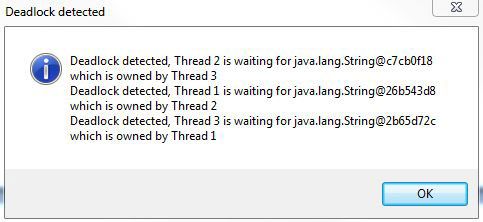
监视死锁
现在,您已经在后台运行死锁监视应用程序和有死锁缺陷的程序。一些消息指示了存在死锁(参见图 10):
图 10. 死锁检测结果面板
结束语
本文介绍了如何开始使用 Health Center API 的基础知识,然后介绍了如何编写一个用于检查应用程序死锁条件的监视工具。您可以应用这些技术来提取和使用 Health Center 中的任何数据。在 第 2 部分 中,将会在这些概念上进行操作,并在死锁检测应用程序中添加一个方法分析视图,以显示应用程序中花费最多 CPU 周期的地方。