归并排序算法原理及JAVA实现
基本思想:归并(Merge)排序法是将两个(或两个以上)有序表合并成一个新的有序表,即把待排序序列分为若干个子序列,每个子序列是有序的。然后再把有序子序列合并为整体有序序列。递归形式的算法在形式上较简洁,但实用性很差。一般情况下,很少利用二路归并排序法进行内部排序。
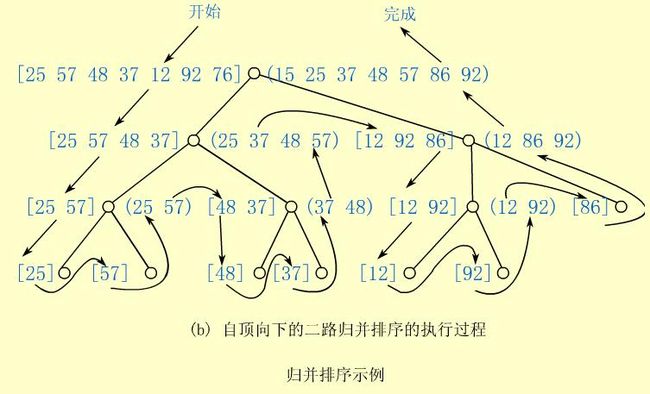
归并排序有两种实现方法:自底向上和自顶向下。本文采用分治法进行自顶向下的算法设计,形式较为简洁。
分治法的三个步骤
设归并排序的当前区间是R[low..high],分治法的三个步骤是:
①分解:将当前区间一分为二,即求分裂点 mid = (low + high)/2
②求解:递归地对两个子区间R[low..mid]和R[mid+1..high]进行归并排序; 递归的终结条件:子区间长度为1(一个记录自然有序)。
③组合:将已排序的两个子区间R[low..mid]和R[mid+1..high]归并为一个有序的区间R[low..high]。
每次归并操作,均是将两个有序的子文件合并成一个有序的子文件,故称其为"二路归并排序"
算法 public static void mergeSort(int []array,int left,int right) 执行过程:
稳定性: 归并排序是一种稳定的排序。
存储结构要求:可用顺序存储结构。也易于在链表上实现。一趟归并排序都可在O(n) 的时间量级上实现
时间复杂度:对长度为n的文件,需进行 ceil(log2n) 趟二路归并,每趟归并的时间为 O(n),故其时间复杂度无论是在最好情况下还是在最坏情况下均是 O(nlogn)。
空间复杂度:需要一个辅助向量来暂存两有序子文件归并的结果,故其辅助空间复杂度为O(n),显然它不是就地排序。
数据结构教学:http://sjjp.tjuci.edu.cn/sjjg/DataStructure/DS/web/paixu/paixu8.5.1.2.htm
JAVA源代码(成功运行):
package testSortAlgorithm;
public class MergeSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int array[] = { 49, 38, 65, 97, 76, 13, 27, 49, 78, 34, 12, 64, 5, 4,
62, 99, 98, 54, 56, 17, 18, 23, 34, 15, 35, 25, 53, 51 };
mergeSort(array, 0, array.length - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
}
public static void mergeSort(int[] array, int left, int right) {
if (left < right) {
int center = (left + right) / 2;
// 将数组拆分为两份,并递归拆分子数组,直到数组中只有一个元素
mergeSort(array, left, center);
mergeSort(array, center + 1, right);
// 合并相邻数组
merge(array, left, center, right);
}
}
// 合并子数组的函数
public static void merge(int[] array, int left, int center, int right) {
// 临时数组,用于排序
int[] tempArray = new int[array.length];
// 用于将排好序的临时数组复制回原数组
int mark = left;
// 第二个数组的左端
int mid = center + 1;
// 用于临时数组的下标
int tempLeft = left;
while (left <= center && mid <= right) {
// 从两个子数组中取出最小的放入临时数组,即按从小到大的顺序重新排布
if (array[left] <= array[mid]) {
tempArray[tempLeft++] = array[left++];
} else {
tempArray[tempLeft++] = array[mid++];
}
}
// 剩余部分依次放入临时数组
while (left <= center) {
tempArray[tempLeft++] = array[left++];
}
while (mid <= right) {
tempArray[tempLeft++] = array[mid++];
}
// 将中间数组中的内容复制回原数组
while (mark <= right) {
array[mark] = tempArray[mark++];
}
}
}