Android Service的启动方式
Service没有用户界面,运行与后台。一般用于给前台Activity提供特定服务。服务不能自己运行,启动Service的方式有两种:Context.startService 或 Context.bindService。
(一)startService
使用startService()方法启用服务后,调用者与服务之间没有关连。调用者直接退出而没有调用stopService的话,Service会一直在后台运行。下次调用者再起来仍然可以
1)启动流程:
如果调用前服务没有被创建,则会引起onCreate()->onStart();
如果已被创建,则多次调用startService只会引起onStart()被多次调用。
2)结束方式:
只能调用Context.stopService()结束服务,系统会自动调用到onDestroy()方法。
(二)bindService
使用bindService()方法启用服务,调用者与服务绑定在一起了,调用者一旦退出,服务也就自动终止。
1)启动流程:
如果调用前服务没有被创建,则会引起onCreate()->onBind();
如果已被创建但没有被绑定,则会引起onBind();
如果服务已被绑定,则多次调用bindService并不会引起onCreate()和onBind()被多次调用。
2)结束方式:
调用者退出,系统会自动调用服务到onUnbind()->onDestroy()方法。
如果调用者希望与正在绑定的服务解除绑定,可以调用Context.unbindService(),该方法会导致系统调用服务的onUnbind()-->onDestroy()方法。
注意:
1)如果第一次调用startService(), 系统会onCreate()->onStart();此时调用bindService, 只会onBind();如果第一次调用bindService(), 系统会onCreate()->onBind();此时调用startService, 只会onStart();
2)如果start和bind都调用了, 那么一旦服务被绑定(只要成功调用了bindService, 不管是先start后bind还是后bind先start), 就必须调用unbindService和stopService(先unbindService(导致onUnbind())再stopService(导致onDestroy()), 或者先stopService再unbindService(导致onUnbind()->onDestroy())都行)才能终止服务。
首先编写一个类继承Service这个基类,重写里面的方法,然后在Activity中调用startService()和stopService()来启动和停止服务。
运行界面:
工程目录结构:
ExampleService.java
package com.service.activity;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class ExampleService extends Service{
private static final String TAG = "ExampleService";
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.i(TAG, "ExampleService-onCreate");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
Log.i(TAG, "ExampleService-onStart");
super.onStart(intent, startId);
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
//执行文件的下载或者播放等操作
Log.i(TAG, "ExampleService-onStartCommand");
/*
* 这里返回状态有三个值,分别是:
* 1、START_STICKY:当服务进程在运行时被杀死,系统将会把它置为started状态,但是不保存其传递的Intent对象,之后,系统会尝试重新创建服务;
* 2、START_NOT_STICKY:当服务进程在运行时被杀死,并且没有新的Intent对象传递过来的话,系统将会把它置为started状态,
* 但是系统不会重新创建服务,直到startService(Intent intent)方法再次被调用;
* 3、START_REDELIVER_INTENT:当服务进程在运行时被杀死,它将会在隔一段时间后自动创建,并且最后一个传递的Intent对象将会再次传递过来。
*/
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Log.i(TAG, "ExampleService-onBind");
return null;
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.i(TAG, "ExampleService-onDestroy");
super.onDestroy();
}
}
MainActivity.java
package com.service.activity;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener{
private static final String TAG = "MainActivity"; //日志输出标志
private Button btnStartService;
private Button btnStopService;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
btnStartService = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btnStartService);
btnStopService = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btnStopService);
btnStartService.setOnClickListener(this);
btnStopService.setOnClickListener(this);
}
//点击事件处理监听器
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,ExampleService.class);
switch(v.getId()){
case R.id.btnStartService:
startService(intent);
break;
case R.id.btnStopService:
stopService(intent);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
最后在AndroidManifest.xml中对service进行声明,它跟Activity同一级,都写在Application标签里面:
<service android:name=".ExampleService"/>
创建完运行
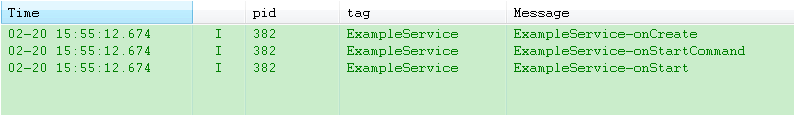
在运行点击"启动service"之后(第一次启动service),我们可以查看LogCat控制台输出的日志如下:
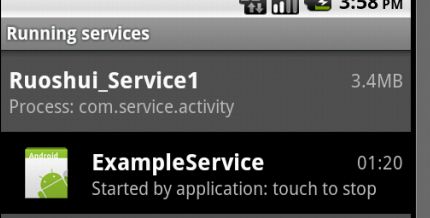
这个时候我们点击"返回",Activity被干掉了,但是我们的服务仍然在运行,可以查看Setting-->Application-->Running Service,截图如下:
然后回到我们的Activity,再次点击启动Service,控制台输出日志如下:
onCreate()方法没有被调用,说明它并没有重新被创建。
然后我们点击停止Service,输出日志如下: