Android开发——MediaPlayer源码不完整分析
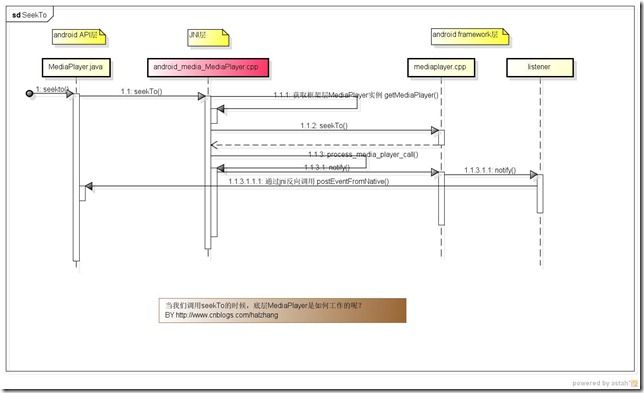
seekTo在MediaPlayer的调用流程如下图:
在MediaPlayer.java中的seekTo是一个native修饰的方法
1: /**
2: * Seeks to specified time position.
3: *
4: * @param msec the offset in milliseconds from the start to seek to
5: * @throws IllegalStateException if the internal player engine has not been
6: * initialized
7: */
8: public native void seekTo(int msec) throws IllegalStateException;
好,我们来看看此方法的JNI是如何实现的。
1: static void android_media_MediaPlayer_seekTo(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz, int msec)
2: {
3: sp<MediaPlayer> mp = getMediaPlayer(env, thiz);//获取MediaPlayer实例
4: if (mp == NULL ) {
5: jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/IllegalStateException", NULL);
6: return;
7: }
8: LOGV("seekTo: %d(msec)", msec);
9: status_t result = mp->seekTo(msec);//1,调用MediaPlayer的seekTo方法
10: process_media_player_call( env, thiz, result, NULL, NULL );//2,处理MediaPlayer方法调用的返回结果
11: }
1: status_t MediaPlayer::seekTo_l(int msec)
2: {
3: LOGV("seekTo %d", msec);
4: if ((mPlayer != 0) && ( mCurrentState & ( MEDIA_PLAYER_STARTED | MEDIA_PLAYER_PREPARED | MEDIA_PLAYER_PAUSED | MEDIA_PLAYER_PLAYBACK_COMPLETE) ) ) {
5: if ( msec < 0 ) {
6: LOGW("Attempt to seek to invalid position: %d", msec);
7: msec = 0;
8: } else if ((mDuration > 0) && (msec > mDuration)) {
9: LOGW("Attempt to seek to past end of file: request = %d, EOF = %d", msec, mDuration);
10: msec = mDuration;
11: }
12: // cache duration
13: mCurrentPosition = msec;
14: if (mSeekPosition < 0) {
15: getDuration_l(NULL);
16: mSeekPosition = msec;
17: //调用seekTo了
18: return mPlayer->seekTo(msec);
19: }
20: else {
21: LOGV("Seek in progress - queue up seekTo[%d]", msec);
22: return NO_ERROR;
23: }
24: }
25: LOGE("Attempt to perform seekTo in wrong state: mPlayer=%p, mCurrentState=%u", mPlayer.get(), mCurrentState);
26: return INVALID_OPERATION;
27: }
28:
29: status_t MediaPlayer::seekTo(int msec)
30: {
31: mLockThreadId = getThreadId();
32: Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
33: status_t result = seekTo_l(msec);
34: mLockThreadId = 0;
35: return result;
36: }
1: static void process_media_player_call(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz, status_t opStatus, const char* exception, const char *message)
2: {
3: if (exception == NULL) { // Don't throw exception. Instead, send an event.
4: if (opStatus != (status_t) OK) {
5: sp<MediaPlayer> mp = getMediaPlayer(env, thiz);
6: if (mp != 0) mp->notify(MEDIA_ERROR, opStatus, 0);//调用MediaPlayer的notify
7: }
8: } else { // Throw exception!
9: if ( opStatus == (status_t) INVALID_OPERATION ) {
10: jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/IllegalStateException", NULL);
11: } else if ( opStatus != (status_t) OK ) {
12: if (strlen(message) > 230) {
13: // if the message is too long, don't bother displaying the status code
14: jniThrowException( env, exception, message);
15: } else {
16: char msg[256];
17: // append the status code to the message
18: sprintf(msg, "%s: status=0x%X", message, opStatus);
19: jniThrowException( env, exception, msg);
20: }
21: }
22: }
23: }
接下来看看MediaPlayer的notify方法,这个方法主要是通过判断MediaPlayer的状态向我们的app发送回调:
1: void MediaPlayer::notify(int msg, int ext1, int ext2)
2: {
3: LOGV("message received msg=%d, ext1=%d, ext2=%d", msg, ext1, ext2);
4: bool send = true;
5: bool locked = false;
6:
7: // TODO: In the future, we might be on the same thread if the app is
8: // running in the same process as the media server. In that case,
9: // this will deadlock.
10: //
11: // The threadId hack below works around this for the care of prepare
12: // and seekTo within the same process.
13: // FIXME: Remember, this is a hack, it's not even a hack that is applied
14: // consistently for all use-cases, this needs to be revisited.
15: if (mLockThreadId != getThreadId()) {
16: mLock.lock();
17: locked = true;
18: }
19:
20: if (mPlayer == 0) {
21: LOGV("notify(%d, %d, %d) callback on disconnected mediaplayer", msg, ext1, ext2);
22: if (locked) mLock.unlock(); // release the lock when done.
23: return;
24: }
25:
26: switch (msg) {
27: case MEDIA_NOP: // interface test message
28: break;
29: case MEDIA_PREPARED://prepared结束
30: LOGV("prepared");
31: mCurrentState = MEDIA_PLAYER_PREPARED;
32: if (mPrepareSync) {
33: LOGV("signal application thread");
34: mPrepareSync = false;
35: mPrepareStatus = NO_ERROR;
36: mSignal.signal();
37: }
38: break;
39: case MEDIA_PLAYBACK_COMPLETE://播放完毕
40: LOGV("playback complete");
41: if (!mLoop) {
42: mCurrentState = MEDIA_PLAYER_PLAYBACK_COMPLETE;
43: }
44: break;
45: case MEDIA_ERROR://出错
46: // Always log errors.
47: // ext1: Media framework error code.
48: // ext2: Implementation dependant error code.
49: LOGE("error (%d, %d)", ext1, ext2);
50: mCurrentState = MEDIA_PLAYER_STATE_ERROR;
51: if (mPrepareSync)
52: {
53: LOGV("signal application thread");
54: mPrepareSync = false;
55: mPrepareStatus = ext1;
56: mSignal.signal();
57: send = false;
58: }
59: break;
60: case MEDIA_INFO://logcat经常可以看到
61: // ext1: Media framework error code.
62: // ext2: Implementation dependant error code.
63: LOGW("info/warning (%d, %d)", ext1, ext2);
64: break;
65: case MEDIA_SEEK_COMPLETE://seek完毕
66: LOGV("Received seek complete");
67: if (mSeekPosition != mCurrentPosition) {
68: LOGV("Executing queued seekTo(%d)", mSeekPosition);
69: mSeekPosition = -1;
70: seekTo_l(mCurrentPosition);
71: }
72: else {
73: LOGV("All seeks complete - return to regularly scheduled program");
74: mCurrentPosition = mSeekPosition = -1;
75: }
76: break;
77: case MEDIA_BUFFERING_UPDATE://缓冲
78: LOGV("buffering %d", ext1);
79: break;
80: case MEDIA_SET_VIDEO_SIZE://设置视频大小
81: LOGV("New video size %d x %d", ext1, ext2);
82: mVideoWidth = ext1;
83: mVideoHeight = ext2;
84: break;
85: default:
86: LOGV("unrecognized message: (%d, %d, %d)", msg, ext1, ext2);
87: break;
88: }
89:
90: sp<MediaPlayerListener> listener = mListener;
91: if (locked) mLock.unlock();
92:
93: // this prevents re-entrant calls into client code
94: if ((listener != 0) && send) {
95: Mutex::Autolock _l(mNotifyLock);
96: LOGV("callback application");
97: //调用监听器,回调应用的监听器
98: listener->notify(msg, ext1, ext2);
99: LOGV("back from callback");
100: }
101: }
在监听器的notify方法中,是通过jni“反向调用”MediaPlayer.java中的postEventFromNative,在通过mEventHandler根据不同的消息类型调用不同的监听器。
1: private static void postEventFromNative(Object mediaplayer_ref,
2: int what, int arg1, int arg2, Object obj)
3: {
4: MediaPlayer mp = (MediaPlayer)((WeakReference)mediaplayer_ref).get();
5: if (mp == null) {
6: return;
7: }
8:
9: if (mp.mEventHandler != null) {
10: Message m = mp.mEventHandler.obtainMessage(what, arg1, arg2, obj);
11: mp.mEventHandler.sendMessage(m);
12: }
13: }
OK,至此我们分析了seekTo的整个流程。其他方法的流程是很相似的,大家不妨亲自去看看。